
Electronic Product Certification in India
The full name of BIS is the Bureau of Indian Standards, which is the national standards body of India. Its headquarters is located in New Delhi, with five regional offices in Kolkata (East), Chennai (South), Mumbai (West), Chandigarh (North), and Delhi (Central). These regional offices oversee 22 branch offices across the country.
Categories of BIS Certification
BIS certification is primarily divided into two types:
- ISI Mark Certification: Applicable to industrial and certain consumer products. It requires factory audits and product testing.
- CRS (Compulsory Registration Scheme): Applicable to electronic products, including most wireless devices. Products must be tested in BIS-recognized laboratories and registered accordingly.
Important Note: Wireless products often require dual certification—BIS and RF certification from WPC (Wireless Planning and Coordination Wing), especially for products with Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or other wireless communication features. This dual-certification mechanism means manufacturers of wireless products must invest more effort to meet India's compliance requirements.
Legal Status of BIS Certification
BIS certification is mandatory, not optional. Under the Compulsory Registration Order issued by India's Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), wireless products that are not BIS-certified risk being seized by customs, banned from the market, or even subject to legal penalties. Indian customs strictly inspect imported products to ensure that product labels match the BIS certificate—especially key information like model numbers and trademarks.
Validity of Certification
BIS certification is usually valid for 1–2 years (CRS registrations are valid for 2 years). Renewal applications must be submitted three months before expiration. During the validity period, BIS has the right to conduct market surveillance to ensure continued compliance. Therefore, obtaining certification is just the first step—establishing a long-term compliance mechanism is equally important.
Which Products Require BIS Certification?
First Batch (MANDATORY):
BIS certification applies to manufacturers from any country. Key sectors include:
1. Tyres
2. Household appliances such as electric irons, kettles, stoves, heaters
3. Cement and concrete
4. Circuit breakers
5. Steel products
6. Electricity meters
7. Automobile components
8. Food products, milk powder
9. Baby bottles
10. Tungsten filament lamps
11. Oil-fired heaters
12. Large transformers
13. Plugs
14. Medium and high-voltage cables
15. Self-ballasted lamps
(Mandatory in batches since 1986)
Second Batch (COMPULSORY):
Applies to electronic and IT equipment:
1. Set-top boxes
2. Portable computers
3. Notebooks
4. Tablets
5. Monitors (≥32 inches)
6. Video monitors
7. Printers, plotters, scanners
8. Wireless keyboards
9. Telephone answering machines
10. Automatic data processors
11. Microwave ovens
12. Projectors
13. Electronic clocks with mains power
14. Power amplifiers
15. Electronic music systems
(Mandatory since March 2013)
Additional Products (COMPULSORY since Nov 2014):
16. IT device power adapters
17. AV device power adapters
18. UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
19. DC or AC LED modules
20. Batteries
21. Self-ballasted LED lamps
22. LED luminaires
23. Mobile phones
24. Cash registers
25. Point of Sale (POS) machines
26. Photocopiers
27. Smart card readers/writers
28. Postal franking machines
29. Passport readers
30. Power banks
BIS Certification Testing for Electronic Products
The core of BIS certification lies in product testing, which verifies compliance with Indian standards. Testing is carried out in BIS-recognized labs and covers aspects like safety, performance, and EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility). Understanding these test requirements in advance helps manufacturers prepare better and avoid delays or added costs due to test failures. Wireless products typically undergo more complex testing compared to wired ones.
Key Tests for Electrical Safety:
- Insulation strength test: Ensures the insulation system can withstand high voltage without breakdown.
- Dielectric withstand test: Assesses product safety under abnormal voltage.
- Leakage current test: Ensures current leakage remains within safe limits.
- Temperature rise test: Checks if temperature remains within permissible limits during full load operation.
- Mechanical strength test: Evaluates the structural integrity of casings and connectors.
For Battery-Powered Devices (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds):
Specific battery safety tests are required, including overcharge, over-discharge, short circuit, and crush tests. Indian Standard IS 14155 governs battery safety. Test failures are a common cause of certification delays. Manufacturers should pay special attention to battery protection circuit design to ensure cells remain protected under all conditions.
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) Testing:
EMC testing ensures that a device neither emits nor is affected by unwanted electromagnetic interference. Typical tests include:
- Conducted emissions: Measures interference through power lines.
- Radiated emissions: Assesses electromagnetic noise emitted to the air.
- ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) immunity
- RF conducted immunity
- Electrical fast transient/burst immunity
RF Testing for Wireless Products:
Though primarily part of WPC certification, RF testing is closely tied to BIS certification and includes:
- Frequency range verification: Ensures operation within India-approved bands.
- Transmission power test: Verifies RF output power is within limits.
- Bandwidth measurement: Assesses signal spread.
- Spurious emissions: Detects unwanted signals.
- Receiver blocking test: Measures resistance to interference.
Energy Efficiency Tests:
Especially important for battery-powered devices. These tests may include:
- Standby power consumption
- Efficiency during operation
- Battery life testing to verify advertised runtime
Environmental Tests:
Ensures product reliability under Indian climate conditions, such as:
- High temperature and humidity tests
- Temperature cycling
- Vibration and shock tests (to simulate transport and usage stress)
Note: BIS has strict requirements for sample consistency. Test samples must be identical to mass-produced versions. Any discrepancies (e.g., material changes, supplier swaps) can invalidate test results. A robust sample management system is essential to reflect actual production accurately.
