
What is E Mark Certification?
E/e-mark Certification Introduction
Europe has safety certification requirements for complete motor vehicles and safety-related parts and systems, which are specifically reflected in the E mark and e mark certification.
The e-mark is mandatory and mainly applies to complete vehicles.
E-mark is optional and mainly applies to spare parts.
E-mark

Certification is a certification system implemented by the Economic Commission of Europe (ECE) for vehicles and parts entering the markets of its member states.
Europe has safety certification requirements for motor vehicles and parts and systems related to safety, which are specifically reflected in the E mark and e mark certification. The E mark originates from the regulations promulgated by the Economic Commission of Europe (ECE). At present, ECE includes 28 European countries, including non-European countries such as Eastern Europe and Southern Europe in addition to EU member states. Ece regulations are recommended for application by all members and are not mandatory standards. Member states can apply ECE regulations or continue to use their own regulations. From the perspective of market demand, ECE members are usually willing to accept test reports and certificates that comply with ECE regulations. The products involved in the E mark certificate are parts and system components, and there are no corresponding regulations for vehicle certification. Products that have obtained the E mark certification are accepted by the market. The executive testing agency of the E mark certification is generally the technical service agency of the ECE member states. The issuing agency of the E mark certificate is the government department of the ECE member states.
e-mark

Certification is a directive issued by the European Union (EEC), which is implemented under the EU framework in accordance with the EC Directive and is mainly aimed at complete vehicles.
The e-mark is a certification mark for motor vehicle complete vehicles, safety components and systems that the European Commission forces member states to use in accordance with EU directives. The testing agency must be a technical service agency within the EU member states, and the issuing agency is the government transportation department of the EU member states. Products that have obtained the e-mark certification will be recognized by all EU member states. Like the E-mark certification, the certificates of each member state have corresponding numbers.
The difference between E-mark and e-mark certification
The differences between E-mark and e-mark are mainly as follows:
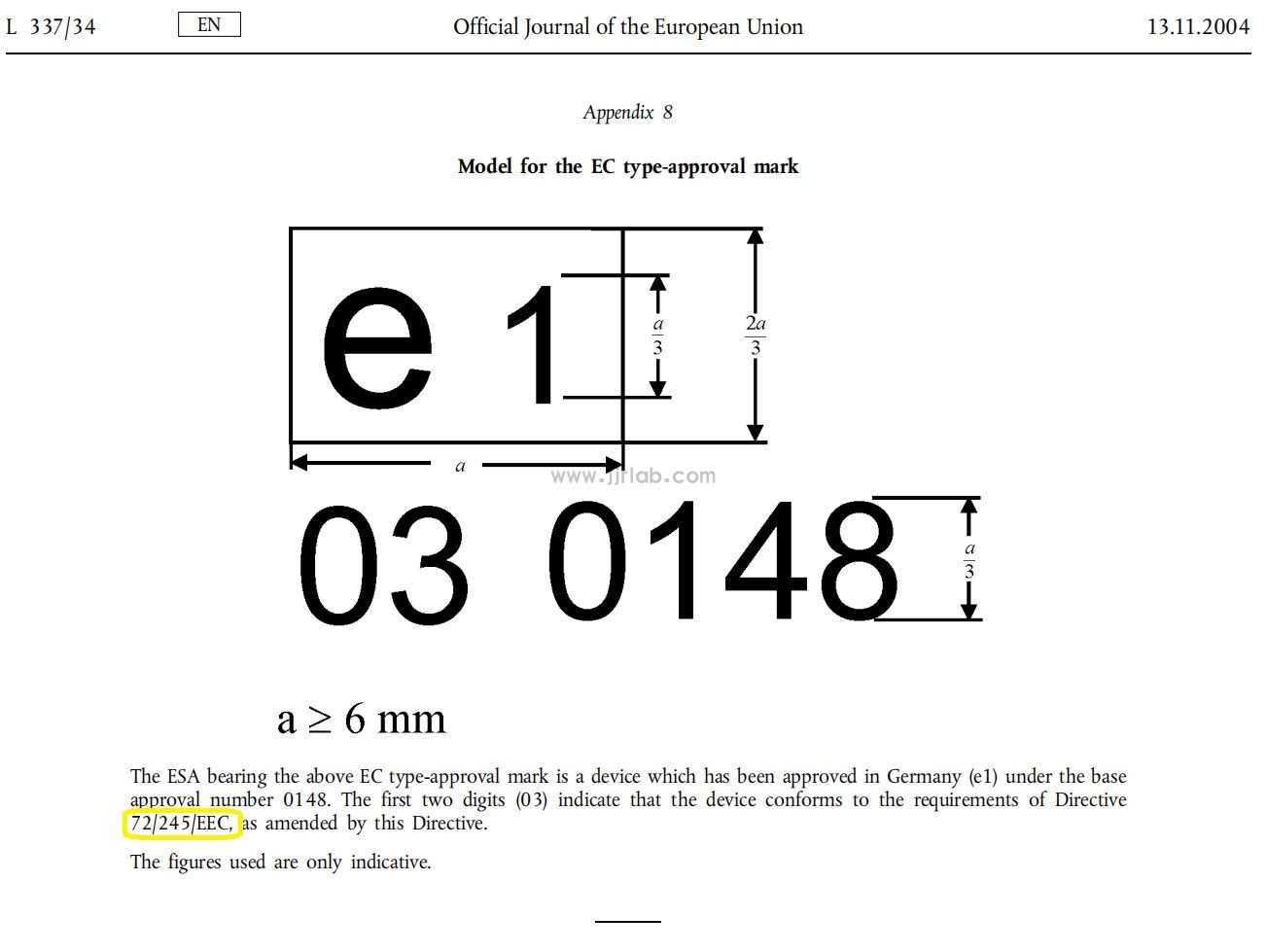
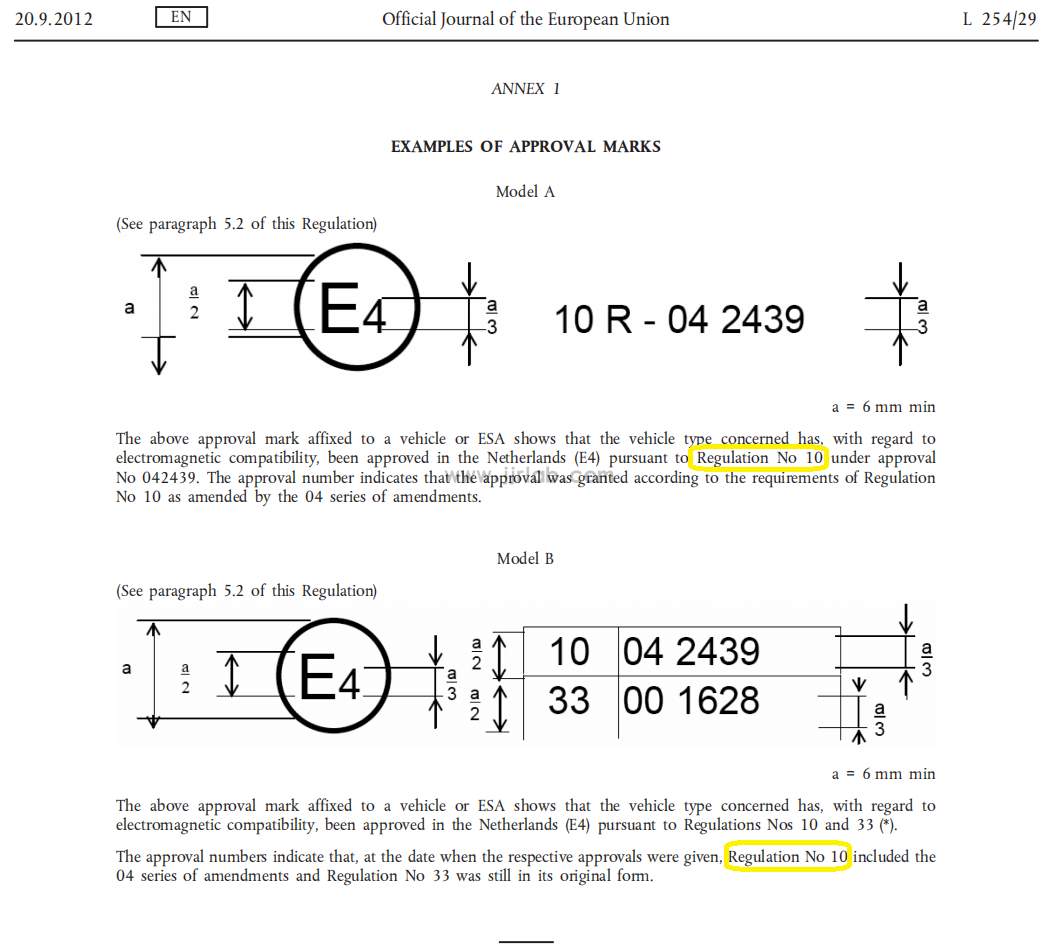
(1) Different origins: E-mark originates from Regulation No. 10 promulgated by the Economic Commission of Europe (ECE); e-mark originates from EU Directives 72/245/EEC, 95/54/EC and 2004/104/EC (2004/104/EC is the latest technical revision, and the latest non-technical revision is 2009/19/EC);
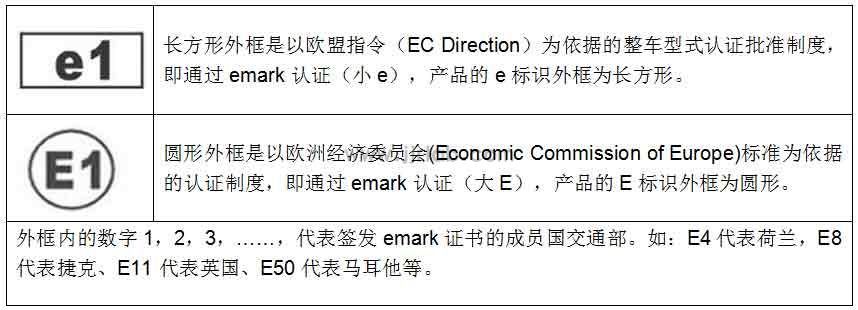
(2) Different logos
E-mark Use the big E logo in a round frame
The e-mark uses a small e logo in a rectangular frame;
(3) Different geographical scope and nature
The E-mark is applicable worldwide, including non-EU countries such as Eastern and Southern Europe (such as Russia), but the E-mark is non-mandatory and member states may refuse to accept it.
