
Wireless product Thailand NBTC Certification fee
What is Thailand nbtc certification?
The NBTC in Thailand stands for the "National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission," which is a typical governmental regulatory body with administrative enforcement powers. It oversees telecommunications products and networks. Starting from July 1, 2008, the existing mandatory regulations for telecommunications equipment and terminal devices expanded to include wireless-related products, not just limited to mobile communication products. Generally, wireless products like mobile phones exported to Thailand need to obtain NBTC certification before being allowed to be sold in the local market.

Products that require NBTC certification include:
1. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) devices;
2. Short-Range Devices (SRD) and Wireless Local Area Networks;
3. WiFi and Bluetooth devices;
4. Fiber optic communication systems;
5. Various digital processing equipment like telephones and fax machines;
6. Low-power short-range wireless devices;
7. RFID devices and non-RFID devices operating in the 920 to 925MHz frequency band;
8. Automotive radars.

NBTC Regulatory Scope:
Telecommunication devices sold in Thailand are classified into three groups by the NTC:
- Class A: Registration
- Class B: Approval Certification
- SDoC: Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity
Detailed Explanation of NBTC Certification Product Testing Standards:
1. NBTC TS 1033-2560 standard specifies the technical requirements for RFID open-loop and non-RFID devices operating in the 920-925MHz frequency band in Thailand. The technical standard for RFID wireless communication devices at 920-925MHz is NBTC TS 1010-2560.
2. LTE Band 40 came into effect on May 28, 2018, for wireless wide area network devices and mobile products:
- NBTC TS1015-2560
- NBTC TS 1004-2560
NBTCTS 1027-2560 specifies the technical standards for LTE devices using Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) technology for International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT). All products with WWAN/Cellular functionality require a test report for LTE Band 40, including reports for Radio, SAR, and EMF testing.

