
Do I Need FCC Certification?
FCC (Federal Communications Commission) Overview
The FCC, or Federal Communications Commission, operates under relevant sections of the United States Federal Communications Regulations (CFR 47). According to these regulations, all electronic products entering the United States must undergo electromagnetic compatibility certification (FCC certification). FCC certification applies to products intended for use in over 50 states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. territories.

Scope of FCC Certification
Applicable to over 50 states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. territories.
FCC Certification Standards
FCC establishes technical standards for testing electronic and electrical equipment based on the type of radiofrequency emissions. According to regulations, these can be categorized as follows:
- fcc part 15 Intentional Radiators
- fcc part 18 Industrial, Scientific, and Medical Equipment Products
- FCC PART 22 Public Mobile Communications Service Products
- FCC PART 24 Personal Communication Service Products
- FCC PART 25 Satellite Communication Service Products
- FCC PART 27 Other FCC Wireless Communication Service Products
- FCC PART 68 Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
Among these, FCC PART 15 and PART 18 are the most widely applied.

Product Range Requiring FCC Certification
1. Personal Computers and Peripheral Devices (Monitors, Printers, Keyboards, Power Adapters, Mice, Scanners, Interface Cards, Electronic Instruments, Power Supplies, UPS, Fax Machines, Modems, Answering Machines, Switches, etc.)
2. Household Appliances, Power Tools (Refrigerators, Irons, Food Processors, Electric Kettles, Electronic Sterilizers, Microwaves, Air Conditioners, Vacuum Cleaners, Electric Toys, Rice Cookers, Electric Shavers, Clippers, Hair Dryers, Toasters, Massagers, Battery Chargers, Home Stoves, Cooktops, Washing Machines, Induction Cookers, Electric Food Processing Tools, Low-Power Motors, etc. Electric Tools: Drills, Grinders, Circular Saws, Nail Guns, Drills, etc.)
3. Audio-Visual Products (Radios, CRT/LED/LCD TVs, Set-Top Boxes, DVD/VCD Players, MP3 Players, Home Theaters, etc.)
4. Lighting Fixtures (LED Fixtures, LED Screens, LED Power/Driver Units, Ballasts, Energy-Saving Lamps, Stage Lights, Dimmers, Transformers, Electronic Dimming Devices for Entertainment Venues, AC Electronic Ballasts for Tubular Fluorescent Lamps, Tubular Fluorescent Lamps, Ballasts, Ballasts for Discharge Lamps, Fixed Luminaires, Portable Luminaires, Recessed Luminaires, etc.)
5. Wireless Products (e.g., Bluetooth, Wireless Remote Control Toys, Wireless Remote Switches, Wireless Thermometers, Wireless Mice and Keyboards, Wireless Monitors & Cameras, Wireless Microphones, FM Transmitters, and various wireless devices)
6. Electronic Toys (Metal Toys, Plastic Toys, Wooden Toys, Cloth Toys, Paper Toys, and Electronic Toys)
7. Security Products (Alarms, Security Products, Access Control, Monitors & Cameras, etc.)
8. Industrial Machinery (Punching and Cutting Machinery, Woodworking Machinery, Packaging Machinery, Plastic Machinery, Metal Cutting Machinery, Food Processing Machinery, Printing Machinery, Die Casting Machinery, Electrical Control Systems for Machinery, Amusement Facilities, Hydraulic Machinery, etc.)

FCC Certification Modes
On November 2, 2017, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) officially announced the transition of the DoC & VoC programs to the SDoC program to simplify the certification process for wireless devices and clarify the usage specifications of electronic labels.
During the transition period from November 2, 2017, to November 2, 2018, both the FCC VoC and DoC certification programs or the new fcc sdoc certification program could be utilized. After the one-year transition period, the FCC SDoC certification program will officially replace the original FCC VoC and DoC certification methods.
Specific Requirements for FCC Certification
1. FCC Verification - Self-Verification: Manufacturers or importers ensure that their products undergo necessary testing in FCC-accredited laboratories to ensure compliance with relevant technical standards and retain testing reports. The FCC reserves the right to request manufacturers to submit testing data for device samples or products.
2. FCC DoC - Declaration of Conformity: Responsible parties (usually manufacturers or importers) have their products tested by FCC-designated accredited testing bodies to ensure compliance with relevant technical standards and retain testing reports. The FCC reserves the right to request responsible parties to submit testing data for device samples or products. Upon successful testing, the product receives a DoC and testing report, and the manufacturer can affix the fcc logo on the product.

3. FCC Certification - FCC ID Certification: Products must undergo testing at FCC-registered laboratories for FCC listing, and after obtaining testing reports, compile technical documentation for the products, including detailed photos, circuit diagrams, schematic diagrams, user manuals, etc. These documents, along with the testing reports, are submitted to an FCC-approved certification body (TCB) for review and approval. Once the TCB confirms the accuracy of all information, a certificate is issued, authorizing the applicant to use the fcc id. For customers applying for FCC certification for the first time, they must first apply to the FCC for a GRANTEE CODE (company code). After testing and certification, the FCC ID is labeled on the product.
FCC Certification Process
(1) Compliance Evaluation Process:
The FCC certification process is similar to CE certification, which involves testing and evaluating the product, preparing testing reports and application documents for submission to TCB, and after certification issuance and information entry on the FCC website, manufacturers can label the product accordingly and add corresponding FCC guidance to the manual, enabling the product to enter the market for sale.

(2) Documents Required for FCC Compliance Evaluation Application:
1. Applicant's name, product name, model, address, telephone, fax, contact person, and position
2. Authorization letter and confidentiality requirements; for the emission part, the fundamental frequency of emission (i.e., the carrier frequency)
3. Applicant's FCC registration number (FRN), which can be obtained for free at http://www.fcc.gov
4. FCC ID number, consisting of the Grantee Code (3 or 5 uppercase letters or numbers) and the product code (1-14 letters or digits)
5. FCC label location and specifications
6. Brief description of the working principle and function
7. Schematic diagram
8. Circuit diagram
9. User manual
10. Antenna specifications
Note:
All documents must be in English and PDF format. Each PDF should be smaller than 5.5 MB.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
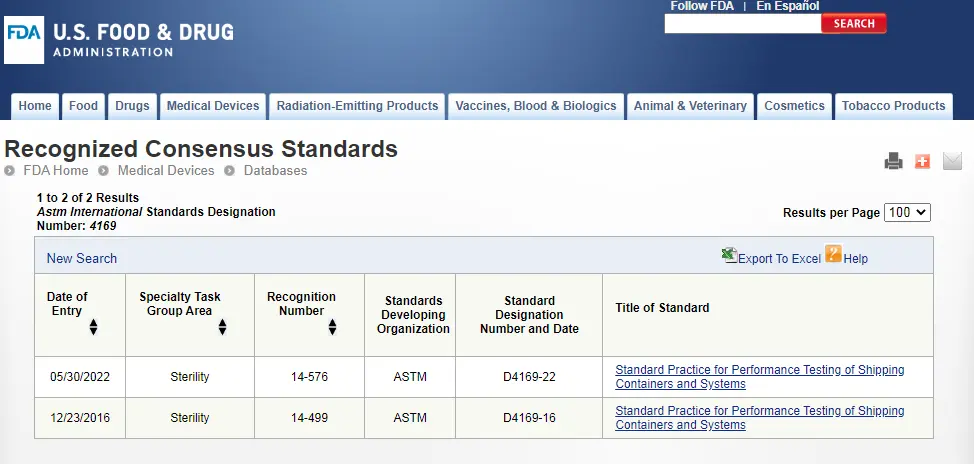 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




