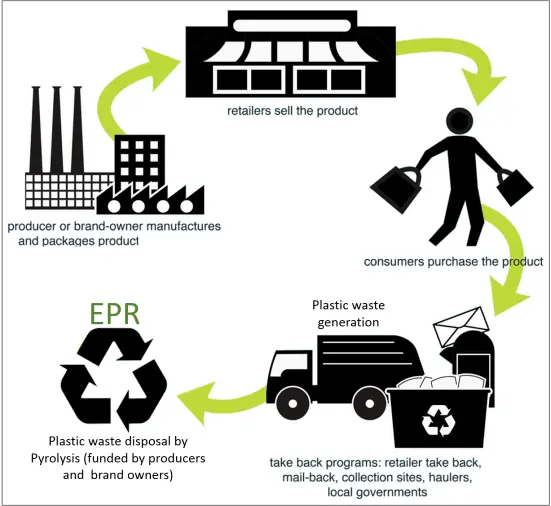
Battery Export Compliance Certification for the EU
As the European Union (EU) continues to raise its standards for environmental protection and product safety, particularly with the ongoing updates to battery-related regulations, Chinese batteries or products containing batteries must comply with multiple new laws and requirements when exporting to the EU. Cross-border sellers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure legal sales.
When listing battery products on platforms such as Amazon, AliExpress, and TEMU, obtaining complianCE certifications is a crucial step. What compliance requirements should be considered when exporting battery products to the EU? Let’s take a closer look.
EPR Environmental Directive Requirements
1. What is EPR?
EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) is an EU environmental policy that holds producers accountable for reducing the environmental impact of their products throughout their lifecycle. This includes organizing the collection of waste batteries and developing key technologies for battery recycling.

2. Relevant Regulations
- Battery Recycling Directive
The European Battery Law promotes the sustainability of the entire battery lifecycle. Amazon requires sellers to provide registration numbers by August 18, 2025. This applies to manufacturers and suppliers of both standalone batteries and batteries embedded in products.
- WEEE Directive
Under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE), producers of products containing batteries are responsible for their recovery. They must register with designated EU agencies and establish or participate in recycling programs.
CE Certification Requirements
1. The Importance of CE Certification
CE certification is mandatory for any battery or product containing batteries sold in the EU, indicating that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental standards.
2. Relevant EU Directives
- Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU): Applies to electrical products with voltage ranges of 50–1000V AC or 75–1500V DC, ensuring safe operation within specified voltage limits.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC 2014/30/EU): Ensures that battery-containing devices do not generate harmful electromagnetic interference and can withstand normal electromagnetic disturbances.
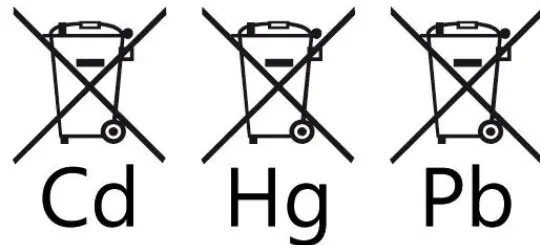
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (RoHS 2011/65/EU): Limits the content of hazardous substances like mercury, cadmium, and lead in batteries.
- EU Representative (EU Rep) Requirements: Products must include contact information for an EU representative on the product, packaging, or accompanying documents.
New Battery Law Implementation (EU 2023/1542)
As of February 18, 2024, the EU's new battery regulation is enforced, governing the production, reuse, and recycling of batteries throughout their lifecycle. Key highlights include:
1. Sustainability and Safety Requirements
- Carbon Footprint Declaration: EV batteries, LMT batteries, and rechargeable industrial batteries (over 2kWh) must include a carbon footprint declaration and labeling.
- Hazardous Substance Limits: Batteries must comply with REACH Annex XVII and EU ELV Directive requirements.
2. Digital Battery Passport
Starting February 18, 2027, large industrial batteries and EV batteries must have a digital passport recording information about their manufacture, usage, and recycling to ensure traceability.
3. Labeling and Information Requirements
- From February 18, 2024, all battery types must display a “waste bin symbol.”
- From August 18, 2024, manufacturers must provide information on battery health status and expected lifespan.
4. Compliance Requirements
By August 18, 2024, manufacturers must draft an EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and affix the CE marking to products.

Other Considerations
1. Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Technical Specifications: Labels must clearly indicate battery type, chemical composition, capacity, manufacturer details, etc.
- Safety Information: Batteries containing hazardous substances must include warning symbols, such as recycling and waste disposal marks.
2. un38.3 certification
UN38.3 certification ensures the safety of lithium batteries during transport. Testing and auditing must be conducted by internationally recognized third-party agencies to meet the International Air Transport Association (IATA) requirements.
3. ROHS certification
Batteries must comply with RoHS directives, which limit harmful substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers.
4. Other Compliance Measures
- Understand Regulations: Sellers must ensure compliance with EU standards, including battery type, capacity, charging speed, etc.
- Battery Recycling and Environmental Requirements: Compliance with EU battery recycling plans, eco-friendly packaging, and waste management is essential.
- Safety and Stability: Batteries must meet high safety standards, including protection against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.

Exporting batteries to the EU requires compliance with various certifications, including CE, RoHS, WEEE, UN38.3, and conformity assessments. These standards encompass performance, environmental adaptability, safety, and chemical properties.
Battery certification is a complex process, and regulations are continually updated. Sellers must stay informed and strictly adhere to these requirements to ensure their products successfully enter the EU market.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!