
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC Standards
Lithium batteries, as the core power source for many electronic products, play a vital role in the growing export industry. For lithium battery exporters, obtaining authoritative certifications is crucial to accessing international markets. Among these certifications, the cb certification has become one of the most essential due to its wide recognition across multiple countries. This article will explore the relationship between CB Certification and IEC standards and offer guidance for export businesses.
CB Certification: The "Universal Key" for Lithium Battery Exports
In international trade, different countries have varying certification requirements, which can be challenging for businesses. When exporting lithium batteries to multiple countries, companies face the daunting task of meeting diverse certification standards, which can be time-consuming, costly, and labor-intensive. The advent of CB Certification simplifies this process. A lithium battery with CB Certification can be used in several countries, streamlining the export procedure, reducing certification costs, and enhancing competitiveness in the global market.
IEC Standards: The Foundation of CB Certification
To understand the relationship between CB Certification and IEC standards, it is essential to first understand IEC. The IECEE (International Electrotechnical Commission Conformity Assessment) is the certification body under the International Electrotechnical Commission, which publishes standards for various electrical products, such as IEC 62133, IEC 60086-4, and IEC 62368-1. These standards form the basis of the CB Certification system. Without IEC standards, CB Certification would not be possible.
For example, the IEC 62133 standard plays a crucial role in the certification of lithium batteries. The current IEC 62133-2 standard specifically addresses lithium batteries and sets requirements for safety and electrical performance.
Safety Requirements
IEC 62133-2 mandates that lithium batteries must have overcharge and over-discharge protection mechanisms to ensure safety. These features prevent fires or explosions caused by overcharging and extend the battery's lifespan by avoiding excessive discharge.
Electrical Performance Requirements
The standard also outlines specific requirements for parameters such as battery capacity, charge/discharge cycles, and internal resistance. For instance, the actual capacity of a lithium battery must meet the specified ratio, and capacity loss after charge/discharge cycles must not exceed the standard limits to ensure stable performance over time.
The Relationship Between CB Certification and IEC Standards
As long as a lithium battery meets IEC standards, it can receive CB Certification. However, not every organization is authorized to issue certifications for all IEC standards. Only qualified certification bodies can provide these certifications. For example, some organizations specialize in safety testing and can certify IEC 62133-2, but may not be authorized to certify other standards. Therefore, when selecting a CB Certification body, it’s essential to confirm whether they are a CBTL (cb testing Laboratory). Only CBTLs can issue internationally recognized CB Certifications, ensuring a smooth certification process.
Choosing a CBTL for CB Certification
Selecting a CBTL for CB Certification is akin to finding a trusted "navigator" for the certification journey. CBTLs have the necessary professional equipment to precisely test whether a lithium battery complies with IEC standards. For instance, during overcharge testing, specialized equipment simulates various overcharge scenarios to ensure the battery's overcharge protection is functioning correctly.
Additionally, CBTL technicians are experienced in analyzing test data, identifying issues, and providing corrective recommendations, which help companies pass the certification process smoothly.
CB Certification and IEC standards are closely related: IEC standards form the foundation for CB Certification, and CB Certification represents its application in international trade. For lithium battery exporters, understanding this relationship and choosing the right CBTL for certification are critical steps for successful market entry.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
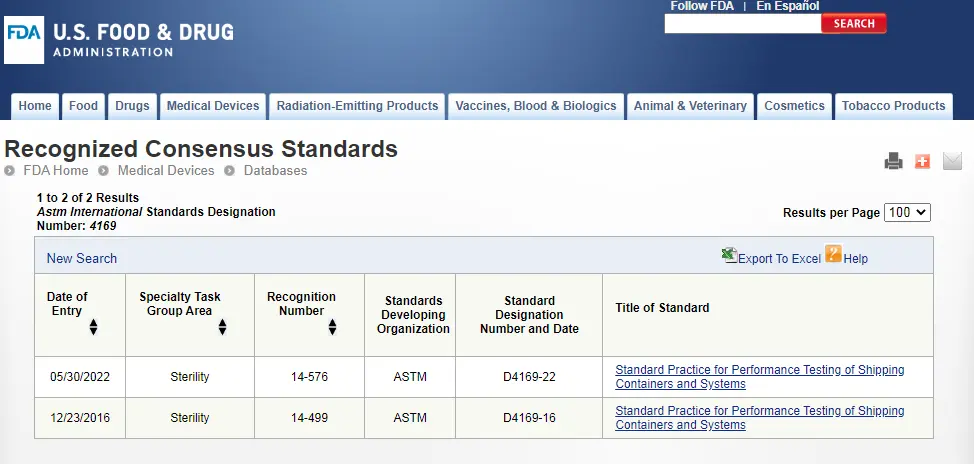 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
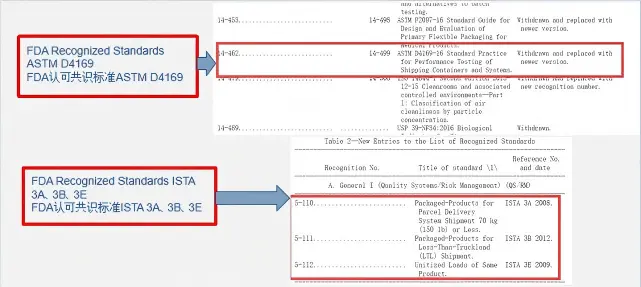 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