The e-mark is applicable to EU member states, which currently (as of May 4, 2011) have 27 member states. All EU member states must enforce the directive requirements, and only need to apply for the e-mark in one member state, and the other member states must recognize the validity of the certificate, that is, mandatory mutual recognition.
(4) One is mandatory and the other is not mandatory
The e-mark is mandatory and mainly applies to complete vehicles.
E-mark is optional and mainly applies to spare parts.
Certification Type | E-mark certification | e-mark certification |
Date of establishment | 1958 Geneva Agreement | Treaty of Rome 1957 |
Logo | AND | It is |
name | ECE, E-Mark, E mark | EU, EC, EEC, e-mark, e-mark |
technical standard | Regulation issued by ECE | EEC Directive issued by the European Union |
Headquarters | Geneva | Brussels |
membership | Members of the United Nations are free to join | Must be a member of the EC member country |
Applicable areas | Europe and other regions | EC Member States |
Acceptance by Member States | Not mandatory, optional | Mandatory, all terms must be accepted |
Vehicle/Parts Certification | Mainly for parts | Mainly for complete vehicles |
E/e-mark certification mark
Rectangular frame-e
Refers to products that can be used normally but are not essential for use whether the vehicle is stopped or moving, such as: car chargers, car lamps, car air pumps, car massage cushions, car heated seat cushions, car fans, car electric kettles, car refrigerators, car coffee pots, car TVs, car audio systems, car electric jacks, car vacuum cleaners, car power tools, etc.
Round frame-E
Refers to products that must be used whether the vehicle is stopped or in motion, such as windshields, seat belts, headlights, etc.
E/e-mark certification country introduction
(1) E-mark is non-mandatory , also known as ECE certification, and written as emark certification. It is an approval system based on the technical quality standards formulated by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UN Economic Commission of Europe). The authorized agency tests and certifies vehicles and related parts and components, and issues certificates for qualified products. After obtaining the certificate, the manufacturer will be allowed to sell its products in ECE member countries only after marking the E mark on its products. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe is a subsidiary agency of the United Nations. Currently, its members include 48 member countries in Europe, Africa and Asia. Certificates issued by any member country are mutually recognized by other member countries.
The certificates of ECE member countries have corresponding numbers: E1 - Germany E2 - France E3 - Italy E4 - Netherlands E5 - Sweden E6 - Belgium E7 - Hungary E8 - Czech Republic E9 - Spain E10 - Serbia and Montenegro E11 - United Kingdom E12 - Austria E13 - Luxembourg E14 - Switzerland E16 - Norway E17 - Finland E18 - Denmark E19 - Romania E20 - Poland E21 - Portugal E22 - Russia E23 - Greece E24 - Ireland E25 - Croatia E26 - Slovenia E27—SlovakiaE28—BelarusE29—EstoniaE31—Bosnia and HerzegovinaE32—LatviaE34—BulgariaE36—LithuaniaE37—TurkeyE39—AzerbaijanE40—MacedoniaE43—JapanE45—AustraliaE46—UkraineE47—South AfricaE48—New ZealandE49—CyprusE50—MaltaE51—South KoreaE52—MalaysiaE53—ThailandE56—MontenegroE58—Tunisia
(2) e-mark is mandatory , also known as EEC certification, which is a European Community vehicle type approval system based on the EU Directive (EC Directive). The authorized agency tests and certifies vehicles and related parts and components, and issues certificates for qualified products. After obtaining the certificate, manufacturers can only be allowed to sell their products in its 27 member states after marking the e-mark on their products. The certificates issued by the member states are mutually recognized.
