
ISO 10993 Thrombogenicity Test Laboratory
MICrosoft YaHei", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "sans-serif", 宋体; font-optical-sizing: inherit; font-kerning: inherit; font-feature-settings: inherit; font-variation-settings: inherit; margin-top: 0px; margin-bottom: 0px; padding: 0px; color: rgb(51, 51, 51); box-sizing: border-box; text-wrap: wrap; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">1 Thrombogenicity Test Introduction
Thrombosis generally occurs in vivo or semi-vivo. When medical devices/materials come into contact with human blood, the surface of the materials may cause plasma proteins such as albumin to adhere. The adheRED protein layer will activate the coagULation pathway and cause platelet adhesion, forming fibrin and platelet thrombi respectively, which will promote each other and finally form mural thrombi. Therefore, the medical devices/materials are implanted into the cardiovascular system of dogs through appropriate procedures. After a certain period of time, the thrombosis formation on the surface of the materials and in the blood vessels is observed. This can comprehensively reflect the adhesion of the medical devices/materials to proteins in the blood, the activation of the coagulation pathway and the induction of platelet adhesion, thereby judging the thrombosis risk of the medical devices/materials, scoring the degree of thrombosis on the surface of the materials and in the blood vessels, and comparing the differences between the scores of the test samples and the control samples.

2. Thrombogenicity Test standards
2.1 ISO 10993-4 Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood;
2.2 GB/T16886.4 Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 4: Selection of tests for interaction with blood.
3. Thrombogenicity Test system
2 beagles.
4. Thrombogenicity Test samples
In order to ensure sufficient contact between the test sample and the blood, the test sample and control with a length of 15 cm should be selected for intravascular implantation. Depending on the shape and structure of the device, it may be necessary to create a customized device to reduce the length of the component while maintaining the same material ratio as the complete device. If necessary, the device can be subdivided into multiple test samples for testing.
5. Test steps
Figure 1 shows the most commonly used implantation sites for dog intravascular thrombosis testing. It is generally believed that venous implantation is a relatively poor situation and is more likely to form thrombosis. If the product is used in an artery, it can be implanted in the artery for testing. Figure 2 shows the second most commonly used implantation sites for dog intravascular thrombosis. If the shape and size of the sample cannot be implanted in the femoral vein and jugular vein to complete the test, the site in Figure 2 can be selected for testing. For example, vena cava filters can be tested by selecting 1 and 2 in Figure 2.
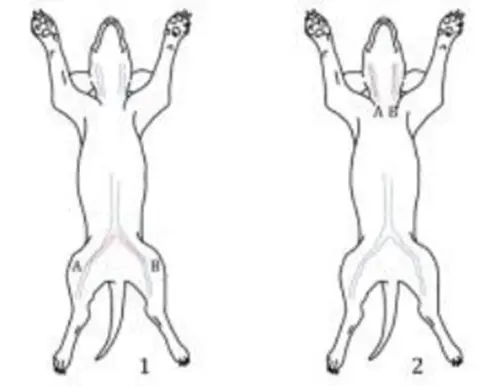
Figure 1. Main implantation sites for canine intravascular thrombosis test (1: femoral vein; 2: jugular vein)
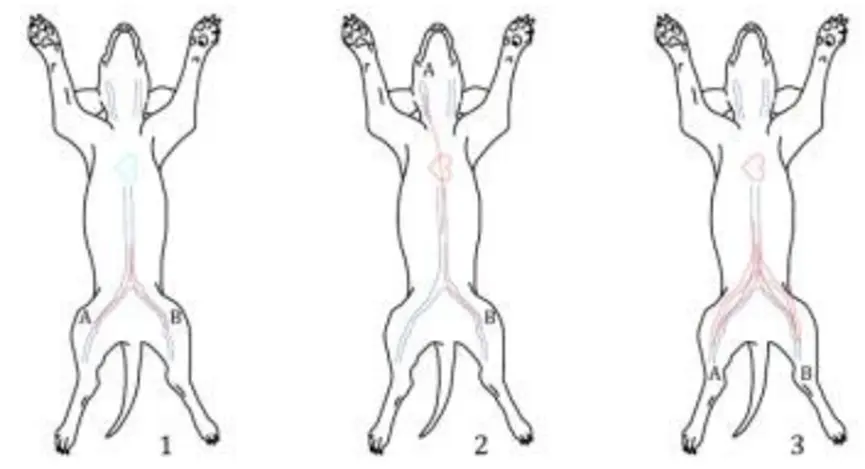
Figure 2. The most commonly used implantation sites in canine intravascular thrombosis testing
(1: inferior vena cava-inferior vena cava; 2: superior vena cava-inferior vena cava; 3: inferior vena cava-abdominal aorta)
The recommended implantation time is greater than 4 hours. If the device is used for no more than 4 hours, the implantation time can be shortened according to the actual use time of the device, or a longer implantation time can be selected according to the use time of the product.
6. Result evaluation
The scoring results of intravascular thrombosis are not statistically analyzed. The difference between the test sample and the control sample is evaluated based on the score, and the score of the test sample should be ≤ the control sample. At the same time, the acceptable scoring results are comprehensively considered based on the clinical use characteristics of the product, and the results of preclinical animal studies and clinical trials can also be comprehensively evaluated. The scoring table is shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1. Thrombosis scoring scheme A
Thrombosis score description | score |
No obvious thrombosis (A very small clot at the insertion site is acceptable) | 0 |
Minimal thrombosis, one | 1 |
Minimal thrombosis, one | 2 |
Significant thrombosis, >1/4 but ≤1/2 of the implant surface, Vascular patency | 3 |
Obvious thrombosis, >1/2 implant surface, vascular patency | 4 |
Complete occlusion of blood vessels | 5 |
Table 2. Thrombosis scoring scheme B
Thrombosis score description | score |
Thrombus is absent or minimal. If present, appears to be related to the implant phlebotomy site | 0 |
The thrombus was extremely small, covering 1% to 25% of the material surface. | 1 |
Moderate thrombus, observed to cover 26% to 50% of the material surface | 2 |
Severe thrombosis was observed, covering 51% to 75% of the material surface | 3 |
The thrombus was extensive, covering 76% to 100% of the material surface. | 4 |
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 SOR/2018-186 Playpen Compliance
SOR/2018-186 Playpen Compliance
 Amazon Mattress 16 CFR 1633 Compliance
Amazon Mattress 16 CFR 1633 Compliance
 What is Amazon TIC Direct Validation?
What is Amazon TIC Direct Validation?
 Amazon Baby Sleeping Bag CPC Certificate Complianc
Amazon Baby Sleeping Bag CPC Certificate Complianc
 Infant Swings 16 CFR 1223 & ASTM F2088 Testing
Infant Swings 16 CFR 1223 & ASTM F2088 Testing
 Amazon TIC Direct Validation Operation Guide
Amazon TIC Direct Validation Operation Guide
 Portable Power Outlet Australian SAA Certification
Portable Power Outlet Australian SAA Certification
 CE Certification for Exporting Game Consoles to th
CE Certification for Exporting Game Consoles to th
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




