
Wireless Charger FCC Certification Testing
As the technology of smartphones continues to advance, wireless charging technology has been more widely used in the market. Wireless charging technology mainly utilizes electromagnetic technology, where the transmitter converts electric current into electromagnetic waves, and the phone, equipped with a built-in chip receiver, converts the electromagnetic waves back into electric current to charge the phone. Products involving wireless electromagnetic technology are subject to strict regulations in various countries.
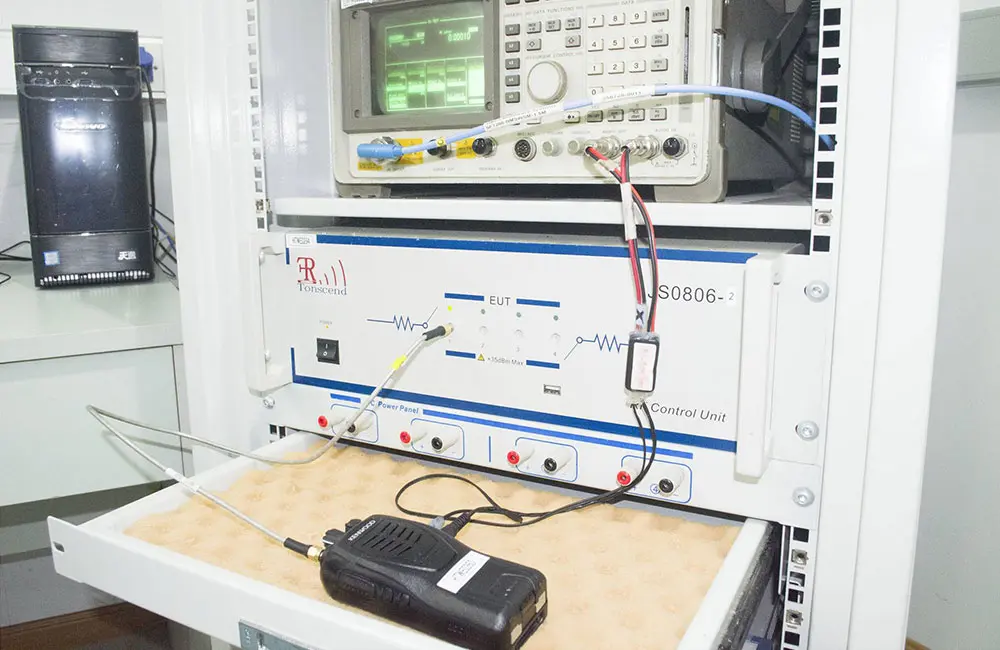

I. Regulatory Requirements
There are no corresponding regulatory requirements for FCC in the North American market for wireless chargers. In the absence of regulations, the FCC has issued Guidance KDB 680106 requirements. KDB 680106 specifically addresses technical specifications, testing reference standards, RF Exposure testing methods, and certification procedures for QI wireless chargers.
II. Testing Standards
According to the requirements of KDB 680106, different types of wireless chargers may refer to 47 CFR PART 15, 47 CFR PART 18, or both for testing regulations.
III. RF Testing Requirements
For common desktop wireless chargers, electromagnetic field strength probes should be used at a distance of 15cm from the product (for multi-coil synchronous transmission, the top should be tested at 20cm) on the top and four sides. For vehicle-mounted wireless chargers, testing should be conducted at distances of 0cm, 2cm, 4cm, 6cm, 8cm, and 10cm respectively. The measured values should not exceed 50% of 614V/m and 50% of 1.63A/m.

IV. Certification Form Requirements
Certification can be done through SDoC or Certification procedures. When the product meets the following requirements, there is no need to consult the FCC or follow the PAG procedure. The product can be directly tested and reported through the SDoC procedure, or tested by an FCC authorized laboratory and submit a TCB application for fcc id.
- Charging operating frequency is below 1MHz;
- Charging output power of each coil is equal to or less than 15W;
- The wireless charging device only contains a single primary coil and a single secondary coil for paired transmission. When there are multiple primary and secondary coil transmissions, they are also paired one by one;
- The wireless charging receiver directly contacts the transmitter for charging;
- Products that only meet the RF Exposure requirements for non-fixed category products;
- When the measurement probe is 15 cm away from the wireless charging device, the measured value of the magnetic field strength is less than 50% of the MPE limit. If the device contains multi-coil synchronous transmission, the testing distance at the top is 20cm;
- For vehicle-mounted wireless chargers, RF Exposure reports need to be submitted to the FCC for consultation in advance, and follow the consultation guidelines.
Email: hello@jjrlab.com
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
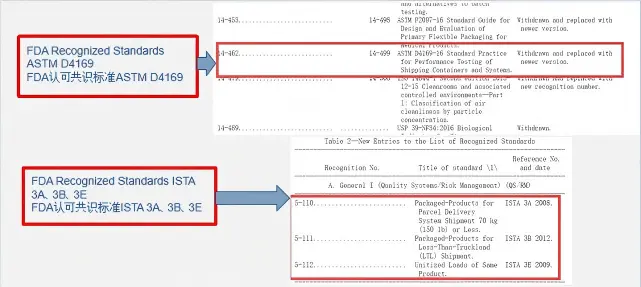 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




