
What is the UL 4200A-2023 Test?
In September 2023, the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) voted to adopt UL 4200A-2023 as a mandatory consumer product safety rULe for products containing button batteries, aiming to REDuce the ingestion hazard of button batteries for infants and young children.
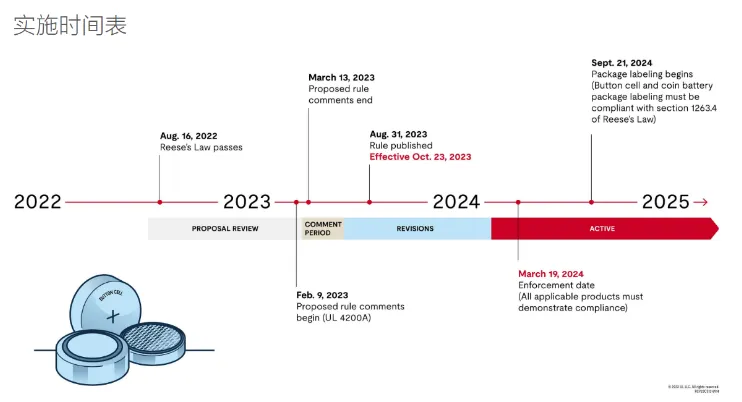
Safety Rule Overview:
The rule consists of two key Federal Register notices:
1. The 2023 industry standard UL 4200a has been incorporated into federal mandatory rules (adopted as 16 cfr 1263).
2. Additional packaging and labeling requirements have been introduced for standalone button batteries not covered by UL 4200A.
Applicable Products:
1. All consumer products containing button batteries.
2. Consumer products that contain or are designed to use one or more button batteries, regardless of whether these batteries are intended to be replaced by the consumer, included in the product, or sold separately. (These products must comply with ANSI/UL 4200A).
3. Consumer (household) products equipped with button lithium batteries with a diameter of ≤32mm, where the diameter exceeds the height.
Structural Requirements:
1. For products where batteries need to be replaced, the structure must meet the following:
- Using probe 11 from IEC61032 for testing, the battery must not be accessible. During inspection, if the enclosure can be opened without tools or with fewer than two independent consecutive actions, it must be opened for evaluation.
- The product must be designed to prevent infants and toddlers from accessing the battery:
- The battery compartment must require a tool (e.g., screwdriver, coin) to open.
- If using hands, at least two independent and simultaneous actions are required to open the battery compartment’s cover or door.
- If the battery compartment is secured with screws or similar fasteners, the fasteners must be captured within the cover or door.
2. If the product has a "non-user-replaceable battery," it must effectively prevent users or children from removing it. The product must be designed such that:
- The battery is inaccessible via the enclosure or similar methods.
- The battery is fully secured by welding, riveting, or similar means.
Test Requirements for UL 4200A:
1. Stress Relief Test: The maximum temperature rise of the plastic enclosure during heating is +10°C or 70°C minimum, for 7 hours.
2. Battery Replacement Test: Open/lock the cover and replace the battery for 10 cycles. Minimum torque for loosening/tightening screws with a head is 0.4 Nm. Complete 10 cycles even if the screw head slips after the second loosening/tightening cycle.
3. Drop Test: 3 times for portable devices, 10 times for handheld products.
4. Impact Test: 3 times, 2J impact.
5. Crush Test: Apply 330±5N force to a 100x250mm area for 10 seconds.
6. Torque Test: 0.5 Nm torque when a child can grip the battery cover with thumb and forefinger or teeth.
7. Pull Test: 72N pull force when a child can grip the battery cover with thumb and forefinger or teeth.
8. Compression Test: If the battery cover is accessible to children, but unlikely to be removed by them, apply a downward pressure of 136N.
9. Conformance Test: After tests such as the drop test, impact test, and compression tests, apply 50±10N force for 10 seconds with a rigid finger; the battery should not be accessible.
10. Safety Test: Non-replaceable button batteries must comply with the fixing methods outlined and pass relevant contact tests. Use a hook with 20±2N force for 10 seconds to test battery contact.
Product Warning Labels:
- If there is sufficient space on the product, use the following labels:


- For products with insufficient surface space, use a specific symbol, ensuring its meaning is explained in the user manual or other printed materials accompanying the packaging.

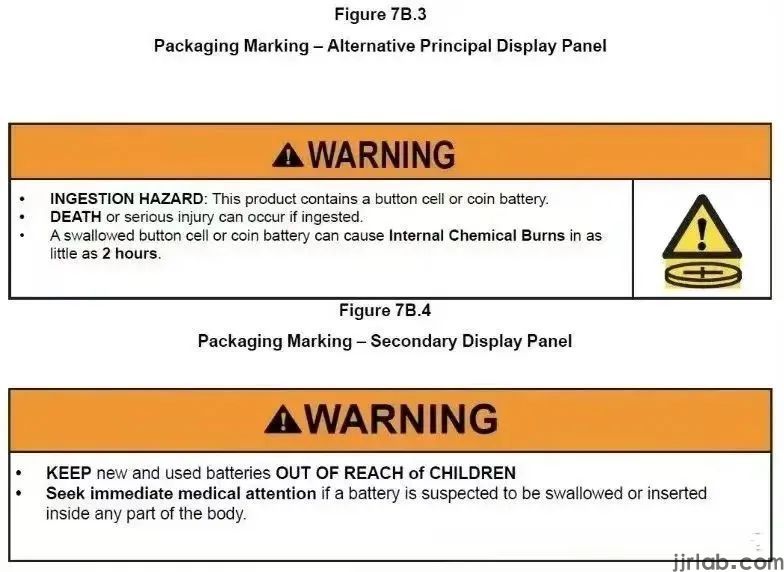
Packaging Warning Labels:
- If there is sufficient space on the packaging, use specific figures for warnings.
- If packaging space is insufficient, use the same warning figures but ensure clarity in any accompanying materials.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 What is the European Accessibility Act (EAA)?
What is the European Accessibility Act (EAA)?
 Compliance Guidelines for India IS/IEC 62368-1:202
Compliance Guidelines for India IS/IEC 62368-1:202
 16 CFR Part 1512 Compliance Testing Laboratory
16 CFR Part 1512 Compliance Testing Laboratory
 Electromagnetic Compatibility and Interference Tes
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Interference Tes
 What is 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance and Regulations
What is 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance and Regulations
 2026 California Prop 65 Regulations and Warnings
2026 California Prop 65 Regulations and Warnings
 What are the export compliance for electric fans
What are the export compliance for electric fans
 Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




