
FCC/ISED certification for household appliances
Household electrical appliances applying for FCC/ISED certification must comply with its certification specifications and process requirements. The certification process involved in FCC/ISED is referred to as SDoC (supplier's Declaration of Conformity) or Certification in English. Certification is also commonly known as fcc id or IC ID.
FCC/ised certification specifications and process list for home appliances
Product Category | FCC Certification | ISED Certification | ||
Certification Process | standard | Certification Process | standard | |
Ordinary household appliances | SDoC or FCC ID | SDoC | ICES-003 | |
Home appliances with wireless functions | Home appliance function: SDoC or FCC ID | Home appliance function: fcc part 15b | Home appliance function: SDoC | Home appliance function: ICES-003 |
Industrial, scientific and medical home appliances | SDOC or FCC ID | SDoC | ICES-001 | |
Note: The certification level of FCC ID is higher than SDoC. Ordinary home appliances can choose SDoC or FCC ID certification. | ||||
SDoC : The supplier self-declares that it complies with the technical specifications of FCC/ISED. Self-declaration is not an arbitrary claim, but the product must be tested to meet the limit requirements. The product label, manual, importer and product technical data must meet the requirements of the SDoC process before self-declaration can be made.
FCC ID : Product testing needs to be carried out in an FCC-approved laboratory, and the test report and technical information must be submitted to the TCB agency for review before an ID certificate is issued.
IC ID : Canada's certification for wireless products requires testing to be conducted in an ISED-accredited laboratory, and the ID certificate is issued after the report and technical information are submitted to the CB (Certification Body) for review.
Exemptions for some home appliances:
Some home appliances can be exempted from certification according to the requirements of FCC Part 15. The product conditions for exemption from certification are as follows:
Products with an internal operating frequency or a generated operating frequency ≤ 9 kHz are not defined as digital products and are exempt from the requirements of FCC Part 15.
According to FCC Part 15.103(h), battery-powered devices operating at frequencies less than 1.705 MHz are exempt from the requirements of FCC Part 15.
According to FCC Part 15.103(d), digital circuits used in certain home appliances can be exempted from the requirements of FCC Part 15. At the same time, this clause is further explained in KDB 772105, which is summarized as follows:
Devices that help people handle household chores or directly regulate the water or air conditions in the home are exempt. However, household appliances that use radio frequency energy are not exempt. For example, induction cookers, microwave ovens, ultrasonic humidifiers, and microwave therapy devices, which are classified as industrial, commercial, and medical devices, are not exempt.
The exemption only applies to the functions of the home appliance, and other functions are not exempted. For example, a food blender with a video teaching function can be exempted from the food blending function, but not the video function. A coffee machine with a wireless control function can be exempted from the coffee machine function, but not the wireless function.
The exemption only applies to digital circuits contained inside the main unit of home appliances, and does not exempt external wired remote controls or circuits with communication control functions such as remote controls connected by cables. For example, external wired remote controls for air conditioners are not exempt.
According to the no-harmful-interference principle of FCC Part 15.5 and the FCC monitoring principle of FCC Part 15.29, the FCC Commission strongly recommends that even exempted products must meet the requirements of technical standards. If there is interference with the operation of other surrounding equipment during actual use and complaints are received, the FCC Commission still has the right to restrict the sale of its products.
