
How to Get RoHS Certification?
Understanding ROHS certification
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is a mandatory standard legislated by the European Union. Its full name is the Directive on the Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. This standard was officially implemented on July 1, 2006, primarily to regulate the materials and processes of electrical and electronic products, making them more beneficial to human health and environmental protection.
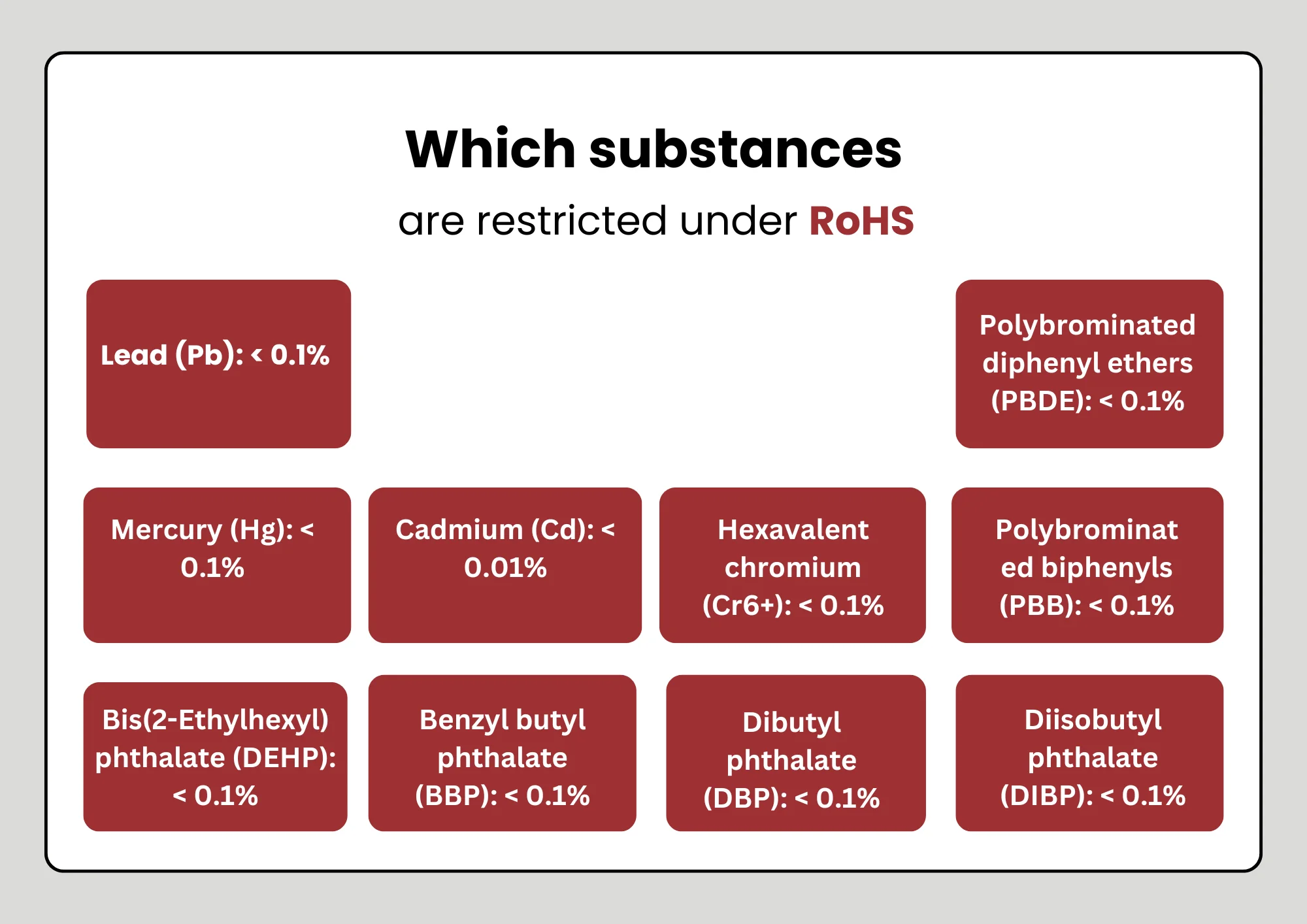
The main goal of RoHS is to eliminate six hazardous substances from electrical and electronic products:
- Lead (Pb)
- Mercury (Hg)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI)
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBBs)
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs)
Additionally, the lead content must not exceed 0.1%.
