
Automotive Electronics ISO 7637-4 Standard Testing
Explanation and Interpretation of ISO 7637-4 Standard
As is well known, automotive electronic products undergo ISO 7637-2/-3 standard testing, which is included in the specifications of many major automotive manufacturers. With the development of the automotive electronics industry, the maximum voltage of products has gradually increased, such as in the cases of new energy series, high-voltage BMS battery packs, and more.
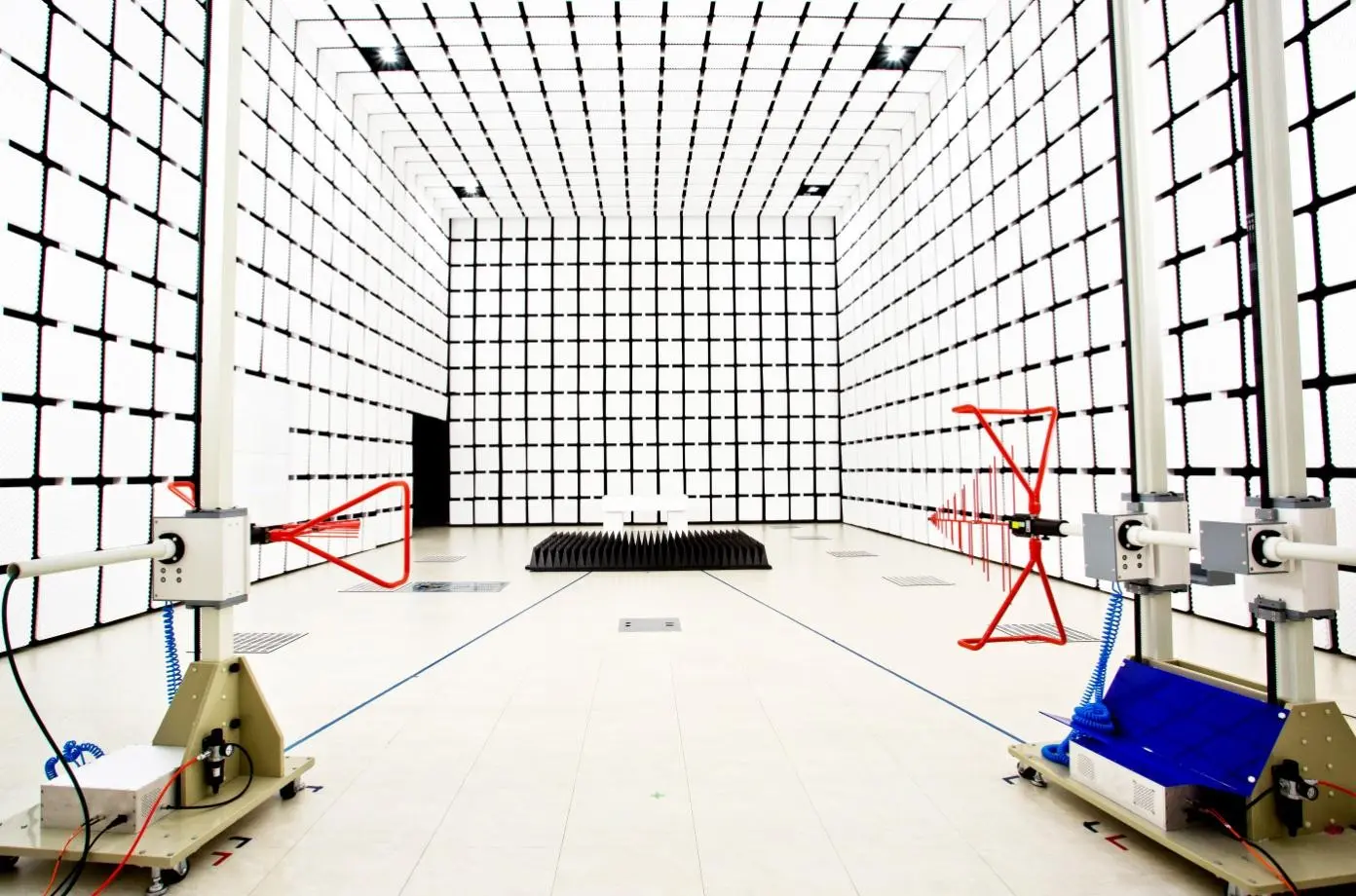
For products with DC voltage greater than 60V and less than 1500V, the ISO system implemented the ISO 7637-4 standard in May 2020. Therefore, when the product voltage exceeds 60V, the commonly used ISO 7637-2/-3 standards are no longer applicable, and the ISO 7637-4 standard must be followed for testing. ISO 7637-2 cannot perform custom standard testing for products above 60V, making it irrelevant.
