
Where Can the Battery Be Tested for UL4200A?
A button battery is a small, round battery named for its button-like shape. They are commonly used to provide power to various small electronic devices, such as remote controls, electronic toys, calculators, blood glucose meters, smart watches, etc. Button batteries are made of lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) or other types of lithium-ion battery materials. They have the characteristics of small size, light weight and high power capacity.

As a portable power source, button batteries play an important role in various small electronic devices and instruments. With the continuous development of technology, the application range of button batteries will be more extensive, and its safety cannot be ignored.
Standard background
Reese Act: It is a law that the U.S. Congress began to enact after an 18-month-old girl died after swallowing a button battery in 2020.
Mandatory requirements
The 180 days from September 21, 2023 to March 19, 2024 is the enforcement transition period. If your consumer products use button batteries or coin batteries, this standard update notice applies. Enforcement date: March 19, 2024





definition
Button or coin batteries: Single-cell batteries with a maximum diameter of 32 mm (1.25 inches) and a diameter greater than the height; handheld products not exceeding 4.5kg; portable products not exceeding 18kg.
structural requirements
Products using coin/button batteries should be designed to minimize the risk of children removing, ingesting or inhaling the batteries.
For removable/replaceable batteries
1) Remove the detachable parts (the user can open or take them out by moving two independent movements at the same time without using tools or effortlessly.), and then use the test probe 11 to probe, and do not touch the button/coin battery.
2) Products that place removable or replaceable button/coin batteries in the battery compartment should be designed to prevent children from removing the battery through one of the methods in (a) or (b) below. Test to check compliance
a) Tools are required to open the battery box, such as screwdrivers, coins, etc. For battery compartments secured by screws or screw-in access covers, opening the battery compartment requires a torque of at least 0.5 Nm and a rotation angle of at least 90 degrees, or the fastener should engage at least two full threads; note that if screws or similar are used fasteners to secure the door or cover leading to the battery compartment, the fastener shall be secured to the door, cover or equipment.
b) The battery compartment door or cover requires at least two independent and simultaneous movements to open by hand. The opening movement cannot be combined with a single finger or a single movement of a finger.
Test process: pretreatment; drop test; impact test; rolling test; torque test; tensile test; compression test
preprocessing
Stress release test: add 10°C to 70°C or the highest temperature during normal operation of the equipment, whichever is the maximum temperature, and then place it in the oven for 7 hours;
Battery replacement test: Open and close the battery compartment ten times as one cycle. The torque force is in accordance with the requirements of Table 20 in UL60065. Note: The screws cannot be dropped during this period.
Drop test
The product is dropped from a height of 1 meter onto a horizontal hardwood surface, the hardwood surface is at least 13mm thick, installed on nominal two layers of 19mm thick plywood, placed on concrete, three drops for portable products, ten drops for handheld products .
Impact test
Use an iron ball with a diameter of 50.8mm and a weight of 0.5kg to drop at a certain height to give a 2J impact to the battery compartment or casing. Or the iron ball is suspended by a rope, swings like a pendulum, and impacts the battery compartment casing through the required height.
Rolling test
Apply a force of 330±5N to the product shell for 10 seconds. This force is exerted by a 100X250mm plane.
Torque test
If a child can grasp any part of the battery compartment casing with his thumb and forefinger or teeth, the battery compartment or cover needs to be tested with a torque of at least 0.5NM according to the toy safety standard consumer safety specification ASTMF963.
Pull test
If a child can grasp any part of the battery compartment casing with his thumb and forefinger or teeth, the battery compartment or cover needs to be tested with a 72N pull force in accordance with the toy safety standard consumer safety specification ASTMF963.
Stress test
If a child is able to contact any surface of the battery compartment enclosure during the drop test in 6.3.2, apply the compression test in ASTM F963, Standard Consumer Safety Specification for Toy Safety, using a force of at least 136 N (30.6 lbf). the surface
judgement
According to the test probe 11 in IEC 61032 "Protection of persons and equipment by enclosures - Standard for verification probes", apply a force of 50 +10/-0 N to the battery compartment door/cover or enclosure with a rigid test finger for 10 s. Battery door/cover does not open and remain functional; battery is not accessible.
For non-removable/replaceable batteries
structure
a) An enclosure or similar device that passes the applicable tests of 6.2 and 6.3 rendering it inaccessible; or
b) Completely fixed by the use of welding, fasteners (such as rivets) or equivalent means. The fixation method shall pass the safety test of 6.4.
Safety test
For the installation firmness of "batteries that are not allowed to be moved or replaced by the user", the battery shall not be separated by testing the hook and applying an outward force of 20 ± 2 N for 10 seconds.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
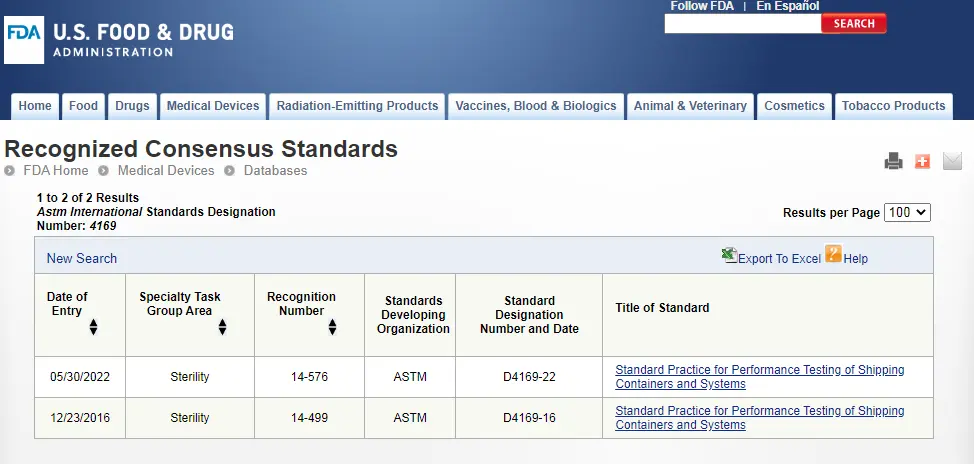 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
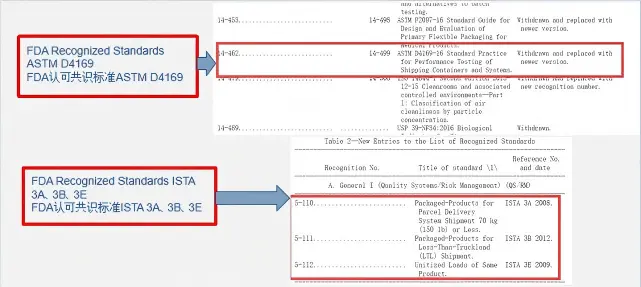
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




