
CE Certification Compliance for Household Appliances
As a large and highly regulated market, the European Union (EU) has a range of complex technical and safety requirements for imported household appliances. This article will delve into the key requirements for exporting household appliances to the EU, focusing particularly on CE certification and compliance with related directives, offering businesses a clear compliance guide.

The Importance of CE Certification
CE certification is a prerequisite for household appliances entering the EU market. This certification not only serves as a safety mark but also indicates that the product complies with the EU's essential safety, health, and environmental requirements. Manufacturers or their authorized representatives in the EU must affix the CE mark on the product to demonstrate that it has undergone the conformity assessment procedure and meets all relevant EU directive requirements.
(1) CE Certification Process
To obtain CE certification, manufacturers need to identify the directives their products must comply with, such as the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMCD). Then, they must select the appropriate conformity assessment procedure and perform the assessment according to the directive requirements. Finally, manufacturers need to create or affix the CE mark and additional information related to the directives.
(2) Specific Requirements of the Directives
Household appliances need to comply with multiple directives, including LVD, EMC, ErP, RoHS, and WEEE. Each directive has its specific technical and safety requirements, and manufacturers must ensure their products meet these standards.
(3) Technical Documentation and Declaration of Conformity
After completing the conformity assessment, manufacturers must prepare technical documentation and the EU Declaration of Conformity to prove that the product meets all the relevant directive requirements.
Detailed Explanation of Key Directives
(1) Low Voltage Directive (LVD)
The LVD Directive primarily concerns the safety requirements of electrical equipment, such as protection against electric shock and overheating protection. Manufacturers must ensure their products comply with the latest LVD Directive and related harmonized standards.
(2) Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMCD)