The certificates of each EEC member country have corresponding numbers: e1 - Germany e2 - France e3 - Italy e4 - Netherlands e5 - Sweden e6 - Belgium e7 - Hungary e8 - Czech Republic e9 - Spain e11 - United Kingdom e12 - Austria e13 - Luxembourg e17 - Finland e18 - Denmark e19 - Romania e20 - Poland e21 - Portugal e23 - Greece e24 - Ireland e26 - Slovenia e27 - Slovakia e29 - Estonia e32 - Latvia e34 - Bulgaria e36 - Lithuania e49 - Cyprus e50 - Malta
E/e-mark certificate validity period
After obtaining the E-mark certificate, companies usually pay attention to how long the E-mark certificate is valid for. According to the ECE Regulation and EC Direction, all vehicles and parts that need to enter the EU member states must pass the E-mark certification corresponding tests and production consistency inspections. After the company's products obtain the E-mark certificate, as long as the following situations do not occur, the company's E-mark certificate is valid for a long time.
Substantial changes to the product: changes to the product model, specifications, key parameters, etc.;
Failure to accept the requirements of the issuing agency: The enterprise fails to accept factory inspection or pay fees as required by the issuing Ministry of Transport;
There are major updates to the corresponding regulations: There are significant changes in the regulations for testing products that have obtained certificates.
E/e-mark certificate query method
Since the transport ministries of EU member states are independent institutions, there is currently no unified external platform to provide E-mark certificate inquiries. If an enterprise needs to inquire about its own certificate, it can send an email to the certificate issuing agency for confirmation.
E/e-mark certification process
Before applying for E-mark certification, it is beneficial for enterprises to have a general understanding of the E-mark certification process and precautions. It not only ensures that the certificate is issued in a timely and smooth manner, but also avoids additional costs.
Certification application - the manufacturer prepares technical data and samples.
Certification application - submit an E-mark certification application to the Ministry of Transportation of the issuing country.
Document preparation - prepare relevant certification documents according to the requirements of the issuing country.
Product testing - the company sends the samples to be tested to a designated laboratory for formal testing.
Report writing - Write a report based on qualified test data and product description.
Submit for review - The engineer submits the complete report to the Ministry of Transportation of the issuing country for review.
Factory inspection - Factory inspection is required for the first application.
Issuance of certificate - After verification, the European national transportation department will officially issue the E/e-mark certificate.
E/e-mark certification time
Usually, the E-mark certification time is the focus of enterprises before applying for certification, because the E-mark certification time directly determines the delivery time of the enterprise. Generally speaking, the factors that affect the E-mark certification time include the following:
Certified products: Different certified products have different corresponding testing standards, requirements, items and time. For example, the headlight test only takes a few days, while the brake pad test is relatively complex and takes several months.
Issuing country: All EU member states can issue E-mark certificates, and certificates issued by any member state are mutually recognized in other countries. However, the requirements of each member state are different, and E-mark certification will also be different.
Data preparation: Before applying for E-mark certification, if the enterprise can prepare all the certification materials in a timely and sufficient manner, the time for E-mark certification will be greatly shortened.
Generally speaking, the E-mark certification of conventional products (such as vehicle lamps, rearview mirrors, vehicle electronic products, speakers, interior decoration parts, etc.) takes 6-8 weeks. If we can effectively control the time cutoff of each link in the certification process, have our own independent laboratory, and directly invite EU Ministry of Transport officials to issue E-mark certificates in China, the time will be shorter, usually 4 weeks, and the fastest 10 working days.
