
Electronics and Electrical EMC Testing and Certification
During normal operation, electronic devices emit electromagnetic waves. Given that these electromagnetic waves may interfere with the performance of other electronic devices, manufacturers must ensure that their products do not impact the performance of surrounding devices and are also immune to interference from nearby equipment.
For manufacturers of electronic products, ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a critical mission. EMC, a seemingly obscure term, actually embodies the essential principles that safeguard the normal operation of devices and prevent mutual interference. It means that devices containing electrical, mechanical, or electronic components can operate flawlessly in their electromagnetic environment without causing intolerable electromagnetic interference to other objects within that environment.
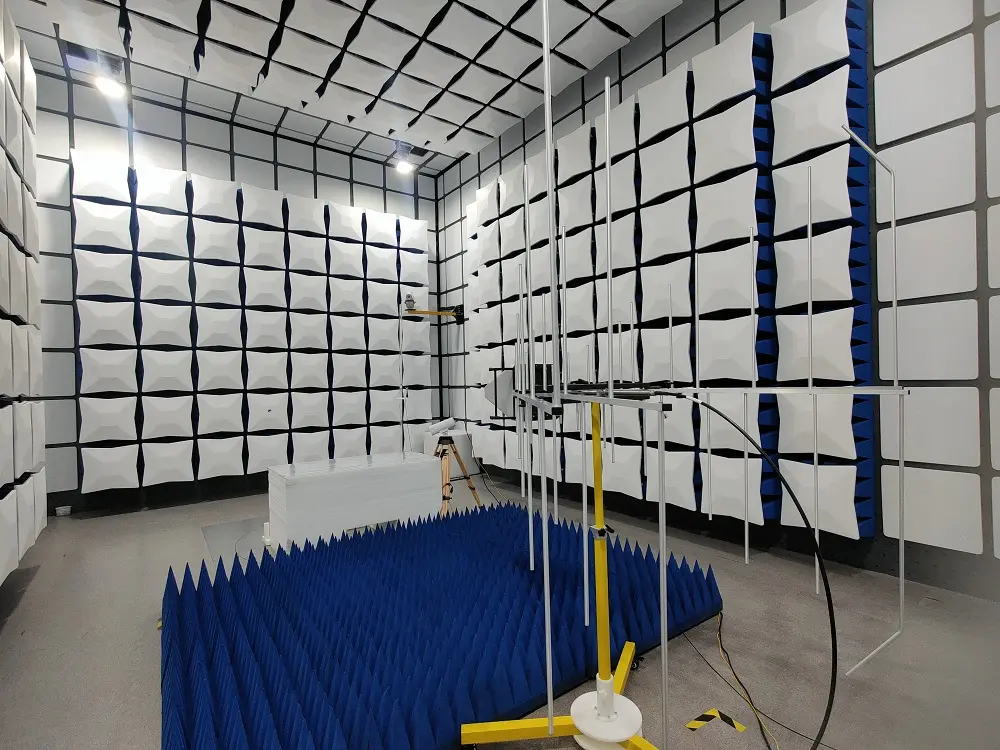

The Importance of EMC for Electronics and Electrical Devices
If your products involve electrical, mechanical, or electronic components, you will likely need to meet EMC requirements before selling them domestically and internationally. Since emc is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of many industrial installations, major markets like the EU, the U.S., China, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand have set specific EMC regULations.
Different markets have varying EMC requirements, clarified through laws, guidelines, and standards. In the EU, the EMC Directive stipulates the EMC requirements, which is a prerequisite for obtaining the ce mark for your product. In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (fcc) has regulations for EMC and spectrum usage in Chapter 47 of the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations (47CFR).
For example, in the automotive industry, modern vehicles are equipped with numerous electronic systems such as engine control, navigation systems, and Bluetooth connectivity. Without proper EMC, these systems could fail, potentially compromising driving safety. Hence, automakers perform stringent emc tests during product development to ensure each component and system works reliably in complex electromagnetic environments.
In addition to ensuring compliance with relevant standards, third-party emc testing and conformity assessment can enhance your competitive edge and position in the market.
Types of EMC Tests for Electronics and Electrical Devices and Applicable Standards
- Conducted Emissions (CE)
Standards: IEC 61000-4-2/-3/-4/-5/-6/-8/-11, IEC 61000-3-2/-3, CISPR 32/35 (en 55032/35), CISPR 22/24 (EN 55022/24), CISPR 15 (EN 55015), CISPR 14-1/-2 (EN 55014-1/-2), CISPR 13 (EN 55013), CISPR 11 (EN 55011), GB 9254, GB/T 17626.2/.3/.4/.5/.6/.8/.11, GB 17625.1/.2, GB/T 17618, GB 13837, GB 17743, GB 4824, GB 4343.1/.2
- Radiated Emissions (RE)
Standards: Same as Conducted Emissions (CE)
- Harmonic Power
Standards: Same as Conducted Emissions (CE)
- Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
Standards: Same as Conducted Emissions (CE)
- Radio Frequency Radiated Immunity (RS)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity (EFT)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Surge Immunity (Impact)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Conducted Immunity from Radio Frequency Fields (CS)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Power Frequency Magnetic Field Immunity (PFMF)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Pulse Magnetic Field Immunity (PMF)
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
- Voltage Dips, Short Interruptions, and Voltage Variations Immunity
Standards: Same as Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (ESD)
Key Factors in Developing an EMC Testing Plan for Electronics and Electrical Devices
1. Understand Product Characteristics
This includes the product's functionality, structure, working principles, operating environment, and its electrical, electronic, and mechanical components. For example, for an industrial robot, it's essential to define the characteristics of its motion control parts, sensor systems, and communication modules.