The EMCD Directive requires household appliances to limit electromagnetic interference to within specified limits and ensures they have a certain level of immunity to electromagnetic disturbances in the environment. Manufacturers must comply with the EMCD's requirements, conduct the conformity assessment, and prepare the corresponding technical documentation and EU Declaration of Conformity.
(3) Energy Efficiency Directive (ErP)
The erp directive aims to improve product energy efficiency and environmental performance. Manufacturers must perform testing according to the specific measures of the ErP Directive and affix energy efficiency labels to their products.
3. Other Important Directives
(1) Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (RoHS)
The RoHS Directive restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic products. Manufacturers must ensure that their products do not contain hazardous substances above the specified limits.
(2) Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE)
The WEEE Directive involves the recycling and disposal of electrical and electronic products. Manufacturers must ensure their products comply with the WEEE Directive and participate in relevant recycling schemes.
Understanding and adhering to the CE certification process and the related directive requirements are crucial to ensuring that products can successfully enter the EU market.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 CE Certification Compliance for Household Applianc
CE Certification Compliance for Household Applianc
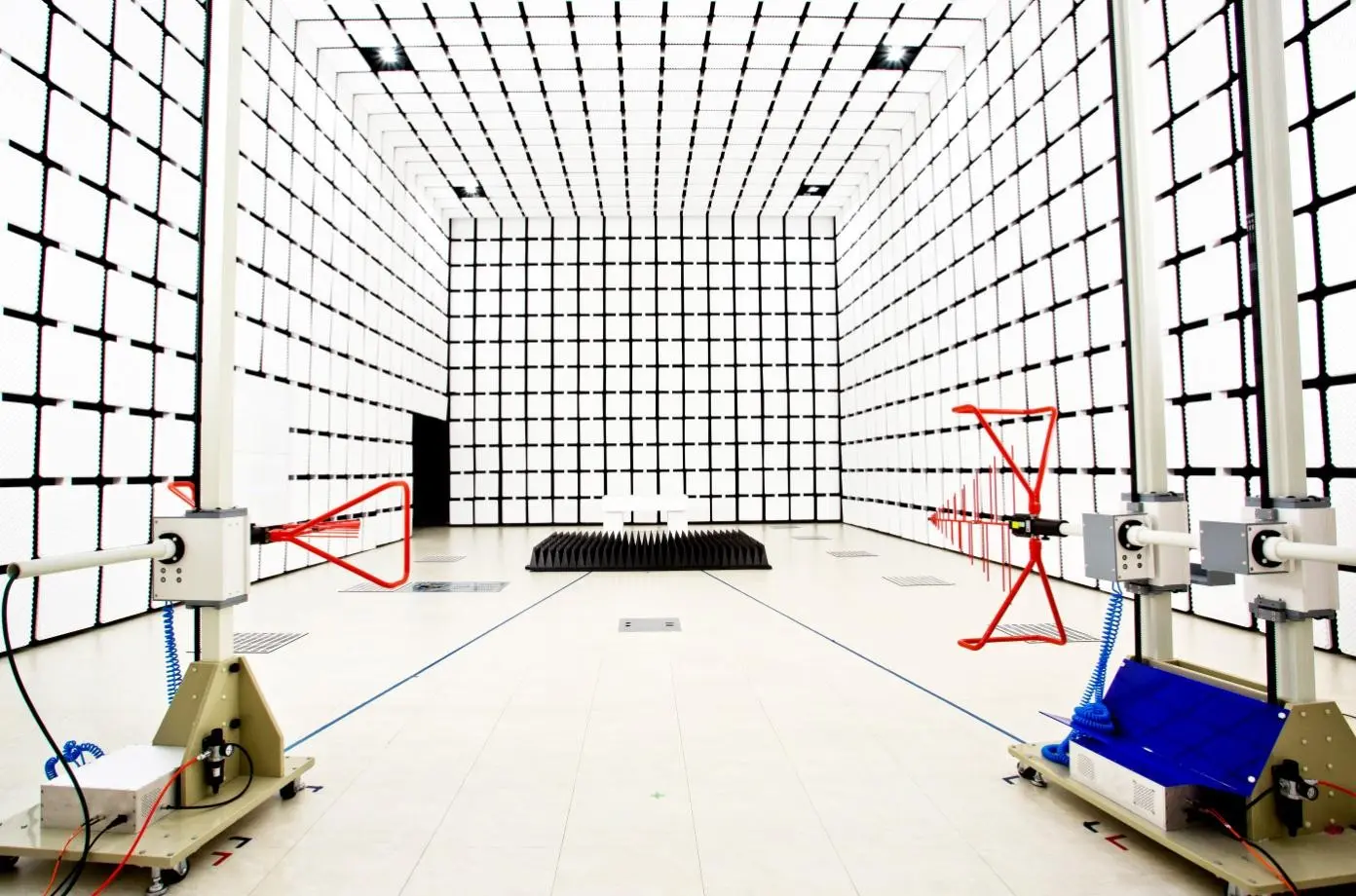
 Malaysia IPv6 Testing
Malaysia IPv6 Testing
 A Detailed Introduction to the EU EN 18031 Standar
A Detailed Introduction to the EU EN 18031 Standar
 Is EN 18031 Cybersecurity Compliance Mandatory?
Is EN 18031 Cybersecurity Compliance Mandatory?
 How to Obtain EU CE Certification for Toys?
How to Obtain EU CE Certification for Toys?
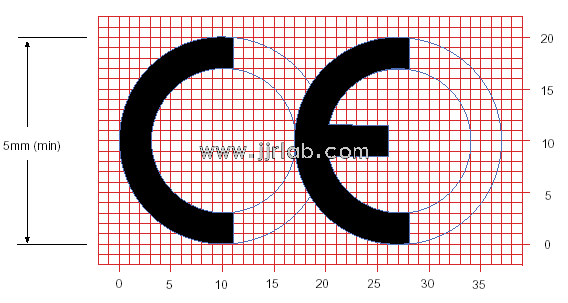 How to get CE Certification for Electronic Electri
How to get CE Certification for Electronic Electri
 ISO 10993-23 Irritation Testing
ISO 10993-23 Irritation Testing
 Guide to Compliance Certification for IVD Devices
Guide to Compliance Certification for IVD Devices
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