Class A Approval: Products must be tested in NTC-designated laboratories and obtain a login number and certification after providing the required data to the NTC.
NBTC Certification Costs:
As a China JJR laboratory, we can save you 30% on certification costs (getting a quote won't waste your time).
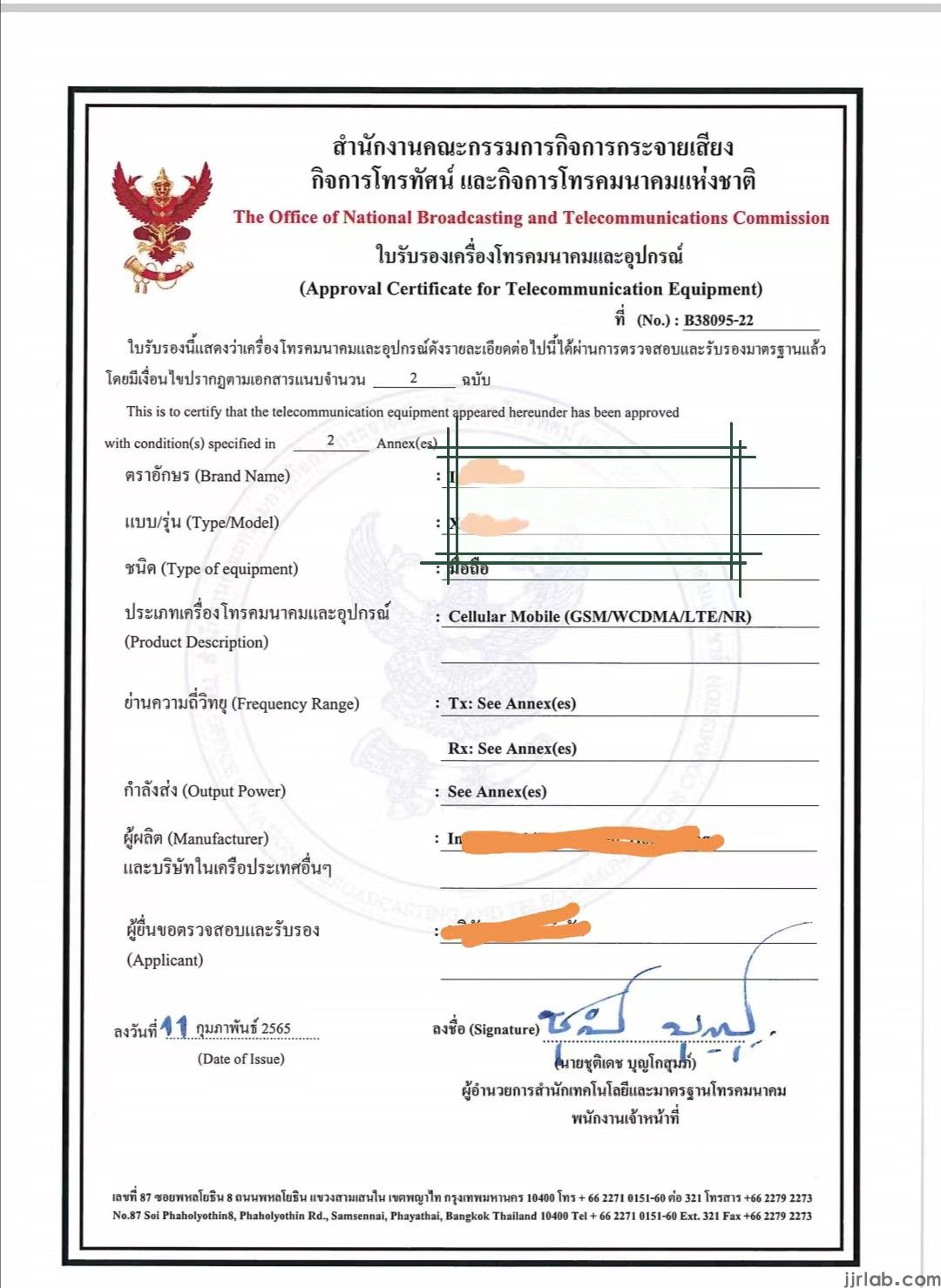
NBTC Declaration Mode:
The Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity (SDoC) mode of compliance is voluntary and must be filled out by a local representative in Thailand.
NBTC Application Process:
1. Provide product specifications and usage instructions.
2. Fill out the testing application form and provide product information.
3. Confirm testing standards; arrange preliminary testing.
4. Rectify the customer's product and arrange testing.
5. After testing is completed, draft a report.
6. Customer confirms report information and seals the report.
7. Key: Use the CE report + apply for NBTC certification with Thailand's deviations.
NBTC Certification Documents:
1. 1-2 prototypes.
2. Product specifications and usage instructions.
3. Adapter safety reports (LVD reports) EN60065 report or EN60950 report or EN62368 report.
4. List of key components; certificates for key components (UL certification/etl certification); and provide key component model numbers, manufacturer UL/ETL certificate numbers.
5. Product label and outer packaging images.
6. Operating environment temperature (tc℃), withstandable temperature (ta℃).
Important Notes:
1. Normal voltage standard 220V 50Hz/60Hz; if it is a plug adapter, it must comply with IEC60065 standard or IEC60950 standard or the new standard IEC62368, and the plug adapter must be a European plug with 220V-240V 50Hz/60Hz; if it is a desk lamp, the rated voltage must be 220V.
2. Label requirements: Text must be in English and include: product name, model number, manufacturer, technical parameters (voltage standard 220V-240V, 230V, 240V, 230V-240V are all acceptable), identifier, country of origin (made in China).
3. Outer box requirements: In addition to the label, include energy efficiency level, ROHS Testing, quantity, and dimensions.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Toothbrush FDA Certification Testing
Toothbrush FDA Certification Testing
 Snoring Device FDA 510k Standard Testing
Snoring Device FDA 510k Standard Testing
 Single Use Intravenous Catheter Certification Test
Single Use Intravenous Catheter Certification Test
 Silicone Material Product Compliance Certification
Silicone Material Product Compliance Certification
 What to Do If Cytotoxicity Test Results Are Positi
What to Do If Cytotoxicity Test Results Are Positi
 ISO 10993:5 Cytotoxicity Testing Methods
ISO 10993:5 Cytotoxicity Testing Methods
 FDA ISO 10993-1 Biocompatibility Evaluation Guidel
FDA ISO 10993-1 Biocompatibility Evaluation Guidel
 In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing for Medical Devices
In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing for Medical Devices
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




