
Automotive LiDAR AECQ Certification
With the development of automotive electrification and intelligence, the strong rise of domestic car manufacturing startups, and the advancement of localization efforts, the term "automotive-grade" is increasingly coming into focus. From the perspective of autonomous driving, what has been the hottest topic in recent years? Undoubtedly, it’s LiDAR. However, what defines "automotive-grade" LiDAR, and what are its standards?

Automotive-Grade Standards for LiDAR
The automotive-grade standard for electronic components is a series of standards formULated by the AEC organization. Its original intent was to promote the generalization of automotive electronic components. AEC standards have significantly enhanced the qualification generalization of automotive electronic components, REDuced the cost of component selection, use, and changes for component manufacturers and OEMs, and greatly improved the reliability and universal applicability of electronic components and vehicles.
Key criteria for automotive-grade products include:
1. All electronic components used in the product must be automotive-grade (AEC-Q Qualified).
2. The product must meet the design and development requirements of automotive electronics.
3. The product must pass the testing requirements of major automakers.
4. The product must achieve mass-production pre-installation (small-volume models, semi-pre-installed, or post-installed applications do not count).
Analysis of LiDAR Electronic Components
LiDAR products apply the following standards for electronic components:
- Laser Emission System: Laser components must meet the AEC-Q102 standard.
- Laser Reception System: Photodetectors must meet the AEC-Q102 standard.
- Information Processing System: Electronic components must meet AEC-Q100, Q101, or Q200 standards.
- Scanning System: MEMS components must meet the AEC-Q100 standard, while electromechanical components are not specified by any AEC standard.
AEC-Q102 is a newly developed standard specifically for the core components of LiDAR, such as lasers and photodetectors, providing a clear framework for LiDAR standards. It includes:
1. Testing considerations for laser components (Section 1.4.5).
2. Process change guidelines for laser components.
3. Minimum parametric test requirements and failure criteria.
4. Qualification test methods (Table 3).
5. Test requirements exclusive to laser components.
Overview of AEC Standards and Their Scope
The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) was established in 1994 by Chrysler, Ford, and General Motors. It currently includes global automakers, automotive electronics, and seMIConductor companies. Components that meet AEC standards are widely adopted by these automakers, fostering data exchange and promoting universal application in automotive components.
The key AEC standards and their scopes include:
- AEC-Q100: Stress testing standards for integrated circuits, covering integrated chips.
- AEC-Q101: Stress testing standards for discrete semiconductor devices, including MOS, IGBT, diodes, and transistors.
- AEC-Q102: Stress testing standards for optoelectronic semiconductors, such as LEDs, photodiodes, phototransistors, and laser devices.
- AEC-Q103: Stress testing standards for MEMS pressure sensors, covering tire pressure sensors and silicon microphones.
- AEC-Q104: Stress testing standards for multi-chip modules (MCMs), such as LED modules and SSDs.
- AEC-Q200: Stress testing standards for passive devices, including capacitors, resistors, inductors, and fuses.
How AEC Standards Address Component Reliability
Ensuring the high reliability of electronic components over a vehicle’s lifecycle involves:
1. High inherent quality for long service life.
2. Batch-to-batch quality consistency during a 15+ year supply period.
3. Effective process changes and requalification during the component lifecycle.
4. Adherence to standards like IATF16949, AEC-Q, and PPAP for design and manufacturing.
For LiDAR, all electronic components, including lasers and detectors certified by AEC-Q102, must pass AEC-Q certification. This ensures the foundation for vehicular applications and guarantees reliability over 15 years of rigorous operation, which is critical for autonomous vehicle safety.
AEC-Q102 Testing Process for Core LiDAR Components
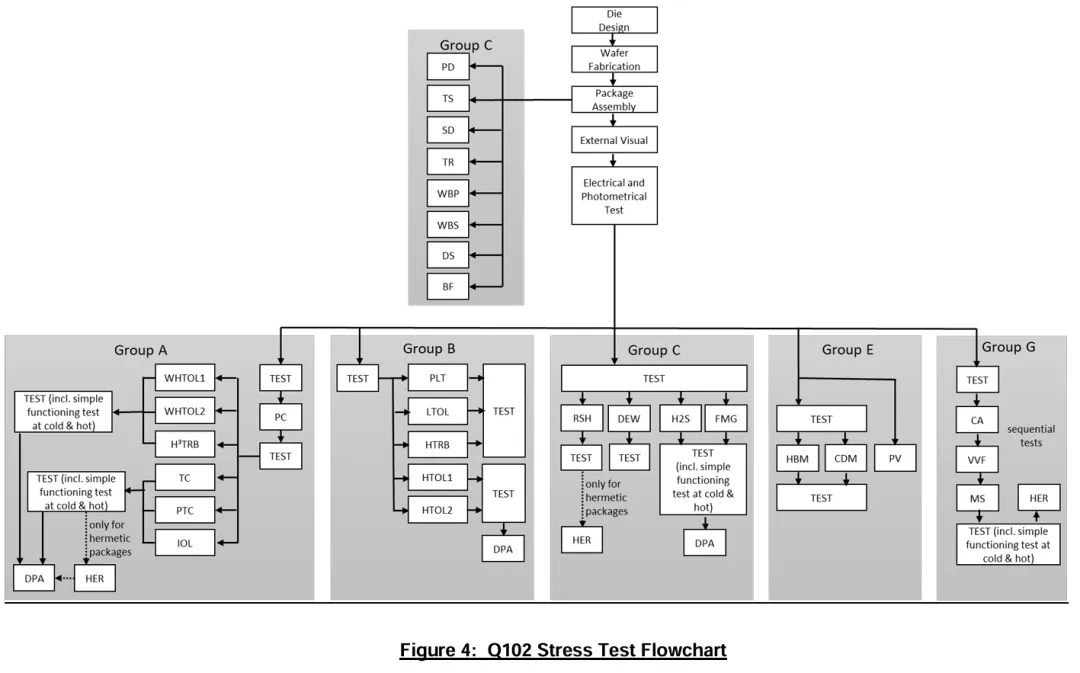
The AEC-Q102 testing process covers:
- Parameter Tests: Evaluation of optical and electrical performance, appearance, parameter validation, physical dimensions, and thermal resistance.
- Environmental Stress Tests: Stress tests such as high-temperature operation, high-humidity operation, thermal cycling, vibration, and mixed gas testing.
- Process Quality Evaluation: Evaluations including ESD, DPA, solderability, bond pull/shear, and whisker growth.
These rigorous standards ensure the reliability and robustness of LiDAR systems, paving the way for safer autonomous driving applications.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 16 CFR Part 1512 Compliance Testing Laboratory
16 CFR Part 1512 Compliance Testing Laboratory
 Electromagnetic Compatibility and Interference Tes
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Interference Tes
 What is 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance and Regulations
What is 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance and Regulations
 2026 California Prop 65 Regulations and Warnings
2026 California Prop 65 Regulations and Warnings
 What are the export compliance for electric fans
What are the export compliance for electric fans
 Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
Amazon US Site Electric Fan UL507 Certification
 What Certifications for Electric Fans in the EU &a
What Certifications for Electric Fans in the EU &a
 How to Choose a Test Laboratory for Amazon UL 507?
How to Choose a Test Laboratory for Amazon UL 507?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