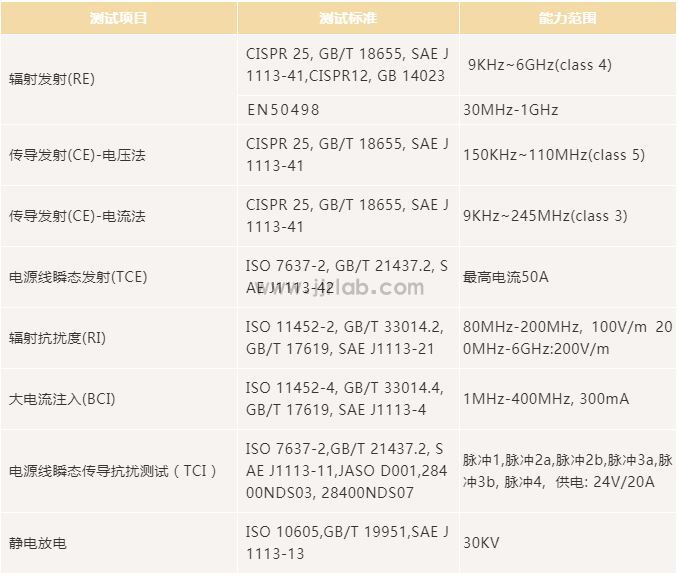
E-mark ECE R10 test items
ECE R10 test items for vehicle E-Mark regulations
1. Emission of Conducted Disturbances
ISO 7637-2 2004
2. Simulated pulse waveform anti-interference test - Immunity to transient disturbances conducted along supply lines
ISO 7637-2 2004
3. Broadband Electromagnetic interference Generated by ESAs
CISPR 25
4. Narrowband emission test - Narrowband electromagnetic interference generated by ESAs
CISPR 25
5. Immunity of ESAs to Electromagnetic Radiation
Absorber Chamber Test substitution method ISO 11452-2
TEM(transverseelectromagneticmode) Cell Testing(see Appendix 2 tothis Annex) ISO 11452-3
Bulk Current Injection Testing ISO 11452-4
or
Stripline Testing ISO 11452-5
Provide convenient and fast E-mark certification (E1, E4, E24, E9, E13, E49, E57) for automotive electronic parts manufacturers to enter the EU market
E/e-mark certification matters needing attention
When applying for E/e-mark certification, enterprises may easily encounter the following problems due to the lack of professionalism of the certification service agency they choose or inadequate certification guidance:
Failure to pass the test: The product needs to be tested repeatedly, increasing the company's certification costs;
Improper use of the logo: The use of the logo does not comply with regulatory requirements, resulting in the product being unsalable;
Error in certificate: Certificate fee will be re-charged, additional fees will be added, and time will be affected.
Therefore, in order to avoid the above problems, it is necessary to be familiar with the certification requirements and make adequate preparations. For example, pre-test the samples in advance and make timely corrections to non-conformities. At the same time, there is a professional service team to provide comprehensive guidance to enterprises and effectively control the certification process.
All complete vehicles, key components and systems entering Europe must be approved by the relevant European transport ministries, which is currently known as the E/e-Mark certification, specifically the E mark and e mark certification.
How to distinguish and choose between big E and small E
First, determine whether the country where the product is sold is a member of the European Union (EC) or the European Economic Commission (ECE). If it is only an ECE member state and not an EC member state, you can only choose Big E.
Secondly, determine which regulations or directives apply to the product. Different products have different corresponding regulations. For example, the front and rear position lights, brake lights, and width lights of motor vehicles are subject to ECE.R7. (Most vehicle-mounted electronic products are subject to ECE R.10 and 2009/19/EC). If the product is subject to ECE regulations and the country of sale is an EC EU member state, but not within the ECE member state, only the small e certification can be obtained.
Finally, if both EC directives and ECE regulations are applicable, it is recommended to apply for Big E certification, which is applicable to more countries.
The technical requirements of E/e mark are mainly the electromagnetic compatibility requirements of products. For E-mark, the regulations are ECE R10 , while the e-mark regulations are 2004/104/EC . The technical requirements of the two are basically the same, requiring the near field (1m test distance) of electromagnetic interference of the whole vehicle or vehicle-mounted components to meet the broadband and narrowband limit requirements respectively. At the same time, the components related to vehicle driving control must meet the anti-interference requirements of electromagnetic radiation.
The e-mark is a certification mark for motor vehicle complete vehicles, safety components and systems that the European Commission forces member states to use in accordance with EU directives. The testing agency must be a technical service agency within the EU member states, and the issuing agency is the transportation department of the EU member state government. Products that have obtained the e-mark certification will be recognized by all EU member states.
The E mark originates from the regulations promulgated by the Economic Commission of Europe (ECE). Currently, ECE includes 28 European countries, including non-European countries such as Eastern Europe and Southern Europe in addition to EU member states. Usually, ECE members are willing to accept test reports and certificates that comply with ECE regulations. The products involved in the E mark certificate are parts and system components. There are no corresponding regulations for vehicle certification. Products that have obtained the E mark certification are accepted by the market. The executive testing agency of the E mark certification is generally the technical service agency of the ECE member countries. The issuing agency of the E mark certificate is the government department of the ECE member countries, and the certificates of each country have corresponding numbers.