RoHS Directive
On February 13, 2003, the European Parliament and the European Commission officially published the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive in the Official Journal of the European Union.
The RoHS and WEEE directives apply to 10 categories and 102 types of products, including:
1. Large household appliances
2. Small household appliances
3. Information and communication technology (ICT) equipment
4. Consumer electronics
5. Lighting equipment
6. Electrical and electronic tools
7. Toys, leisure, and sports equipment
8. Medical devices (excluding implanted or infected products)
9. Monitoring and control instruments
10. Automatic vending machines
On December 3, 2008, the EU proposed amendments to the WEEE Directive (2002/96/EC) and RoHS Directive (2002/95/EC). The key updates include:
- Clarification of scope and definitions
- Introduction of the CE marking and EC declaration of conformity
- Gradual inclusion of medical devices and monitoring instruments
- No change to the restricted six substances, but four additional substances (HBCDD, DEHP, BBP, DBP) were prioritized for evaluation
Scope of RoHS
RoHS applies only to new products placed on the market after July 1, 2006, including household incandescent lamps and light sources.
Exemptions:
- Medical devices and monitoring instruments (Categories 8 and 9 of the WEEE Directive)
- Repair parts for products placed on the market before July 1, 2006
- Reused products originally placed on the market before July 1, 2006
Restricted Hazardous Substances
1. Heavy Metals:
- Lead (Pb)
- Mercury (Hg)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI)
2. Brominated Flame Retardants:
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBBs)
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs)
3. Maximum Concentration Limits:
- Cadmium (Cd): 0.01% (100 ppm)
- Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg), Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI), PBBs, PBDEs: 0.1% (1000 ppm)
4. Common Usage Examples:
- Lead (Pb): Solder, glass, PVC stabilizers
- Mercury (Hg): Thermostats, sensors, switches, relays, light bulbs
- Cadmium (Cd): Switches, springs, connectors, enclosures, PCB, batteries
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI): Anti-corrosion coatings on metals
- PBBs and PBDEs: Flame retardants used in PCBs, connectors, and plastic casings
RoHS Certification Testing Principles
According to the EU WEEE & RoHS directives, qualified third-party testing laboratories conduct hazardous substance testing based on material type. The general testing approach includes:
1. Metal materials: Tested for four heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Hg, Cr VI).
2. Plastic materials: Tested for four heavy metals + brominated flame retardants (PBBs/PBDEs).
3. Packaging materials: Subject to additional heavy metal testing requirements (94/62/EEC).
4. Hazardous substance concentration limits:
- Cadmium: <100 ppm
- Lead: <1000 ppm
- Steel alloys: <3500 ppm
- Aluminum alloys: <4000 ppm
- Copper alloys: <40,000 ppm
- Mercury & Hexavalent Chromium: <1000 ppm
RoHS Certification Process
1. Step 1: The customer provides product images, a Bill of Materials (BOM), and an application form.
2. Step 2: The laboratory evaluates the materials and provides a quotation.
3. Step 3: The customer confirms the quotation, signs the application form and service contract, and pays the testing fee.
4. Step 4: The customer sends the product samples to the certification laboratory for testing.
5. Step 5: If the product passes the test, the RoHS certificate and test report are issued for customer review.
6. Step 6: Once the customer confirms that the certificate and report are correct, the final certificate and report are issued.
Importance of RoHS Certification
RoHS certification is essential for entering the European Union market, as it is a prerequisite for selling electrical and electronic products within the EU. For businesses, obtaining RoHS certification:
- Enhances product credibility
- Improves market competitiveness
- Increases customer trust, particularly in the EU
- Helps boost sales and market share
To ensure long-term success in the EU market, companies should complete RoHS certification as early as possible.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Wireless Microphone Export Certification
Wireless Microphone Export Certification
 Audio-Visual Products SNI Certification in Indones
Audio-Visual Products SNI Certification in Indones
 FCC-ID: Still Needed if Module is Certified?
FCC-ID: Still Needed if Module is Certified?
 FCC Certification Fees for Handheld Fans
FCC Certification Fees for Handheld Fans
 FCC Certification Testing for Smart Lighting Produ
FCC Certification Testing for Smart Lighting Produ
 What is the ETSI EN 303 645 Testing Standard?
What is the ETSI EN 303 645 Testing Standard?
 UL Compliance and ETL Certification for LED Lighti
UL Compliance and ETL Certification for LED Lighti
 What is the IEC 60598 Standard?
What is the IEC 60598 Standard?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




