
Socket CE Certification EN/IEC60884-1 Testing
Socket CE Certification is mandatory and must comply with the regulatory requirements of the European market. The socket must meet the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive (CE LVD) and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (CE EMC) of the European Union, which form the basis of CE certification. The CE mark indicates that the product can be freely circulated within the European Economic Area (EEA) and demonstrates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection regulations.
Types of Sockets:
- Smart sockets
- Wiring sockets
- Wall sockets
- Adapter sockets
- Industrial sockets
- Cabinet sockets
- Floor sockets
- USB sockets, etc.
Standards for Socket CE Certification:
- Regular sockets: EN 60884-1
- With USB: EN 62368 + EN55032 and EN55035 (EMC)
Socket CE Certification Process:
1. Identify Applicable Directives:
Sockets usually need to comply with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC) of the European Union. Ensure you understand the applicable directives and relevant requirements.
2. Conduct Product Testing:
Perform necessary product testing according to the applicable directives. These tests may include electrical safety tests, mechanical safety tests, and electromagnetic compatibility tests. Tests can be conducted by accredited laboratories or third-party agencies. JJR in China is an IEC 17025 laboratory providing relevant services.
3. Prepare Technical Documentation:
Compile technical documentation as required by the directives, including product specifications, design documents, test reports, manuals, etc. Ensure the documentation contains the necessary information to demonstrate compliance with applicable directives.
4. Declare Conformity:
Prepare a CE Declaration of Conformity, confirming the product complies with applicable directives. The declaration must provide necessary information, such as product description, applicable directive standards, and manufacturer information.
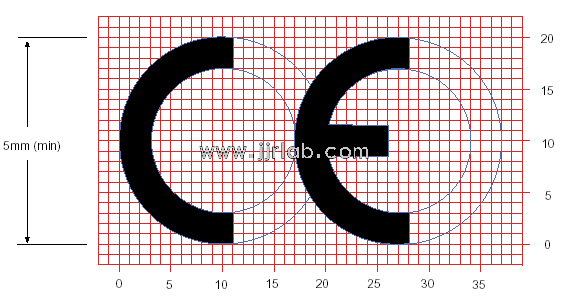
5. Affix CE Marking:
Place the CE mark on the product, indicating compliance with European regulations. The CE mark must comply with the requirements of the directives, including size, proportion, and visibility.
Socket CE Certification Safety Standard IEC60884 Testing Items:
1. Markings
2. Dimensions check
3. Protection against electric shock
4. Earthing measures
5. Terminals and terminal ends
6. Structure of fixed sockets
7. Structure of plugs and portable sockets
8. Interlocked sockets
9. Resistance to aging, protection provided by enclosures, and moisture resistance
10. Insulation resistance and electric strength
11. Operation of earthing contacts
12. Temperature rise
13. Breaking capacity
14. Normal operation
15. Withdrawal force of the plug
16. Flexible cables and their connection
17. Mechanical strength
18. Resistance to heat
19. Screws, current-carrying parts, and connections
20. Creepage distances, clearances, and distances through sealing compound
21. Resistance of insulating material to abnormal heat, fire, and tracking
22. Additional tests on pins with insulating sleeves
Additional Testing and Certification for Socket Export to the EU Market:
1. RoHS Certification (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive):
The RoHS directive restricts the use of specific hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium. Sockets must ensure that their materials and manufacturing processes comply with RoHS directive requirements.
2. WEEE Certification (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive):
The WEEE directive requires producers to take responsibility for the collection and recycling of waste electronic products sold in the EU market to reduce environmental impact. Socket manufacturers typically need to register and participate in a compliance recycling system.
3. Other Specific Requirements:
Depending on the specific function and design of the socket, compliance with additional technical or safety standards may be required, such as the Medical Device Directive (if applicable) and waterproof rating tests.
China's JJR laboratory also provides services for socket and plug products' export certifications, including FCC and UL for the USA, PSE for Japan, UKCA for the UK, and KC for Korea. For quotes, please feel free to contact us.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 FCC Certification Fees for Handheld Fans
FCC Certification Fees for Handheld Fans
 FCC Certification Testing for Smart Lighting Produ
FCC Certification Testing for Smart Lighting Produ
 What is the ETSI EN 303 645 Testing Standard?
What is the ETSI EN 303 645 Testing Standard?
 UL Compliance and ETL Certification for LED Lighti
UL Compliance and ETL Certification for LED Lighti
 What is the IEC 60598 Standard?
What is the IEC 60598 Standard?
 What is the Canada IC Logo?
What is the Canada IC Logo?
 EMC Pre Compliance Testing
EMC Pre Compliance Testing
 PAHs Testing (Food and Textile)
PAHs Testing (Food and Textile)
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




