
What Are the EMC Test Standards for Robots?
With the investment in smart manufacturing and the development of smart products, robots have become increasingly important in recent years. The emergence and application of robots have created significant opportunities and attention. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of robots is one of the crucial product compliance issues. The IEC and ISO standard committees are currently working on the EMC requirements for robots. The IEC subcommittee CISPR released a guideline on this matter in 2021. Our following post is based on this guideline.
The CISPR guideline document is an updated version of CISPR/1412/INF, initially written by CISPR/S AHG 3. It aims to provide some basic information about robots, guidance on the types of robots covered by the CISPR subcommittees, and recommendations for EMC testing of robots.
Definitions
- Robot: A programmable actuator with two or more axes, possessing a degree of autonomy, capable of moving within its environment to perform intended tasks.
- Industrial Robot: An automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator, programmable in three or more axes, which can be fixed or mobile for industrial automation applications.
- Service Robot: A robot that performs useful tasks for humans or equipment, excluding industrial automation applications.
- Personal Service Robot: A service robot used for non-commercial tasks, typically by non-professionals.
- Professional Service Robot: A service robot used for commercial tasks, typically operated by properly trained personnel.
Classification of Robots
Robots are mainly divided into two categories:
1. Industrial Robots
2. Service Robots
- 2.1 Personal Service Robots
- 2.2 Professional Service Robots
- 2.2.1 Public Service Robots
- 2.2.2 Special Robots
General EMC Aspects
1. Emission:
- The radiation and conducted emissions of the robot and/or robot device can be maximized when there are dynamic operating parts such as arms, moving based on the specified operating modes associated with each function.
2. Immunity:
- Before testing according to the test plan, manufacturers should define and document all aspects of the test robot. The test plan should include the immunity testing requirements for the robot and/or robot device, including the selection of applicable tests, interference levels applied during the tests, configuration, performance standards, and other necessary details.
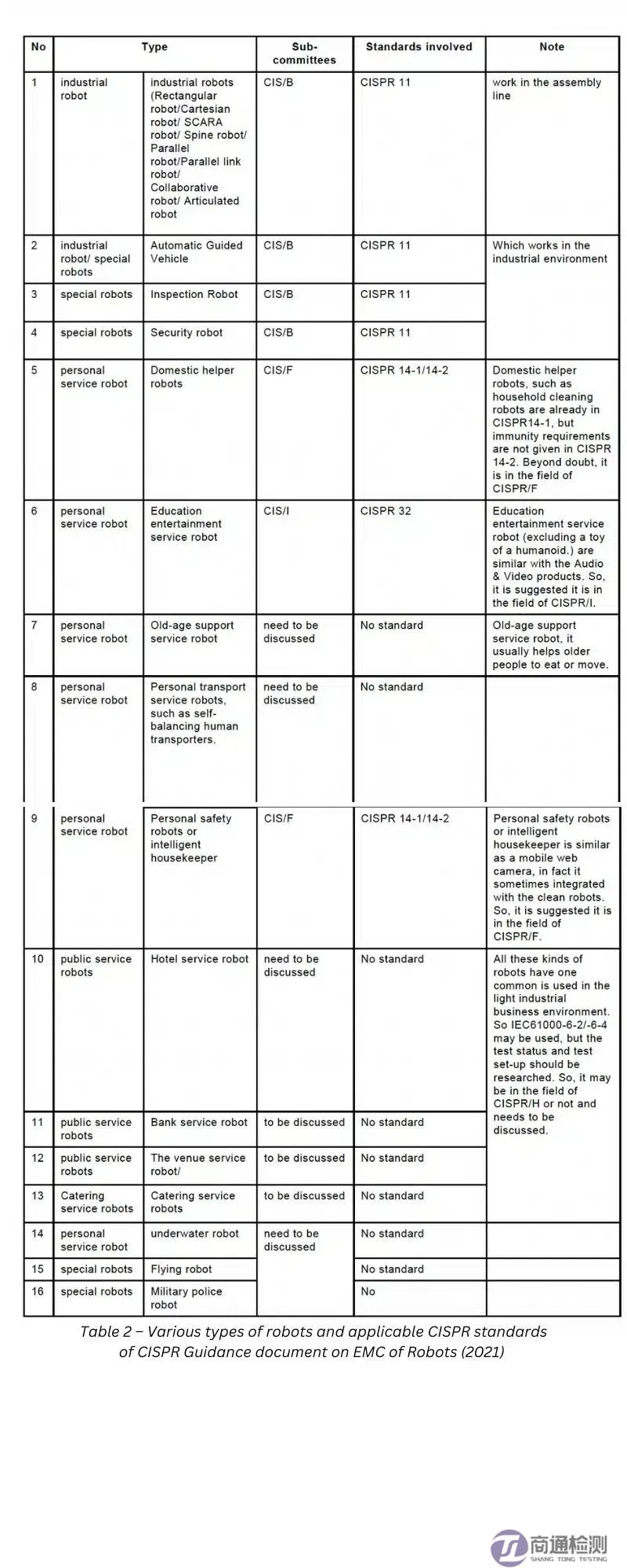
CISPR Standards Applicable to Different Types of Robots
As mentioned in the table above, the CISPR guidelines reference CISPR 11, CISPR 14-1, CISPR 14-2, IEC 61000-6-2, and IEC 61000-6-4. The CISPR committee is still working on defining standards for each robot category due to the standardization of technology.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Toy Toxicology Testing CA
Toy Toxicology Testing CA
 CPSIA Compliance for Children's Products
CPSIA Compliance for Children's Products
 Food Contact Items Testing
Food Contact Items Testing
 Energy Star Testing Laboratory
Energy Star Testing Laboratory
 Do I Need to Test Every Color for CPSIA Compliance
Do I Need to Test Every Color for CPSIA Compliance
 Accredited Medical Device Testing Lab
Accredited Medical Device Testing Lab
 Safety Testing for Baby Wrap
Safety Testing for Baby Wrap
 United States Electrical Plug Certification
United States Electrical Plug Certification
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