European Union Automobile Standards and Regulations System (ECE)
Standard No. Name
ECE R1 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing and/or high beam and fitted with R2 and/or HS1 category filament lamps
ECE R2 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of incandescent lamps for headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing and/or high beam
ECE R2 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of retro-reflective devices for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R4 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of lighting devices for the rear registration plates of motor vehicles (other than motorcycles) and their trailers
ECE R5 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of sealed-beam headlamps for motor vehicles emitting asymmetrical passing and/or high beams of the European type (SB)
ECE R6 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of direction indicators for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R7 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of front and rear position (side) lights, brake lights and clearance lights for motor vehicles (excluding motorcycles) and their trailers Concerning the approval of lamps emitting asymmetrical passing and/or high beam and equipped with halogen filament lamps (H1, H2, H3, HB3, HB4, H7, H8,
ECE R8 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of direction indicators for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R9 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles in the L2, L4 and L5 categories with regard to noise emissions
ECE R10 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to electromagnetic compatibility
ECE R11 Uniformity in the approval of vehicles with respect to door locks and door retaining parts
ECE R12 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to the protection of steering mechanisms against injury to the driver in the event of a collision
ECE R13 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles of categories M, N and O with regard to braking
ECE R13--H Uniform provisions for the approval of passenger cars with respect to brakes (European, American and Japanese coordinated version)
ECE R14 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to seat belt anchorage points
ECE R15 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles equipped with spark-ignition or compression-ignition engines with respect to emissions of engine gaseous pollutants / Methods of measuring power of spark-ignition engines --- Methods of measuring fuel consumption of vehicles
ECE R16 concerning: 1 Approval of seat belts and restraint systems for adult occupants in motor vehicles; 2 Uniform provisions for the approval of vehicles equipped with seat belts
ECE R17 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with respect to seats, seat anchorages and head restraints
ECE R18 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles with regard to protection against theft
ECE R19 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of front fog lamps for motor vehicles
ECE R20 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing and/or main beam and fitted with halogen filament lamps (H4)
ECE R21 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to interior parts
ECE R22 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of helmets and visors for drivers and passengers of motorcycles and mopeds
ECE R23 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of reversing lights for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R24 Concerning 1. Approval of compression ignition (CI) engines with respect to visible pollutant emissions; 2. Approval of motor vehicles with respect to the installation of type-approved CI engines; 3. Approval of vehicles equipped with CI engines with respect to visible pollutant emissions from the engine; 4. Uniform provisions for the measurement of power of CI engines
ECE R25 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of head restraints, whether integral or not with vehicle seats
ECE R26 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to external projections
ECE R27 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of advance warning triangles
ECE R28 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of sound warning devices and motor vehicles with regard to acoustic signals
ECE R29 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to the protection of occupants in the cab of commercial vehicles
ECE R30 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R31 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of halogen sealed beam (HSB) motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and/or high beam
ECE R32 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to the structural characteristics of the vehicle struck in a rear-end collision
ECE R33 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to the structural characteristics of vehicles struck in a frontal impact
ECE R34 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to fire protection
ECE R35 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with respect to the arrangement of foot controls
ECE R36 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of large passenger vehicles with respect to their general construction
ECE R37 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of incandescent lamps for use in approved lamps for motor vehicles and trailers
ECE R38 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of rear fog lamps for motor vehicles and trailers
ECE R39 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with respect to speedometers and their installation
ECE R40 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motorcycles equipped with spark-ignition engines with respect to the emission of gaseous pollutants from the engines
ECE R41 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motorcycles with regard to noise
ECE R42 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to front and rear protective devices (bumpers, etc.)