The exempted household appliances listed in KDB 772105 are as follows:
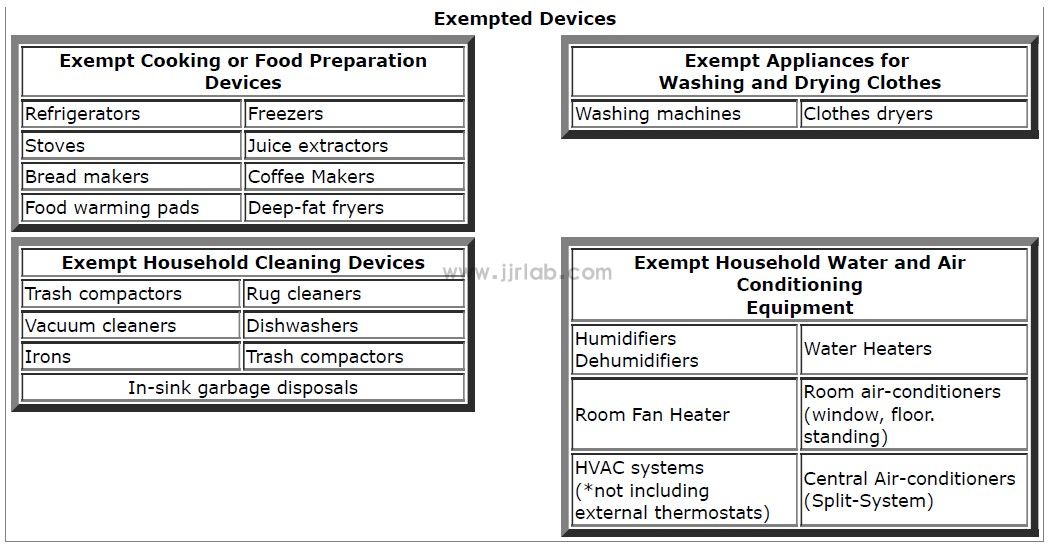
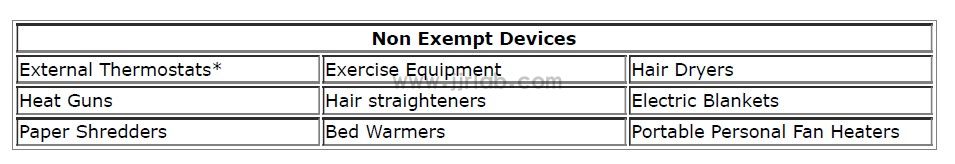
The non-exempt household electrical appliances listed in KDB 772105 are as follows:
Labeling requirements for household appliances
According to the requirements of KDB 89681, household appliances that have passed the SDoC process evaluation can voluntarily be marked with the fcc logo, while exempted household appliances cannot be marked with the FCC Logo. Exempted household appliances can only voluntarily be marked with the FCC Logo after they have passed the SDoC process evaluation.

At the same time, the label or manual of the household appliance product needs to have the following statement of compliance with the requirements of Part 15. Exempt household appliances cannot have the following declaration of compliance unless the exempted household appliances meet the requirements of SDoC.
“This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.”
China JJRLAB at your service
China JJRLAB Guangzhou and Shanghai EMC laboratories are A2LA, CNAS, CMA accredited laboratories, CBTL laboratories, FCC, ISED listed laboratories, South African SABS accredited laboratories, and CCC home appliances/lighting accredited testing laboratories;
We can provide customers with CE, CB, FCC, ISED, RCM, PSE, GCC, SABS EMC COC, CCC and other certification services;
We can provide testing site rental and rectification consulting services.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
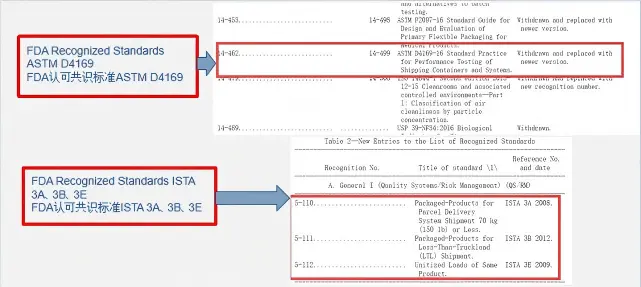 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
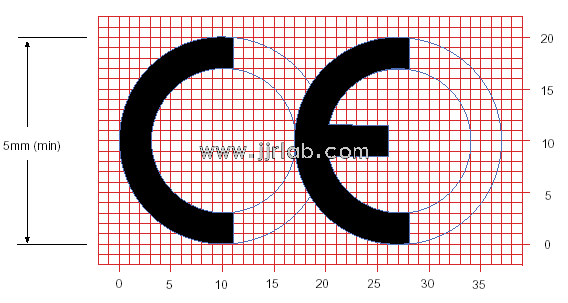 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




