ISO 10993 Intradermal reaction test
There may be a variety of cheMICal components in the final medical device, such as various additives, including lubricants, dyes, adhesives, and sterilizer residues produced during the sterilization process. It shoULd be consideRED whether these components have potential irritation activity. The characteristics of irritation will manifest as inflammation, redness, swelling, fever and pain. Therefore, irritation testing is essential to evaluate the potential of medical devices to cause irritation reactions immediately after exposure to the human body. Irritation tests include intradermal reaction, skin irritation, eye irritation, and mucosal irritation tests. When the device is not suitable for the use of the device (eyes, skin or mucous membranes), such as implantable devices and external access devices, it is necessary to select intradermal reaction tests. Intradermal reaction tests are an in vivo test that evaluates the possibility of irritation by intradermally injecting the extract of the medical device.
1. Purpose of the test
Assess the potential skin contact hazards caused by chemicals released from medical devices.
2. Test Method
was evaluated by intradermal injection in rabbits . The test samples were extracted using polar extraction media (0.9% sodium chloride solution) and non-polar extraction media (sesame oil). Each extract was injected into 5 different locations on one side of the back of 3 animals, with 0.2 ml injected at each location. Similarly, each extraction medium (control group) was injected into the contralateral side of the back of each animal (see Figure 1 for the distribution of sites). After injection, the injection site was observed immediately. Erythema and edema were observed and scored within 24, 48 and 72 hours (see Table 1).
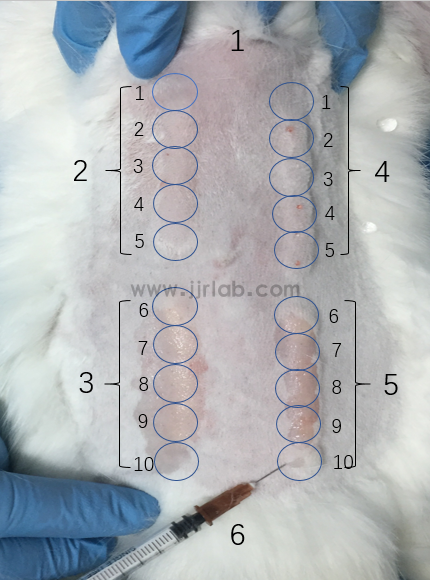
figure 1
Injection point arrangement
Description: 1-head end, 2-0.2 ml polar extract injection point, 3-0.2 ml non-polar extract injection point, 4-0.2 ml polar medium control injection point, 5-0.2 ml non-polar Medium controls injection point and 6-tail.
Table 1: Intradermal Reaction Scoring System
reaction | Keep score |
Erythema and eschar formation (ER) |
_ |
No erythema | 0 |
Very slight erythema (barely visible) | 1 |
clear erythema | 2 |
moderate erythema | 3 |
Severe erythema (purple red) to eschar formation that cannot be graded. | 4 |
Edema formation (OE) |
_ |
No edema | 0 |
Very mild edema (barely visible) | 1 |
Clear edema (swelling with clear edges) | 2 |
Moderate edema (swelling about 1mm) | 3 |
Severe edema (swelling exceeds 1mm and extends beyond the contact area) | 4 |
Stimulate the highest score | 8 |
Other abnormalities at the injection site should be recorded and reported. |
_ |
3. Result evaluation
Statistically analyze the original data and obtain the test results. If the final score of the test sample is not greater than 1.0, it meets the test requirements.
4. Relevant standards
1) iso 10993-10:2010 Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 10: Tests for irritation and skin sensitization;
2) GB/T16886.10-2017 Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 10: Irritation and skin sensitization tests;
3) GB/T14233.2-2005 Inspection methods for medical infusion, blood transfusion and injection equipment Part 2: Biological test methods;
4) GB/T 16175-2008 Test methods for biological evaluation of medical silicone materials;
5) EN ISO 10993-10:2010 Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 10: Tests for irritation and skin sensitization;
6) ISO 7405-2018 Dentistry — Evaluation of biocompatibility of medical devices used in dentistry.