BIS Certification Process:
1. Sample Shipment
2. Samples should ideally retain original packaging
3. Monitors, TVs must be in original packaging; soft pack cells/batteries require blister trays; large batteries must be individually packaged
4. Shipping Time:
- 1–2 working days to dispatch from our company
- Typically 1–2 weeks to arrive in India (may face customs delays; larger items more prone to being held)
BIS Certificate Validity:
1. Validity refers to the R-No. (Registration Number)
2. Each R-No. is initially valid for 2 years
3. An R-No. corresponds to one manufacturer + one brand + one product type
4. A single R-No. can be linked to multiple certificates of the same manufacturer, brand, and product category
5. All certificates remain valid as long as the associated R-No. is valid
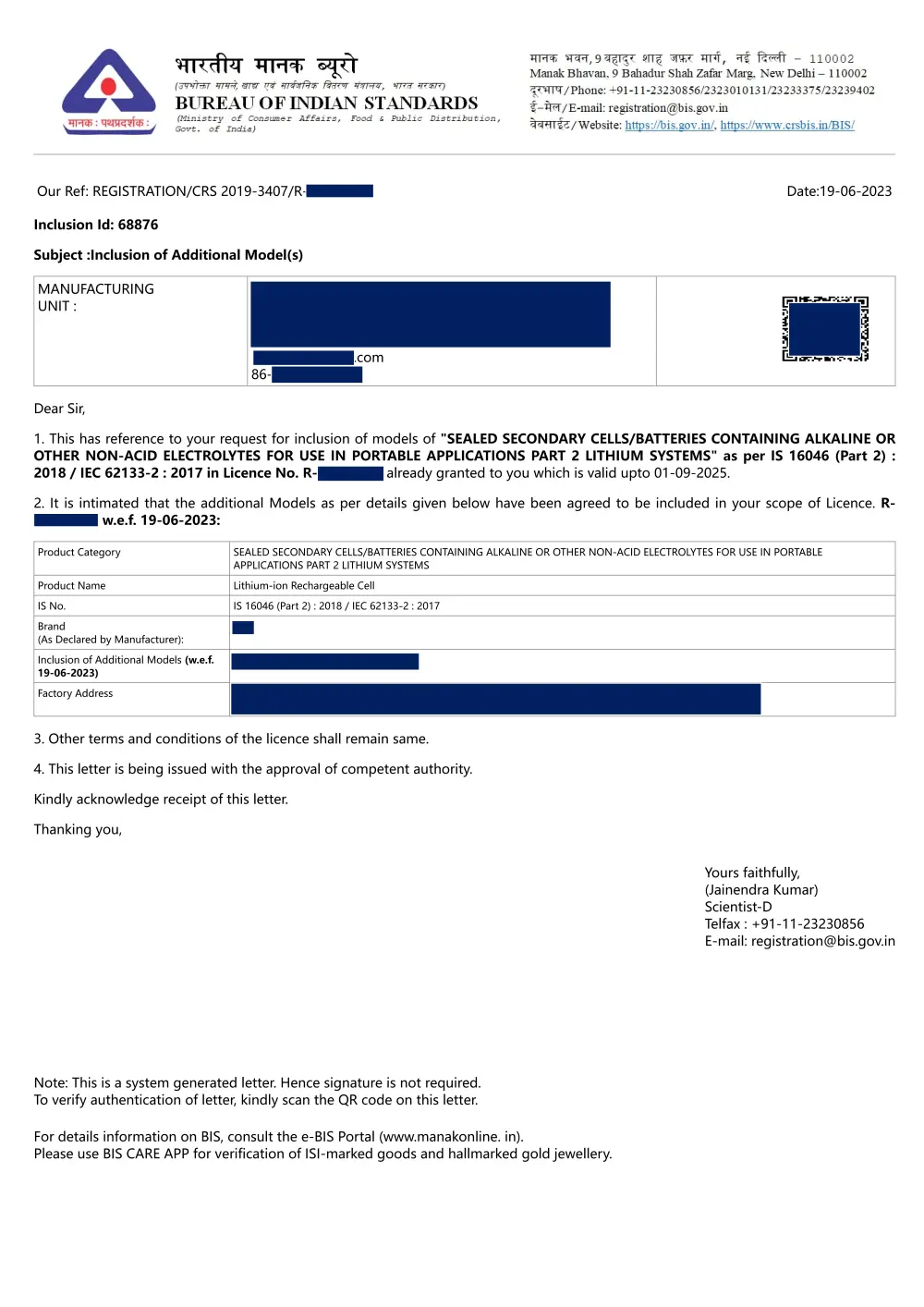
BIS Certificate Template
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Toothbrush FDA Certification Testing
Toothbrush FDA Certification Testing
 Snoring Device FDA 510k Standard Testing
Snoring Device FDA 510k Standard Testing
 Single Use Intravenous Catheter Certification Test
Single Use Intravenous Catheter Certification Test
 Silicone Material Product Compliance Certification
Silicone Material Product Compliance Certification
 What to Do If Cytotoxicity Test Results Are Positi
What to Do If Cytotoxicity Test Results Are Positi
 ISO 10993:5 Cytotoxicity Testing Methods
ISO 10993:5 Cytotoxicity Testing Methods
 FDA ISO 10993-1 Biocompatibility Evaluation Guidel
FDA ISO 10993-1 Biocompatibility Evaluation Guidel
 In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing for Medical Devices
In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing for Medical Devices
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