2. Identify Applicable Standards and Regulations
It is crucial to research the target market for the product and understand the EMC standards and regulations applicable in that market. For instance, if the product is intended for sale in the EU, the plan should be based on the EU EMC Directive and related standards.
3. Evaluate Testing Items and Parameters
Based on product characteristics and applicable standards, determine the types of electromagnetic interference (e.g., radiated emissions, conducted emissions) and immunity projects (e.g., electrostatic discharge immunity, radio frequency radiated immunity), along with corresponding testing parameters and limits.
4. Plan Reasonable Testing Schedule and Timeline
Consider the product development cycle, production plans, and market launch timeline to ensure that the testing process is completed on time without delaying the product launch.
5. Establish Budget
Include costs for testing, possible rectification expenses, and other related costs. For example, if the product fails the test and requires modifications, the budget should account for part replacements, retesting, and other necessary expenses.
In conclusion, EMC is not just a technical challenge but also a cornerstone for ensuring the harmonious coexistence and stable operation of various electronic devices in modern society. Only by fully understanding and rigorously adhering to EMC standards and requirements can manufacturers help create a world of electronic devices that operate efficiently and free from electromagnetic interference.
emc certification Services for Electronics and Electrical Devices
- Multimedia Devices: Personal computers and peripherals (computers, monitors, MICe, keyboards, switches, cameras)
- Audio-Visual Products: Speakers, projectors, TVs, radios
- Home Appliances: Coffee machines, ovens, microwave ovens, induction cookers
- Lighting: LED bulbs, LED lights, downlights, street lights
- Industrial Equipment: Industrial humidifiers, various portable power tools, drills, saws, angle grinders, industrial air conditioners
Testing Duration
5 to 7 days
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Amazon Japan METI A Domestic Administrator Service
Amazon Japan METI A Domestic Administrator Service
 What is "Amazon Japan PSE: A Domestic Adminis
What is "Amazon Japan PSE: A Domestic Adminis
 What Does "ASTM F963-17 Certified" Mean?
What Does "ASTM F963-17 Certified" Mean?
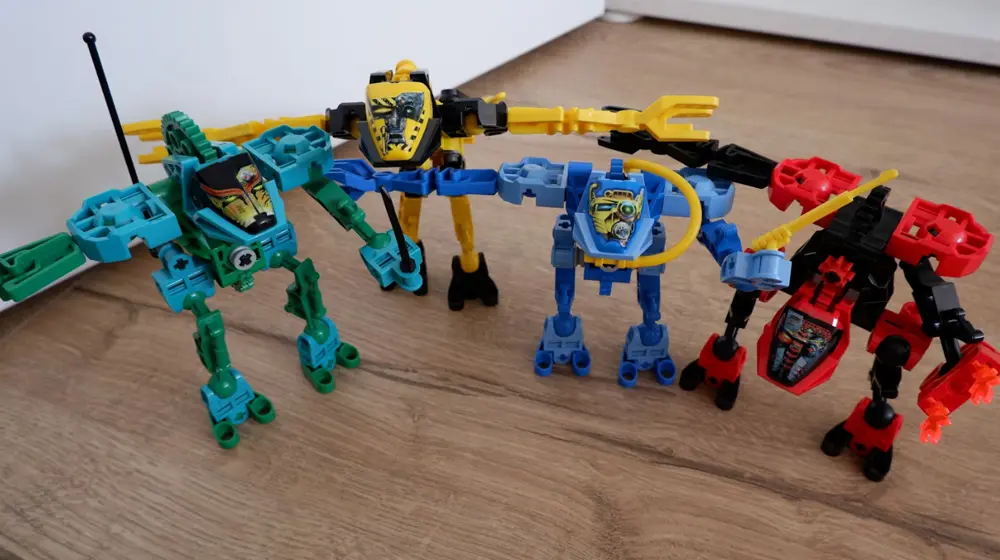 ASTM F963 Board Games Compliance Testing
ASTM F963 Board Games Compliance Testing
 ASTM F963 Flammability Test
ASTM F963 Flammability Test
 ASTM F963 Teether Compliance Testing
ASTM F963 Teether Compliance Testing
 How to get an ASTM F963 Test Report?
How to get an ASTM F963 Test Report?
 ASTM F963-16 Fidget Spinner Compliance Testing
ASTM F963-16 Fidget Spinner Compliance Testing
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




