
EMC Testing for Electric Heaters Exported to the US
With the continuous development of global trade, electric heaters, as an important heating device, are increasingly in demand in the U.S. market. Understanding the requirements for exporting electric heaters to the United States, particularly regarding EMC testing, is crucial for enterprises aiming to export successfully.
Definition of EMC Testing
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) testing assesses the ability of electrical and electronic equipment to function normally in their electromagnetic environment without causing intolerable electromagnetic interference to that environment. EMC testing mainly includes two aspects:
- Electromagnetic Emission Testing (EMI): Ensures the device does not emit electromagnetic disturbances beyond permissible levels.
- Electromagnetic Immunity Testing (EMS): Ensures the device can withstand external electromagnetic disturbances without performance degradation.
EMC Testing Requirements
Exporting electric heaters to the United States requires compliance with FCC certification and UL certification standards, detailed as follows:
(A) FCC Certification
1. Applicable Standards
Electric heaters seeking FCC certification must meet the electromagnetic compatibility requirements outlined in 47 CFR Part 15B, which regulates radiofrequency interference and radiation emissions from electronic devices.
2. Testing Items
- Conducted Interference Testing: Measures interference signals transmitted through power lines to the grid to ensure conducted emission levels stay within allowable limits, preventing interference with other devices on the grid. For instance, testing the electromagnetic noise transmitted by the power line during different operating modes of the heater.
- Radiated Interference Testing: Evaluates whether the electromagnetic energy emitted by the device during normal operation exceeds specified limits. This test is usually conducted in an open area or anechoic chamber, with typical measurement distances of 3 or 10 meters, ensuring the device does not cause harmful interference to nearby radio or communication equipment.
- Immunity Testing: Examines the ability of the electric heater to maintain normal operation when subjected to external electromagnetic disturbances. For example, simulated electromagnetic disturbances such as electrostatic discharge or fast transient pulses are applied to observe if the heater functions properly and its features remain unaffected.
3. Certification Methods
- Certification: Required for products with radio transmission functions, such as smart electric heaters with wireless communication features. This involves mandatory FCC Certification, but infrared emission devices are not regulated under this requirement.
- Declaration of Conformity (DOC): Commonly used for standard electric heaters. Manufacturers must ensure products comply with FCC technical standards and prepare relevant technical documentation and test reports.
- Verification: Applicable to simpler products like small hand warmers. If regulations are met, this method allows for a simpler certification process.
(B) UL Certification
1. Applicable Standards
The primary standard for UL certification of electric heaters is UL 1278, which focuses on the safety and compliance of portable, wall-mounted, or ceiling-mounted indoor electric heaters.
2. Testing Items
- Leakage Current Test: Ensures the leakage current under normal operating conditions does not exceed the permissible value, safeguarding user safety.
- Temperature Rise Test: Evaluates the temperature increase of various components during operation to ensure no fire hazards due to excessive heat.
- Durability Test: Assesses the reliability and stability of the heater over extended use. Simulates real-world conditions such as frequent switching or prolonged continuous operation to verify performance consistency over time.
- Short-Circuit Test: Checks safety in case of internal short circuits. This test ensures no excessive currents lead to fires or other hazards.
- Overload Test: Verifies safety when the heater operates beyond its rated power. This accounts for scenarios where multiple devices are connected, potentially overloading the circuit.
- Component Aging Test: Examines the aging and performance degradation of internal components during long-term use. Specific tests evaluate the reliability and lifespan of critical parts under various conditions.
- Dielectric Withstand Voltage Test: Tests the insulation materials' performance under high voltage, ensuring no breakdown that could lead to leakage or electrical accidents.
- Insulation Resistance Test: Measures the insulation resistance value of the heater, indicating its insulation quality. Higher resistance values suggest better insulation and lower leakage risks.
- Mobile Heater Stability Test: Ensures portable heaters remain stable during use to prevent tipping or falling, which could cause fires or harm to users.
Precautions
1. Stay Updated on Regulations: FCC and related standards may evolve with technological advancements and market demands. Companies must stay informed about regulatory updates to ensure ongoing compliance with the latest EMC testing requirements.
2. Representative Test Samples: Ensure the provided test samples accurately represent the product's functional characteristics. Samples should be in good condition and fully operational.
3. Strict Testing Procedures: Adhere to prescribed testing protocols, completing all required emc testing items. Testing personnel must follow the operating procedures of testing equipment and methods.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
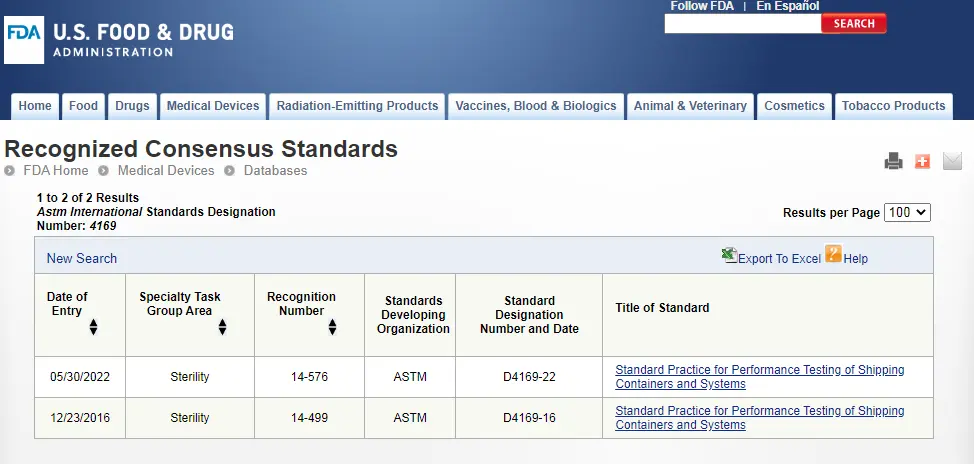 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
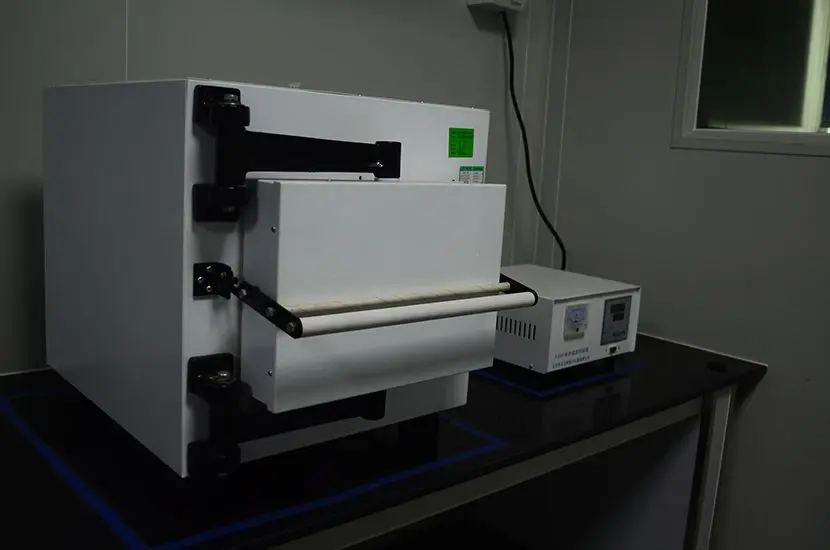 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