ECE R43 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of safety glazing materials
ECE R44 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of child occupant restraint devices (child restraint systems) in motor vehicles
ECE R45 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles with regard to headlamp washers and the approval of headlamp washers
ECE R46 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of rear-view mirrors and the approval of motor vehicles with respect to the fitting of rear-view mirrors
ECE R47 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of mopeds equipped with spark-ignition engines with regard to the emission of gaseous pollutants from the engines
ECE R48 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with respect to the installation of lights and light-signalling devices
ECE R49 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of compression ignition engines, natural gas engines and spark-ignition engines burning liquefied petroleum gas and vehicles equipped with these engines with respect to engine pollutant emissions
ECE R50 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of front and rear position lamps, brake lamps, turn signal lamps and rear registration plate lighting for mopeds, motorcycles and similar vehicles
ECE R51 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles with four or more wheels with respect to noise emission
ECE R52 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of small public transport vehicles (M2, M3) with respect to their general construction
ECE R53 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles of category L3 (motorcycles) with respect to the installation of lights and light-signalling devices
ECE R54 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers
ECE R55 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of mechanical couplings between vehicles and trains
ECE R56 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of headlights for mopeds and similar vehicles
ECE R57 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of headlights for motorcycles and similar vehicles
ECE R58 Uniform provisions concerning 1. Approval of rear underbody guards; 2. Approval of vehicles with respect to the installation of approved rear underbody guards; 3. Approval of vehicles with respect to rear underbody guards
ECE R59 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of alternative silencer systems
ECE R60 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of two-wheeled motorcycles with respect to controls operated by the driver, including the identification of controls, tell-tale devices and indicators
ECE R61 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of commercial vehicles with regard to external projections in front of the rear tailgate of the cab
ECE R62 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles with control handles with regard to the protection against theft
ECE R63 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of two-wheeled mopeds with regard to noise
ECE R64 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles equipped with an emergency spare wheel/tyre
ECE R65 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of special warning lights for motor vehicles
ECE R66 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of large passenger vehicles with respect to the strength of superstructures
ECE R67 concerning: 1. Approval of special equipment for motor vehicles for use with liquefied petroleum gas in their drive system; 2. Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles equipped with special equipment for use with liquefied petroleum gas in their drive system with regard to the installation of such equipment
ECE R68 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles, including purely electric vehicles, with regard to the measurement of maximum speed
ECE R69 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of rear signs for low-speed vehicles and their trailers
ECE R70 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of rear signs for heavy and long vehicles
ECE R71 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of agricultural tractors with regard to the driver's field of vision
ECE R72 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motorcycle headlamps emitting asymmetrical passing and high beams and equipped with halogen lamps (HS1 lamps)
ECE R73 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of trucks, trailers and semi-trailers with regard to side protection
ECE R74 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles of category L1 with respect to lights and light-signalling devices
ECE R75 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of pneumatic tyres for motorcycles and mopeds
ECE R76 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of headlamps for mopeds emitting high and low beams
ECE R77 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of parking lights for motor vehicles
ECE R78 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles in the L category with regard to braking
ECE R79 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with respect to steering gear
ECE R80 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of large passenger car seats and vehicles with regard to seats and their fixing points
ECE R81 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of rear-view mirrors and two-wheeled motor vehicles with or without sidecars with respect to the fitting of rear-view mirrors on the handlebars
ECE R82 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of headlamps for mopeds fitted with halogen filament lamps (HS2)
ECE R83 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to pollutant emissions according to engine fuel requirements
ECE R84 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicles equipped with internal combustion engines with regard to the measurement of fuel consumption
ECE R85 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of internal combustion engines or electric drive trains for use in powering motor vehicles of categories M and N with respect to the measurement of net power and maximum 30-minute electric drive train power
ECE R86 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of agricultural and forestry tractors with regard to the installation of lights and light-signaling devices
ECE R87 Uniform provisions for daytime running lights for motor vehicles with reversible approval
ECE R88 Uniform Provisions Concerning the Approval of Reflective Tires for Motorcycles
ECE R89 Concerning 1. Approval of vehicles with respect to maximum speed limit or its adjustable speed limit function; 2. Approval of vehicles with respect to the installation of a maximum speed limiter or an adjustable speed limiter of an approved type; 3. Uniform provisions for the approval of speed limiters or adjustable speed limiters
ECE R90 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of replaceable brake lining assemblies and drum brake linings for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R91 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of side marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R92 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of non-original replaceable exhaust silencer systems for motorcycles, mopeds and three-wheeled vehicles
ECE R93 Uniform provisions concerning 1. Approval of front underbody guards; 2. Approval of vehicles with regard to the installation of type-approved front underbody guards; 3. Approval of vehicles with regard to front underbody guards
ECE R94 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to occupant protection in frontal collisions
ECE R95 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to occupant protection in side impacts
ECE R96 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of compression ignition engines for use in agricultural and forestry tractors and non-road motorised machinery with regard to engine pollutant emissions
ECE R97 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicle warning systems and the approval of motor vehicles with regard to warning systems
ECE R98 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas discharge light sources
ECE R99 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of gas discharge light sources for use in gas discharge lamps for motor vehicles that have been type-approved
ECE R100 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of battery electric vehicles with regard to particular requirements for construction, functional safety and hydrogen emissions
ECE R101 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of passenger cars with internal combustion engines with respect to the measurement of CO2 emissions and fuel consumption and of vehicles of categories M1 and N1 with electric drivetrains with respect to the measurement of electrical energy consumption and range
ECE R102 Uniform provisions concerning 1. the approval of tight couplings; 2. the approval of vehicles with respect to the installation of approved tight couplings.
