
What Certifications are Extension Cord Exported to the EU?
Power strips are closely connected with daily life and electrical appliance use, facing a series of complex and critical regulations and requirements when exported to the EU. Here’s a closer look:
General Regulations
On December 22, 2023, the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization released the EN IEC 60335-1:2023/A11:2023 standard. This standard outlines the latest technical requirements for household appliances and similar products, including power strips. Compared to previous versions, it introduces significant updates, such as:
- Clarifying PELV circuit requirements.
- Introducing testing requirements for the mechanical strength of sockets with integrated pins.
Certification Requirements
Power strips exported to the EU must meet several important certification standards. The most critical is CE certification.
- CE Certification is a mandatory product safety certification for the European market. It applies to nearly all industrial and consumer products sold in the EU. After compliance evaluation and testing, manufacturers can affix the CE mark to indicate the product meets the necessary standards.
Key EU Certification Testing Standards
1. EN 60884 Standard
- This is the primary standard for power strips used indoors or outdoors. It applies to household and similar appliances designed for alternating current, with a rated voltage above 50V but not exceeding 440V and a rated current of up to 32A. This standard covers plugs with or without grounding contacts and fixed or portable sockets.
2. EN 62368 Standard
- For power strips with features like USB ports or smart controls, the EN 62368 standard must be met.
Directive Requirements
1. LVD (Low Voltage Directive)
- Power strips must comply with the LVD directive, focusing on electrical safety to prevent harm to users under normal and fault conditions.
2. EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive)
- Power strips must ensure that electromagnetic radiation during operation does not exceed specified limits and must demonstrate sufficient resistance to interference to ensure the normal operation of other electronic devices.
3. Safety Requirements
1. Electrical Safety
- Insulation resistance and grounding resistance must meet the standards.
- The voltage endurance capacity must be sufficient to prevent electric shock risks.
- The power strip’s temperature rise should stay within the allowed range to avoid overheating or fire risks. Live parts inside the strip must be well-protected to prevent accidental user contact.
2. Mechanical Safety
- The appearance should be free of sharp edges, points, or defects that could cause injury.
- The outer casing must be strong and stable enough to withstand the forces of plug insertion and external impact, preventing cracking or damage.
4. Environmental Requirements
1. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive)
- The RoHS directive limits the use of hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and certain brominated flame retardants to reduce potential health and environmental risks.
2. WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive)
- This directive mandates proper recycling, disposal, and reuse of discarded electronic equipment. Manufacturers must take responsibility for recycling or participate in relevant programs.
5. Important Notes
1. Member State Variations: Although the EU has unified standards, there may be slight differences or specific requirements between member states. Businesses should familiarize themselves with the regulations of the target market before exporting.
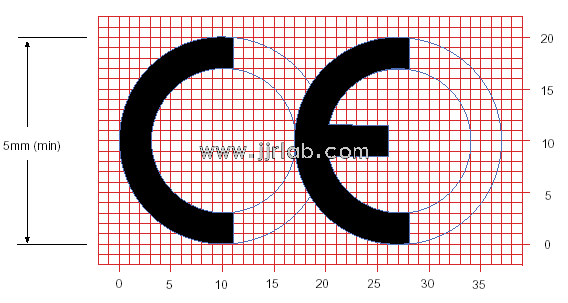
2. CE Marking: Products with CE certification must prominently display the CE mark, which should be clear, durable, and easily identifiable.
3. Packaging Information: The packaging of power strips should include the following information in the official EU languages:
- Manufacturer’s name and address
- Trademark
- Model
- Technical parameters
- Safety warnings and other relevant details
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
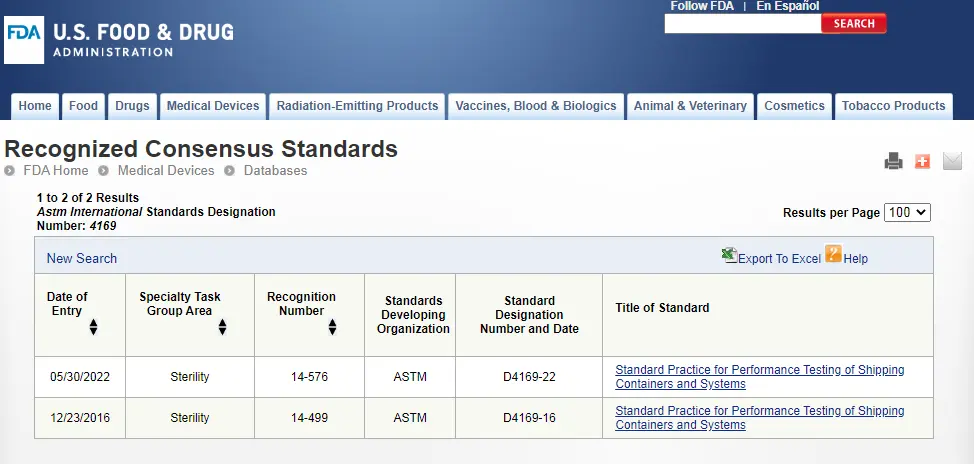
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




