
The Difference Between US DOE and EU ERP Energy Label
In the globalized market, energy efficiency labels have become crucial for consumers choosing energy-saving products. As two major econoMIC entities, the United States and the European Union each have unique energy efficiency label systems: the US Department of Energy (DOE) EnergyGuide label and the EU Ecodesign Ready Product (ERP) label. This article delves into these two systems to help manufacturers and consumers better understand the requirements and impacts of these energy efficiency labels.
US DOE EnergyGuide Label
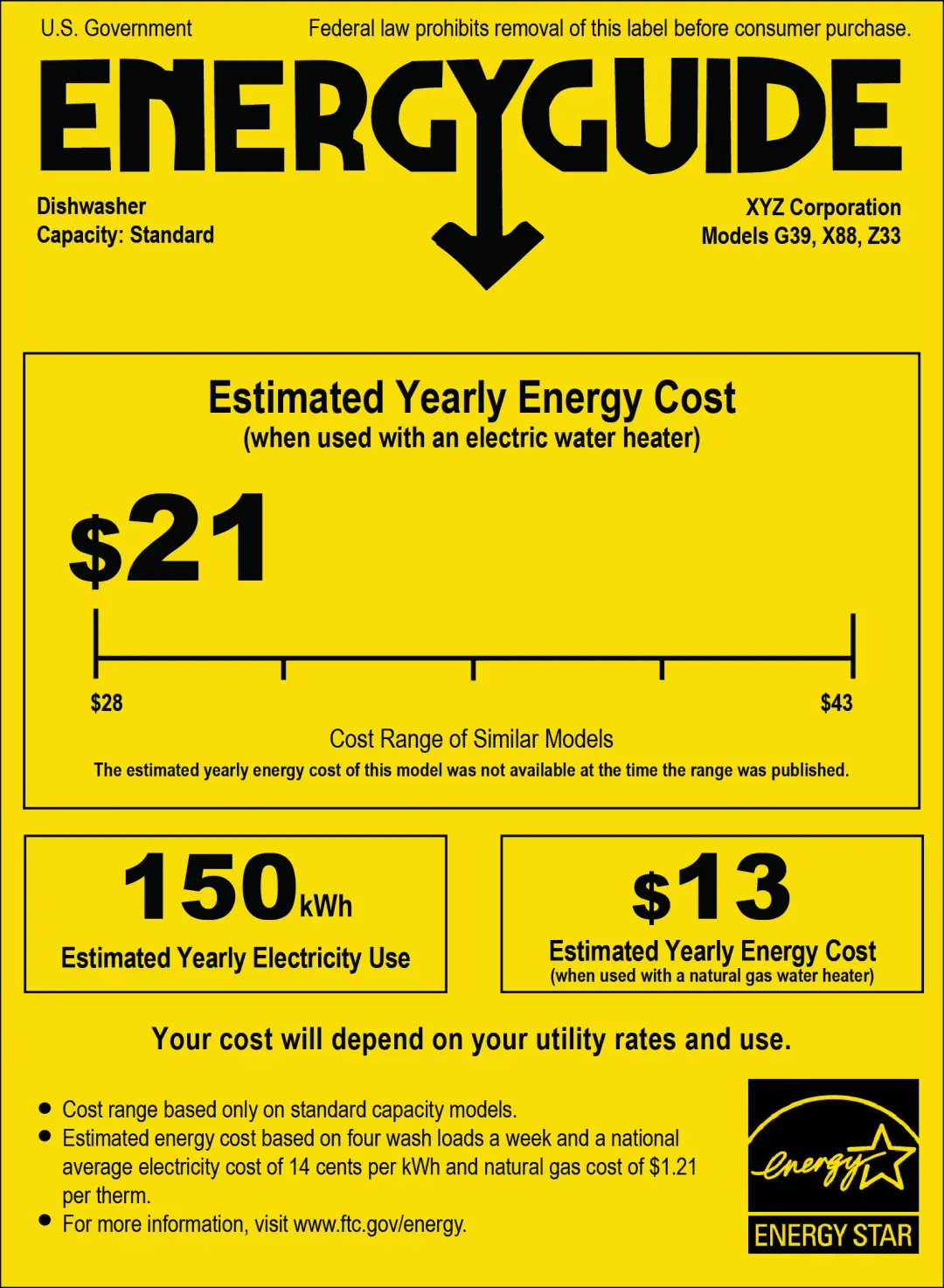
The US Department of Energy (DOE) requires manufacturers to disclose annual energy costs or efficiency information based on DOE test procedures on their products. This information must be reported to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and displayed to consumers at the point of sale. The EnergyGuide label, prominently yellow in color, shows consumers the estimated annual energy consumption of a device, enabling comparisons of energy usage between similar models.