ECE R103 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of replaceable catalytic converters for motor vehicles
ECE R104 Uniform provisions for the approval of retro-reflective markings for heavy and long motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R105 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles for the transport of dangerous goods with regard to special structural features
ECE R106 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of pneumatic tyres for agricultural vehicles and their trailers
ECE R107 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of large double-decker passenger vehicles with respect to general construction
ECE R108 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of the production of retreaded pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers
ECE R109 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of the production of retreaded pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers
ECE R110 Concerning: 1. Approval of special parts for motor vehicles that use compressed natural gas (CNG) in their propulsion systems; / 2. Uniform provisions for the approval of motor vehicles that use compressed natural gas (CNG) in their propulsion systems with respect to the installation of approved special parts
ECE R111 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of tank motor vehicles of categories N and O with regard to rollover stability
ECE R112 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical high and/or low beam and incorporating filament lamps
ECE R113 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting a symmetrical high beam and/or low beam and incorporating filament lamps
ECE R114 Regarding approval: 1. Airbag components for replacement airbag systems; 2. Replacement steering wheels equipped with approved airbag components; 3. Uniform provisions for replacement airbag systems installed other than steering wheels.
ECE R115 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of: 1. Special liquefied petroleum gas filling systems for installation on motor vehicles using liquefied petroleum gas in their drive system; / 2. Special compressed natural gas filling systems for installation on motor vehicles using compressed natural gas in their drive system
ECE R116 Uniform technical provisions for the protection of motor vehicles against theft
ECE R117 Uniform provisions for the approval of tyres with regard to rolling noise
ECE R118 Uniform technical provisions for the combustion characteristics of materials used in the interior structure of certain types of motor vehicles
ECE R119 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of cornering lights (bending lights) for motor vehicles
ECE R120 Uniform provisions concerning the approval of internal combustion engines for agricultural and forestry tractors and non-road motor vehicles with respect to the measurement of net corrugation ratio
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
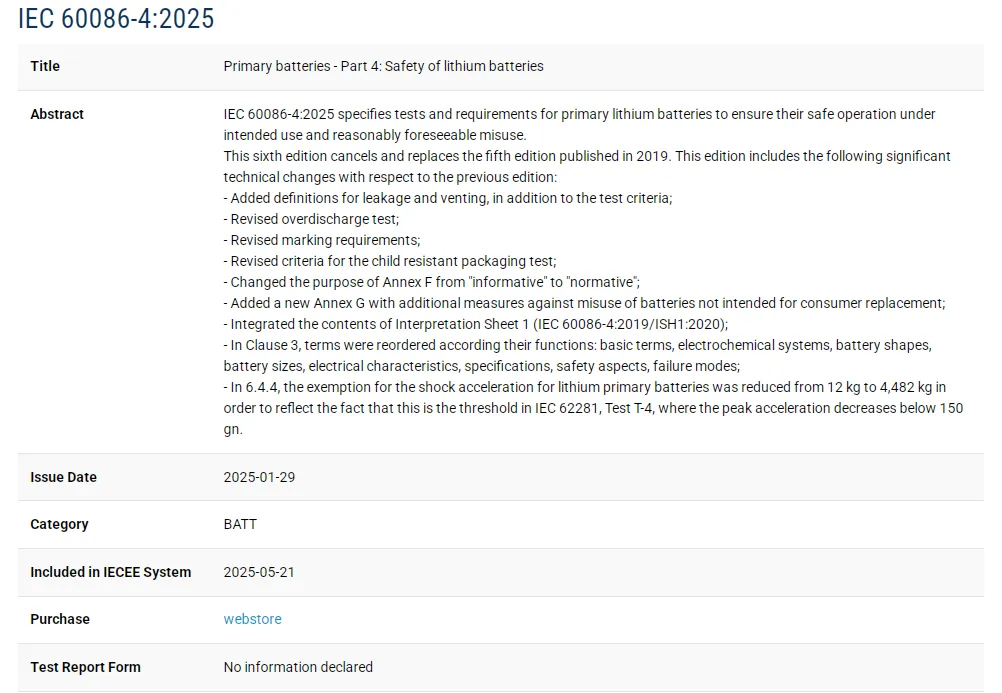 IECEE Releases Safety Testing Standard for Button
IECEE Releases Safety Testing Standard for Button
 EN 17191 Child Seat Compliance Certification Testi
EN 17191 Child Seat Compliance Certification Testi
 Toy CPC Certification: ASTM F963 Amazon Compliance
Toy CPC Certification: ASTM F963 Amazon Compliance
 EN 71 Certified (EN 71-15/16/17:2025)
EN 71 Certified (EN 71-15/16/17:2025)
 Product Compliance Consulting
Product Compliance Consulting
 Electrical Appliance CE EMC Compliance Testing
Electrical Appliance CE EMC Compliance Testing
 How Much Does EPA Certification Cost?
How Much Does EPA Certification Cost?
 How to get the GB 26572-2025 Test Report?
How to get the GB 26572-2025 Test Report?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




