
How to Get RCM Certificate?
What is rcm certification?
RCM Certification is an identification introduced in Australia and New Zealand, replacing the previous SAA, C-Tick, and A-Tick identifications to achieve a unified identification for electrical products. This symbol is a trademark owned by regulatory authorities in Australia and New Zealand, indicating that the product complies with both safety and EMC requirements.

RCM Certification regulates electrical products mainly into two categories: non-regulated and regulated products. Not all products marked with the RCM logo need to be registered. Non-regulated products do not require registration, and currently only Level 3 electrical products are required to be registered. There are a total of 61 major categories, including power adapters, vacuum cleaners, and other high-risk items.
After the requirement was announced on March 1, 2013, there was a three-year transition period, and it became mandatory on March 1, 2016. Therefore, manufacturers must strictly adhere to the requirements and conduct relevant tests according to this standard.

Scope of RCM Certification Services:
In Australia, electrical products are classified into three levels of risk: Level 1 (low risk), Level 2 (medium risk), and Level 3 (high risk), with a total of 61 product categories.
Level 1 Certification Requirements: Refers to DC-powered products (apply for RCM certification directly with EMC report).
Level 2 Certification Requirements: Refers to AC-powered products (apply for RCM certification with EMC report + safety report).
Level 3 Certification Requirements: Refers to the 61 product categories listed (apply for RCM certification with EMC report + safety report + government-issued certificate of compliance or recognized external certification scheme (RECS) such as SAA) + EESS registration.
Any electrical product with a voltage range between AC 50V to 1000V or DC 120V to 1500V must comply with Australian electrical safety laws. Since March 1, 2013, products must be registered in the Australian national database EESS and bear the RCM logo to be sold in the market.
RCM Certification Application Process:
Step 1: Identify and classify the product according to RCM product requirements.
Step 2: Conduct product testing or determine compliance based on existing test reports.
Step 3: Compile and verify necessary technical and management documents, and draft a compliance declaration.
Step 4: Appoint a local authorized representative in Australia and New Zealand.
Step 5: Register the product in the Electrical Equipment Safety System (EESS) database.
Step 6: Apply the rcm mark.
Email: hello@jjrlab.com
rcm compliance Declaration
Relationship between saa certification, C-Tick, A-Tick, and RCM
SAA certification controls safety aspects, C-Tick certification controls EMC and radio products, and A-Tick certification controls telecommunications products. The RCM symbol is an accreditation introduced in 2013. After obtaining safety certification and electromagnetic compatibility registration, products can obtain the RCM symbol through safety certification regulatory authorities. From March 1, 2016, all electronic and electrical products sold must use the RCM symbol uniformly; A-Tick and C-Tick symbols will be replaced. RCM can be understood as a registration system, including SAA and C-TICK."
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
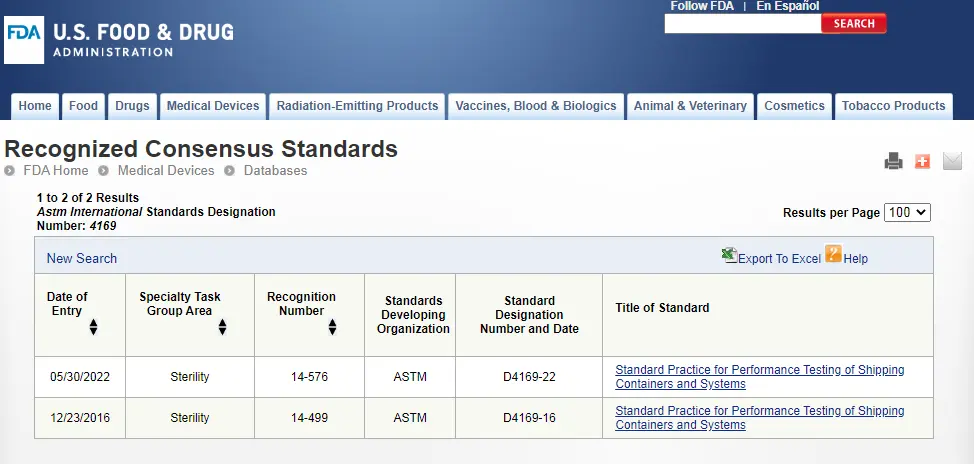 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
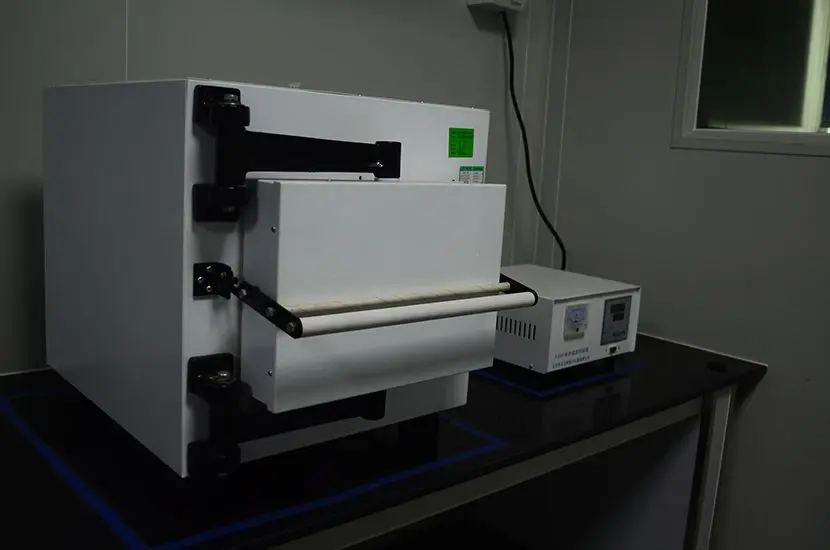 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




