
Differences Between FCC-SDOC and FCC-ID Certifications
Many companies or factories engaged in foreign trade, especially those exporting to the US or selling on Amazon’s e-commerce platform, require products to have FCC certification marks, with some also needing an ID number. This often confuses many clients: What is FCC certification? What is the certification mark, and what is the ID number? How can one obtain FCC certification? Let’s explore the US FCC certification.

Overview of FCC Certification
FCC certification is issued by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the United States, aimed at ensuring that electronic and wireless devices meet specified standards for radio frequency spectrum and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). FCC certification applies to electronic and wireless devices sold or used in the US, including transmitters, receivers, transceivers, antennas, etc. These devices must comply with FCC equipment certification rules to ensure they do not interfere with other electronic devices or radio communications and are not interfered with by other devices. FCC certification is obtained by submitting an application and having the product tested by an FCC-certified laboratory. Before testing, manufacturers must ensure their products meet the FCC’s technical standards. These tests typically include RF radiation measurement, EMC testing, and radiation immunity testing. The FCC certification mark is a "fcc id" label that must be clearly visible on the product. This mark indicates that the product has passed FCC certification testing and complies with FCC technical standards.
Differences Between FCC-ID and FCC-SDOC Certifications
Currently, there are two FCC certification methods in the US: the Self-Declaration of Conformity FCC-SDOC certification and the Product Certification, also known as FCC-ID certification. What are the differences?
fcc sdoc (Self-Declaration of Conformity)
This is for most products without wireless functions, such as household appliances, electronic products, and lighting fixtures. With FCC-SDOC certification, the FCC mark can be affixed to the product’s nameplate. Typically, the applicant only needs to send a sample to the laboratory, which conducts tests according to FCC standards and issues a compliance report. Once the client receives the report, they can affix the FCC mark to the product.
Common products requiring FCC-SDOC certification include:
- Power Supplies: Communication power supplies, switch power supplies, chargers, monitor power supplies, LED power supplies, LCD power supplies, uninterruptible power supplies, etc.
- Lighting Fixtures: Chandeliers, track lights, garden lights, handheld lights, downlights, LED street lights, string lights, table lamps, LED spotlights, LED bulbs, grid lights, aquarium lights, streetlights, LED tubes, LED fixtures, energy-saving lamps, T8 tubes, etc.
- Home Appliances: Fans, electric kettles, speakers, televisions, mice, wireless mice, vacuum cleaners, etc.
- Electronics: Earplugs, mobile phones, routers, mobile phone batteries, laser pointers, vibrators, etc.
- IT and Information Technology: Digital cameras, portable music players, etc.
FCC ID (Certification)
This is a stricter certification for devices that may interfere with radio equipment (e.g., Bluetooth devices, Wi-Fi devices, tablets, Bluetooth headsets). These devices must be tested by TCB or authorized laboratories to ensure they do not interfere with other radio equipment. Test results must be submitted to the FCC for review, and an ID number is registered so consumers can easily identify FCC-certified devices.
Common products requiring FCC-ID certification include:
- Wireless Products: Bluetooth devices, tablets, wireless keyboards, wireless mice, wireless readers, wireless transceivers, walkie-talkies, wireless microphones, remote controls, wireless network devices, wireless video transmission systems, and other low-power wireless products.
- Wireless Communication Products: 2G phones, 3G phones, 3.5G phones, DECT phones (1.8G, 1.9G frequency bands), walkie-talkies, etc.
Important Notes:
1. Whether FCC-SDOC or FCC-ID certification is required, US agent information is needed for shipment. If your company has a US agent, this is not an issue; if not, a laboratory can assist in providing US agent information.
2. When selecting a laboratory for FCC certification, ensure it is A2LA-accredited, as only these laboratories are qualified to perform fcc testing and issue reports.
3. After obtaining FCC-ID certification, an ID number is issued, but the product cannot display the FCC mark. Only FCC-SDOC certification allows the mark to be displayed. Therefore, it’s important to note that wireless products need both FCC-SDOC and FCC-ID certifications.
Main Testing Items for FCC Certification
- Radiation Emission
- Conducted Emission
- Harmonic Current
- Flicker
- Frequency Deviation
- Adjacent Channel Power
- Spurious Emission
- Conducted Carrier Power
- Effective Radiated Power
- Transmitter Modulation Frequency Response
- Modulation Bandwidth of Wideband Equipment
- Frequency Stability Under Low Voltage Conditions
Both FCC-SDOC and FCC-ID certifications require EMC testing. For wireless products, an additional RF test is necessary.
In summary, remember: for products with wireless functions, both FCC-ID and FCC-SDOC certifications are required. For products without wireless functions, only FCC-SDOC certification is needed. Both types of certification require US agent information.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
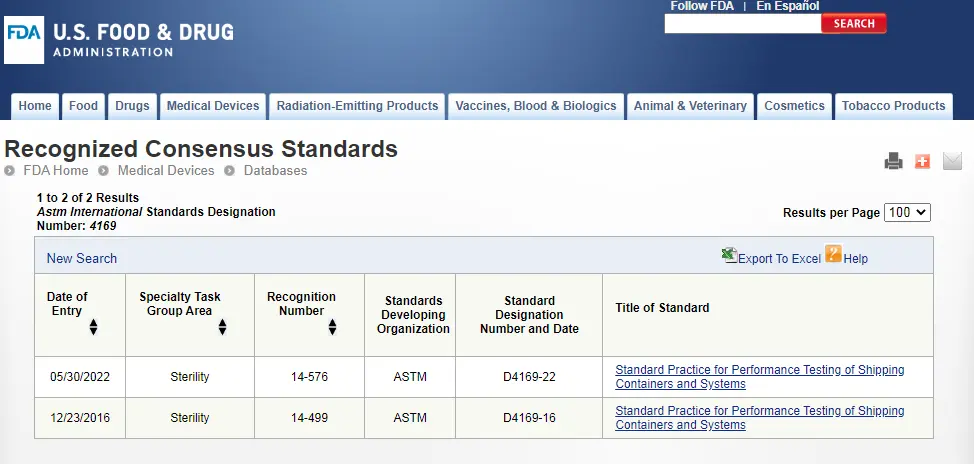 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




