
Can I export to the US without FCC certification?
Can products be exported to the United States without FCC certification?Generally, electronic products need FCC mandatory certification to be exported to the United States. It is essential for customs clearance and sales. UL, on the other hand, is a voluntary certification in the United States and is not mandatory.
FCC certification is a compulsory certification in the United States. It serves as proof of safety for products entering the U.S. market. Products must undergo FCC certification to be listed and sold in the United States. Without FCC certification, customs will not clear the goods.
The responsible party (manufacturer or importer) must have the product tested by an FCC-designated qualified testing agency. A test report will be produced. If the product complies with FCC standards, a corresponding label is affixed to the product, and a statement regarding FCC compliance is included in the user manual. The test report must be retained for FCC inspection.
FCC Certification Methods:
There are two methods of FCC certification: FCC ID and FCC SDoC.
1.1 fcc sdoc (Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity)
This method is used for most non-wireless transmitting devices, household appliances, electronic products, and lighting. Manufacturers can test the products themselves or send them to third-party TCB laboratories for testing and declare compliance with FCC standards before marketing. However, manufacturers must submit technical specifications and test reports to the FCC for review.
1.2 fcc id (Certification)
This method is used for devices that may cause interference to radio equipment (Bluetooth devices, Wi-Fi devices, tablets, Bluetooth headsets). These devices must be tested by TCB or authorized laboratories to ensure they do not interfere with other radio devices. The test results must be submitted to the FCC for review and an ID number registered for consumer identification.
Note: To affix the FCC mark, FCC-SDoC certification is required. Additionally, products listed on platforms like Amazon or for U.S. customs clearance need a U.S. agent (representative) information.
Common FCC Standards:
2.1. Wireless Communication Devices:
- Wi-Fi devices: FCC Part 15
- Bluetooth devices: fcc part 15
- Walkie-talkies: FCC Part 90
- Wireless microphones: FCC Part 15
2.2. IT Equipment:
- Computers and peripherals: FCC Part 15
- Data storage devices: FCC Part 15
- Network devices: FCC Part 15
2.3. Electrical Products:
- Household appliances: FCC Part 18
- Electronic devices: FCC Part 15
- Power adapters: FCC Part 15
- Battery chargers: FCC Part 15
2.4. Telecommunications Terminal Equipment:
- Mobile phones: FCC Part 15 and Part 24
- Telephones: FCC Part 68
- Modems: FCC Part 68
- Fax machines: FCC Part 68
2.5. Auxiliary Equipment:
- Televisions: FCC Part 15
- Audio equipment: FCC Part 15
- Video equipment: FCC Part 15
- Cameras: FCC Part 15
- Surveillance equipment: FCC Part 15
2.6. Industrial, Scientific, Medical (ISM) Equipment:
- High-frequency induction devices: fcc part 18
- Industrial equipment: FCC Part 18
- Medical equipment: FCC Part 18
Other types of equipment standards include:
- Radar equipment: FCC Part 15
- Satellite communication equipment: FCC Part 25 and Part 96
- RFID equipment: FCC Part 15
- Electromagnetic locks and security systems: FCC Part 15
- Automotive electronics: FCC Part 15
- Radio frequency radiators: FCC Part 18
Main fcc testing Items:
3.1. Conducted Testing
Conducted testing measures the electromagnetic interference generated during the conduction process of the product. This test simulates the electromagnetic interference that may occur in the actual use environment to evaluate compliance with FCC standards.
3.2. Radiated Testing
Radiated testing evaluates the product's performance in terms of electromagnetic radiation. The test scans the product within a specified range to detect if it produces electromagnetic radiation exceeding FCC limits.
3.3. Harmonic Testing
Harmonic testing assesses the ability of electronic devices to produce harmonic currents, which are undesirable sources of electromagnetic interference affecting the power grid and other devices.
3.4. Electrostatic Discharge Testing
Electrostatic discharge testing evaluates the product's performance under electrostatic conditions. It is essential as static electricity can cause product malfunctions or performance degradation.
3.5. Radio Frequency Immunity Testing
This test assesses the product's performance under radio frequency interference, which can come from wireless communication devices, radar, and other RF sources.
Once a device passes the FCC tests and meets the technical specifications, it can receive FCC certification. The product can then display the FCC mark, which includes the letters "FCC" and a registration number, on its surface or packaging.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
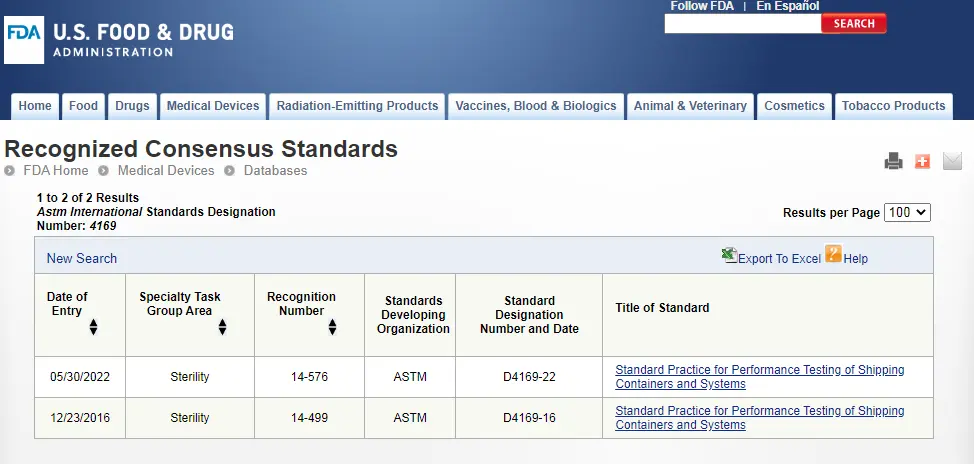 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
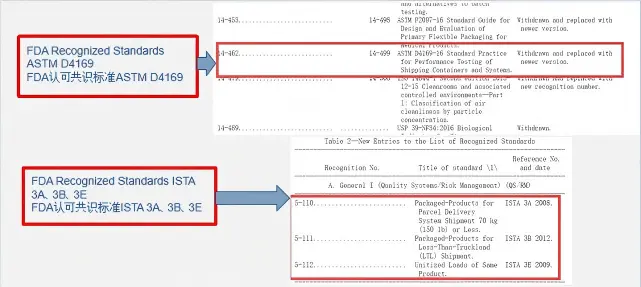
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




