
What Certification Tests Are Required for Textile Exports to Australia?
Australia has strict regulations and technical standards for imported textiles. This article provides a detailed overview of the legal and regulatory framework, testing requirements, and key considerations for exporting textiles to Australia.
Regulatory Standards
1.1 Regulatory Authorities
In Australia, various agencies are responsible for the enforcement of textile-related regulations, setting safety standards, and overseeing imports.
- The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) plays a key role in enforcing textile-related regulations.
- The Standards Australia (SA) is responsible for developing and publishing safety standards for textiles.
- The Australian Border Force (ABF) is in charge of the import release process for textiles.
1.2 Laws and Regulations
Australia has enacted multiple regulations to strictly govern textiles from different perspectives.
- Product safety is governed by the Australian Consumer Law (ACL).
- The Business (Trade Description) Regulations 2016 specifically address textile labeling requirements.
- The Consumer Goods (Care Labelling) Information Standard 2023 stipulates mandatory care labeling requirements.
- The Consumer Goods (Children's Sleepwear and Nightwear) Safety Standard 2017 outlines specific regulations regarding flammability testing, grading, and labeling for children's sleepwear and nightwear.
- The Children's Product Cord Requirements Voluntary Guidelines based on EN 14682 and ASTM F1816 offer voluntary regulations on drawstrings, decorative cords, and functional cords in children's clothing.
- The Consumer Goods Specific Chemical Concentration Safety Guidelines set limits for substances like formaldehyde, azo dyes, and dimethyl fumarate in textiles.
Textile Testing Requirements
2.1 Fiber Composition and Labeling
Textiles must clearly state their fiber content, with the label complying with relevant Australian regulations and standards. The fiber content should typically be listed in percentages, arranged from highest to lowest. Additionally, all labeling information must be in English to ensure consumers in Australia can understand the product’s composition and related details.
2.2 Physical Performance Testing
- Tensile Strength Testing
This test evaluates the strength and durability of textiles when subjected to tensile forces.
- Tear Strength Testing
This test measures the ability of a fabric to resist tearing.
- Abrasion Resistance Testing
This simulates wear and friction to assess how well textiles hold up under normal use, such as clothing parts in contact with the skin or upholstery fabrics, ensuring that they do not wear out, pill, or get damaged easily.
- Shrinkage Testing
This measures changes in the dimensions of textiles after washing or wetting. Different fiber compositions and fabric structures can lead to varying shrinkage rates, so it is important to ensure that the product maintains its size and shape after washing and use.
2.3 Chemical Performance Testing
- Formaldehyde Content and pH Testing
Formaldehyde is a harmful substance that may pose health risks. Australia has strict limits on formaldehyde content in textiles. The pH value of textiles should also be close to that of human skin to avoid skin irritation.
- Azo Dye Testing
Australia has clear regulations on the use of azo dyes, heavy metals (such as nickel release), and dimethyl fumarate in textiles, with corresponding testing requirements and standards.
2.4 Color Fastness Testing
Australia has specific standards for color fastness, covering water, sweat, and abrasion resistance. Different categories of textiles have varying acceptable levels of color fastness. For example, in terms of water fastness, textiles must not excessively fade or transfer color under specific washing conditions.
2.5 Flammability Testing
According to Australian Standard AS 2755.3 "Determination of Surface Burning Time of Textile Fabrics," textiles with a pile surface must undergo surface flammability testing. Samples are ignited with a small heat source near the top, and the spread of the flame along the fabric is timed to assess burning speed and safety.
Key Considerations
3.1 Regulatory Changes
Australian regulations may change in response to market demands or technological developments. Exporters should stay updated on changes to relevant regulations and standards.
3.2 Product Recalls
The ACCC is responsible for regulating product recalls in Australia. If a supplier initiates a product recall, they must notify the ACCC within 48 hours to avoid penalties.
3.3 Focus on Specific Standards
Exporters of textiles to Australia should pay particular attention to AS/NZS 1957:1998 and AS/NZS 1249:2014, particularly with regard to labeling, flammability performance, and requirements related to dimethyl fumarate.
This detailed guide will help textile exporters navigate the necessary testing and compliance requirements for the Australian market.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
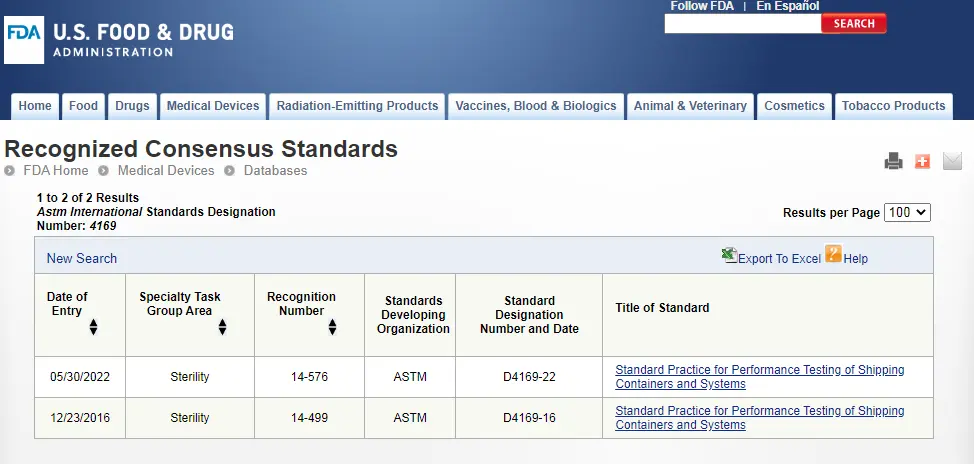
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




