
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtures
In the global business environment, the EU market attracts many companies due to its large consumer base and strict product quality standards. For the lighting industry, CE certification is an essential "key" for LED lighting fixtures to enter the EU market. It is not only a fundamental requirement for market entry but also a bridge of trust between the product and consumers. So, how can LED lighting fixtures obtain CE certification? Below, we will delve into the key points of this process.
CE Certification: The "Key to the Door" for LED Lighting Fixtures Entering the EU Market
CE certification is crucial for LED lighting fixtures as it is the pass for entering the EU market. Obtaining CE certification means the lighting fixture complies with the EU standards on safety, health, environmental protection, and hygiene. This is not just a simple mark but a set of actual requirements that must be strictly followed.
1. Safety Requirements: LED lighting fixtures must ensure that they do not pose safety risks such as electric shocks or fires under normal or foreseeable abnormal conditions. For example, the material of the fixture's casing must have good insulation properties, and the electrical connections must be firm and reliable to prevent current leakage or short circuits.
2. Health Requirements: The light emitted by the fixture must not cause harm to the eyes. This means LED lighting fixtures must carefully control the wavelength, intensity, and flicker frequency of the light during design and manufacturing to reduce blue light damage and eye fatigue.
3. Environmental Requirements: CE certification focuses on the environmental performance of lighting fixtures during production, use, and disposal. The materials used in the fixture should be environmentally friendly and recyclable, minimizing natural resource consumption and environmental pollution.
4. Hygiene Requirements: The fixture must be easy to clean, preventing the accumulation of dust, bacteria, and other substances that could affect hygiene and performance.
Through CE certification, LED lighting fixtures can circulate freely in the EU market, allowing companies to sell them across all EU member states and expand their market. Additionally, CE certification enhances consumer trust. To consumers, the CE mark symbolizes high quality and safety, making them more willing to purchase certified products.
Interpretation of LED Lighting Fixture CE Certification Test Items
EMC Testing: The "Harmonious Ambassador" in Electromagnetic Environments
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) testing is a crucial part of the CE certification for LED lighting fixtures. This test mainly evaluates the fixture’s performance in an electromagnetic environment, ensuring it operates properly in complex electromagnetic surroundings and does not interfere with other nearby electronic devices.
EMC testing includes two main aspects:
1. Electromagnetic Radiation Testing: Lighting fixtures generate electromagnetic radiation during operation. If the radiation is too strong, it could affect the normal operation of surrounding devices. For example, excessive radiation from a fixture near a TV might cause picture interference. Thus, EMC testing strictly checks the fixture's electromagnetic radiation levels to ensure compliance with standards.
2. Anti-Interference Testing: The lighting fixture needs to be resistant to external electromagnetic interference. If the fixture is not resistant, it may flicker, go out, or experience unstable brightness. For instance, in an office environment with many electronic devices, LED fixtures must withstand electromagnetic interference from other equipment, ensuring stable lighting.
LVD Safety Testing: The Robust "Safety Barrier"
For LED lighting fixtures with a working voltage greater than 75V (DC) or 50V (AC), LVD (Low Voltage Device) safety testing is required. LVD testing ensures the electrical safety of the fixture, covering several aspects:
1. Electrical Insulation Testing: The insulation performance of the fixture directly impacts user safety. The test ensures that the fixture's casing and internal wiring have good insulation to prevent current leakage and the risk of electric shock.
2. Grounding Measures Testing: The fixture must have effective grounding measures to quickly direct current to the ground in case of electrical failure, protecting users from electric shock.
3. Overcurrent, Overvoltage, and Short Circuit Protection Testing: These tests ensure the fixture can automatically protect itself when the current exceeds the rated value, the voltage is too high, or there is a short circuit, preventing fires and equipment damage.
LED Lighting Fixture ce certification costs Revealed
The cost of CE certification for LED lighting fixtures mainly depends on the product type and functions. Here are common cost scenarios:
- DC (Direct Current) Products: For DC-powered LED fixtures, only EMC directives need to be followed, and the costs are relatively low since the electrical performance of DC products is simpler, focusing primarily on electromagnetic compatibility.