Standard Analysis
Standard Requirements:
- The ISO 7637-4 standard applies to automotive electronic products with DC voltage greater than 60V and less than 1500V, effective from May 2020.
- Unlike ISO 7637-2, which does not apply high voltage, the ISO 7637-4 standard is now the relevant reference.
Product Types:
- BMS and power battery packs (greater than DC60V)
- New energy vehicle drive motors
- High-voltage motors
- DC/DC converters
- Onboard chargers (OBC)
- High-voltage distribution boxes (PDU), etc.
Test Items:
- High-voltage transient conduction
- Pulse A (RF immunity)
- Pulse B (low-frequency immunity)
Test Difficulty:
- High-voltage transient conduction and Pulse A are relatively common.
- Pulse B is more challenging to test.
Establishment and Future Development of ISO 7637-4
In 2020, ISO released ISO 7637-4 "Road vehicles - Electrical disturbances from conduction and coupling - Part 4: Electrical transient conduction along shielded high-voltage power lines," which specifies the test methods and procedures for electrical transient conduction along shielded high-voltage power lines for vehicles, isolating power supplies from the vehicle body. This applies to all types of electrically driven road vehicles.
This standard defines:
- Pulse Sine Wave Disturbance (Waveform A): Used for high-frequency oscillation tests.
- Low-frequency Sine Wave Disturbance (Waveform B): Used for transient voltage tests.
All transient tests should be conducted:
- Between HV+ and HV- (line-to-line)
- Between HV+ and ground, HV- and ground (line-to-ground)
The standard considers the various types of transients generated by different devices' switches that can appear on high-voltage power lines.
This standard is urgently needed for the automotive industry's high-voltage component testing. It provides the standard basis for electrical transient conduction tests on shielded high-voltage power lines for equipment on road vehicles with electrical system voltages greater than 60 VDC and less than 1500 VDC. It fills the gap in international standards for testing high-voltage component shielded high-voltage power lines.
Currently, the ISO 7637-4 standard has been established within the ISO system. However, due to laboratory testing capabilities and certification requirements, many automotive manufacturers have not yet updated their internal standards. Only BYD and Dongfeng Nissan have included this standard in their specifications. Other manufacturers have not yet incorporated it. According to expert predictions, major manufacturers will likely adopt this standard's testing requirements in the near future.
Authorized Laboratories for ISO 7637-4
JJR Laboratory:
- The JJR Laboratory in China fully meets the requirements for ISO 7637-4 new energy vehicle transient conduction testing, including compliance with ISO 7637-4: A and B waveforms, as well as the supporting coupling devices.
- Currently, JJR Laboratory is the first laboratory in China to be authorized for this standard, with professional testing and interpretation capabilities in the ISO 7637-4 standard.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 China OECD GLP-Certified Laboratory
China OECD GLP-Certified Laboratory
 Packaging Validation ISO 11607 Test Report
Packaging Validation ISO 11607 Test Report
 What is the ISO 11607-1 Packaging Validation Test?
What is the ISO 11607-1 Packaging Validation Test?
 How to get an ISO 11737-1 Test Report?
How to get an ISO 11737-1 Test Report?
 Orthopedic Implant Cleanliness Testing
Orthopedic Implant Cleanliness Testing
 What is ISO 10993-23:2021 Irritation Testing?
What is ISO 10993-23:2021 Irritation Testing?
 ISO 10993-23 Irritation Testing Laboratory
ISO 10993-23 Irritation Testing Laboratory
 EMI Emissions Testing
EMI Emissions Testing
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