Scope of US DOE Energy Efficient Products
Products that require EnergyGuide labels include washing machines, refrigerators, freezers, televisions, water heaters, dishwashers, room air conditioners, central air conditioners, furnaces, boilers, heat pumps, and pool heaters.
US Energy Efficiency Sales Requirements
Any platform selling products with EnergyGuide labels, such as websites or printed catalogs, must clearly and prominently display all information from the EnergyGuide label or show the label itself.
ENERGY STAR Certification
Products meeting the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidelines for energy efficiency can also apply for ENERGY STAR certification, indicating recognition by both the DOE and EPA.

EU ERP Energy Label
The EU's ERP label is implemented under the ErP (Energy-related Products) Directive framework. It sets out energy efficiency requirements, functional requirements, and product information requirements.

Scope and Requirements of EU ERP Energy Efficient Products
The ERP label covers products such as directional lamps, LED lamps, and related equipment. Since September 1, 2013, these products must meet the minimum energy efficiency requirements specified in RegULation (EU) No 1194/2012.
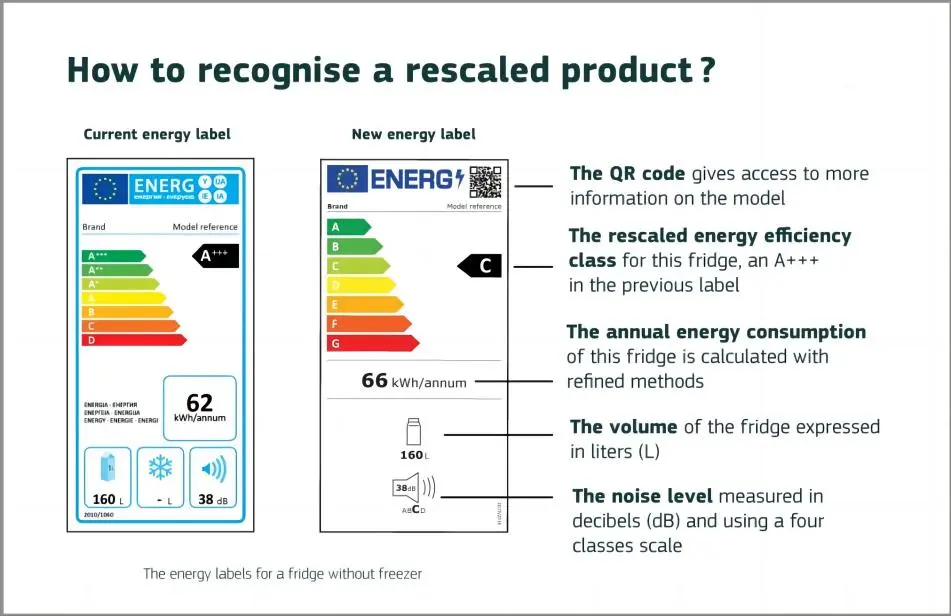
EU Energy Efficiency Grades
The new labels use grades from A to G, replacing the previous A++ to E energy efficiency ratings. Energy consumption information is displayed in kWh per 1000 hours and can be linked via QR code to more information in an online database.
Product Information Sheets and Technical Documentation
Products must provide corresponding product information sheets and technical documentation, including supplier information, model descriptions, reference standards, authorized signatories, and technical parameters.
EU Market Surveillance
The EU has detailed market surveillance procedures requiring companies to carefully study regulatory content, improve production techniques, and conduct certification tests in advance to avoid delays in product exports.
Both the US DOE EnergyGuide label and the EU ERP label aim to enhance energy efficiency and environmental protection. Manufacturers exporting products to these markets must comply with respective energy efficiency label regulations to ensure market access and competitiveness. Consumers can make more environmentally friendly and cost-effective purchasing decisions through these energy efficiency labels.
China JJR Laboratory is an IEC 17025 accREDited laboratory, providing US DOE and EU ERP energy efficiency certification services for products entering the US and EU markets. Our laboratory, located in China, helps businesses save 30% on certification costs.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 What are the export compliance for electric fans
What are the export compliance for electric fans
 Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
 What Certifications for Electric Fans in the EU &a
What Certifications for Electric Fans in the EU &a
 How to Choose a Test Laboratory for Amazon UL 507?
How to Choose a Test Laboratory for Amazon UL 507?
 Humidifier UL 60335 Test Report for Amazon US
Humidifier UL 60335 Test Report for Amazon US
 Neck-Hanging Fan EU CE Compliance
Neck-Hanging Fan EU CE Compliance
 What is SAR Testing for Absorption Ratio
What is SAR Testing for Absorption Ratio
 Children's Model Toys Amazon CPC Testing Service
Children's Model Toys Amazon CPC Testing Service
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