- AC (Alternating Current) Products: For AC-powered LED fixtures, both EMC and LVD tests are required, so certification costs are higher. This is because AC products involve not only electromagnetic compatibility but also a more comprehensive electrical safety test, making the tests more complicated and expensive.
For example, the CE certification cost for a DC-powered nightlight is relatively low, while for an AC-powered LED chandelier, the cost is higher due to the need for both EMC and LVD testing.
LED Lighting Fixture CE Certification Process
1. Confirm the Product: The company submits a certification application to the testing agency, specifying the model, specifications, functions, and usage environment of the lighting fixture to prepare for the certification process.
2. Prepare Documents: The company needs to prepare relevant certification materials, including product manuals, schematics, dimension drawings, and key component lists. These materials help the testing agency understand the product fully, facilitating subsequent testing and review.
3. Send Sample for Testing: The company sends a sample to the laboratory for strict EMC and LVD testing. Testers will evaluate the fixture according to relevant standards to ensure it meets all CE certification requirements.
4. Issuance of Certificate: After passing the tests, the testing agency will issue a CE report and certificate, confirming the fixture meets EU standards and is ready for market entry.
5. CE Marking: After certification, the company can affix the CE mark to the product. This mark indicates that the product can circulate freely in the EU market, and the company can officially begin selling it.
Certification Cycle and Considerations
The CE certification cycle for LED lighting fixtures typically takes 5-7 business days, which is relatively short. However, each step requires careful preparation to ensure smooth certification.
From the significance of certification to testing items, costs, and the process, each step is crucial for successfully entering the EU market. Only by understanding and strictly following these steps can a company successfully pass CE certification and succeed in the EU market. If you have any questions about the CE certification for LED lighting fixtures, feel free to contact us.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
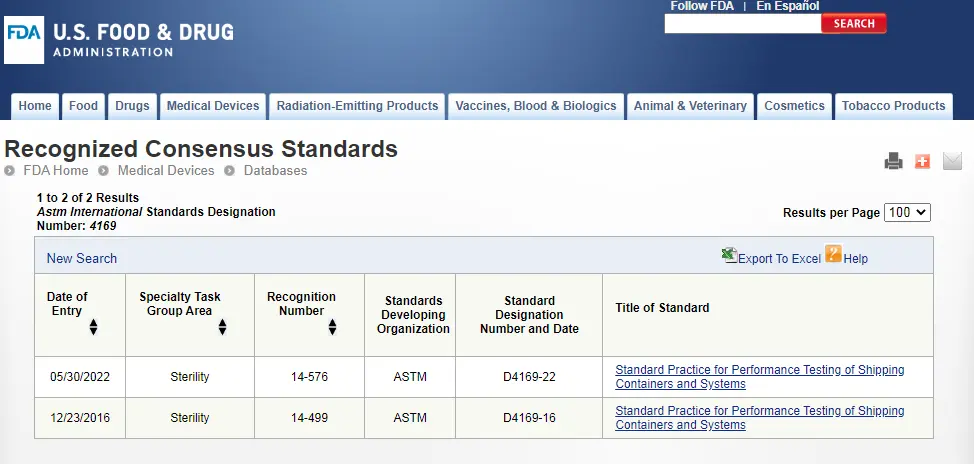 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
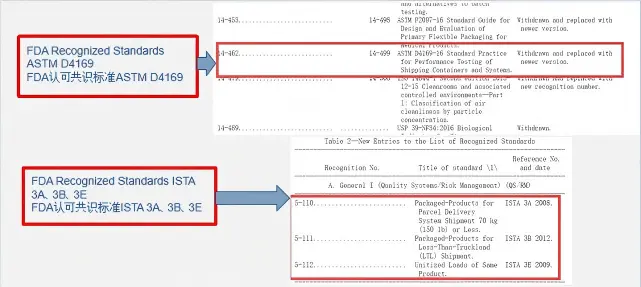
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




