
What standards are used for CE certification of wireless WiFi products?
WiFi, or wireless fidelity, falls under the category of 'Wireless Compatibility Certification' in the realm of wireless local area networks. Essentially, it is a form of commercial certification as well as a wireless networking technology. Previously, computers were connected via Ethernet cables, whereas WiFi enables internet connectivity through radio waves.

The terms '2.4G' and '5G' in WiFi refer to frequency bands (GHz). 2.4G is a wireless technology, abbreviated from the frequency range of 2.400GHz to 2.4835GHz. 2.4G WiFi is based on the IEEE 802.11b standard, which operates within the 2.4GHz frequency band. On the other hand, 5G WiFi refers to wireless technology developed based on the IEEE 802.11ac standard, which operates in the 5GHz frequency band.
What standards are used for CE certification of wireless WiFi 2.4 products?
- radio frequency testing standard: ETSI EN 300 328 V2.2.2
- Electromagnetic compatibility testing standard: ETSI EN 301 489-17 (same for 2.4G/5G WiFi/BT)
- Electrical safety testing standard: EN 62368-1 (same for wireless information technology products)
- Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) testing standard: EN 62209-1 (head SAR), EN 50566 (body SAR), EN 50665, EN 50663
What standards are used for CE certification of wireless WiFi 5G products?
- Radio frequency testing standard: ETSI EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (5G WiFi: 5150-5700MHz), ETSI EN 300 440 V2.2.1 (5G WiFi: 5725-5875MHz)
- Electromagnetic compatibility testing standard: ETSI EN 301 489-17 (same for 2.4G/5G WiFi/BT)
- Electrical safety testing standard: EN 62368-1 (same for wireless information technology products)
- Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) testing standard: EN 62209-1 (head SAR), EN 50566 (body SAR), EN 50665, EN 50663 (MPE)
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
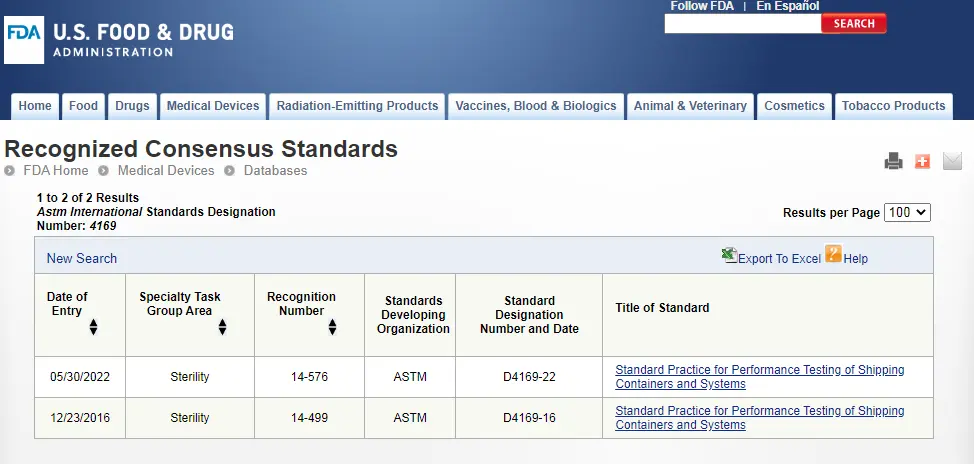 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
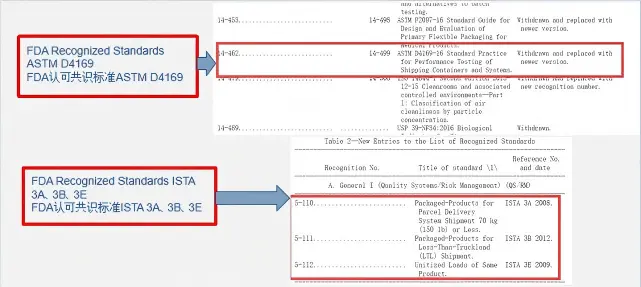 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




