
How Much Does an FCC License Cost?
Overview of FCC License
The FCC (Federal Communications Commission) regulates the use of wireless spectrum in the United States. All devices must receive FCC approval before being deployed on cellular networks, ensuring compliance with relevant FCC requirements.
Key parts for testing include:
- FCC Part 15 (unintentional radiators)
- Part 22 (intentional radiators for 850 MHz)
- Part 24 (intentional radiators for 1900 MHz)
For M2M (Machine-to-Machine) devices, even if the module used within the device has an FCC ID, the device itself may still require its own FCC certification. However, if the device complies with the module's FCC authorization instructions, it can use the module’s fcc id.

Get FCC License Process
1. Authorization Request: Device manufacturers authorize a testing lab to apply for an FCC grantee code.
2. Grantee Code Assignment: The FCC sends the grantee code to the device manufacturer.
3. Device Submission: Manufacturers submit their devices to an accredited testing lab for evaluation.
4. Testing: The testing lab tests the device according to applicable standards.
5. Report Submission: Upon successful testing, the lab creates a detailed test report and submits it to the FCC.
6. FCC Response: The FCC responds to the certification request within 8-12 weeks.
Required Submission Materials
- Application form
- FCC Form 731
- Photos of the test setup
- Test report
- External and internal photos
- FCC ID label
- Description of the device's operation
- User manual
- Block diagram
- Schematics
- Parts list
- Reuse of the FCC ID in the host device
Depending on the type of host device, the module’s FCC ID may be used for the host device. The module supplier can provide guidance on when the module FCC ID can be reused. This guidance might include considerations such as:
1. Whether the host device is for fixed or mobile applications.
2. Whether the host device can be used as a portable device.
3. Whether the module is integrated as recommended by the module manufacturer.
4. Antenna gain recommended by the module manufacturer.
5. Testing requirements under Part 15, even when reusing the module manufacturer’s FCC ID.
How Much Does an FCC License Cost?
The cost of FCC approval for end devices ranges from $600 to $1,500, with the approval cost for modules generally being higher than this range.
How Long Does FCC Certification Take?
FCC certification for connected devices typically takes 3-5 weeks. To expedite the process, the FCC has authorized multiple private organizations to issue certifications. By working with a TCB (Telecommunication Certification Body), FCC certification can be received within 1-2 weeks.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
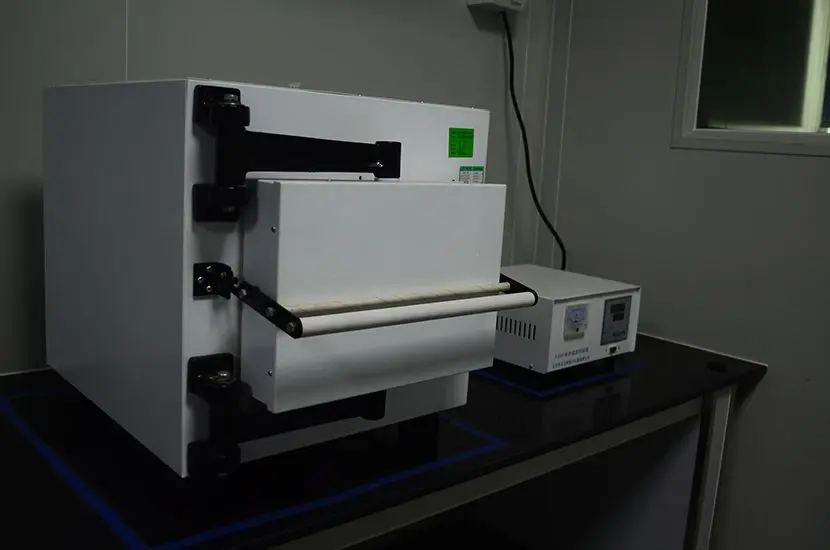 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




