
Animal Experiments in the Development of Medical Devices
In the process of developing medical devices, preclinical animal experiments play a crucial role. These experiments often use higher species animals as models, such as non-human primates, goats, sheep, pigs, and dogs.
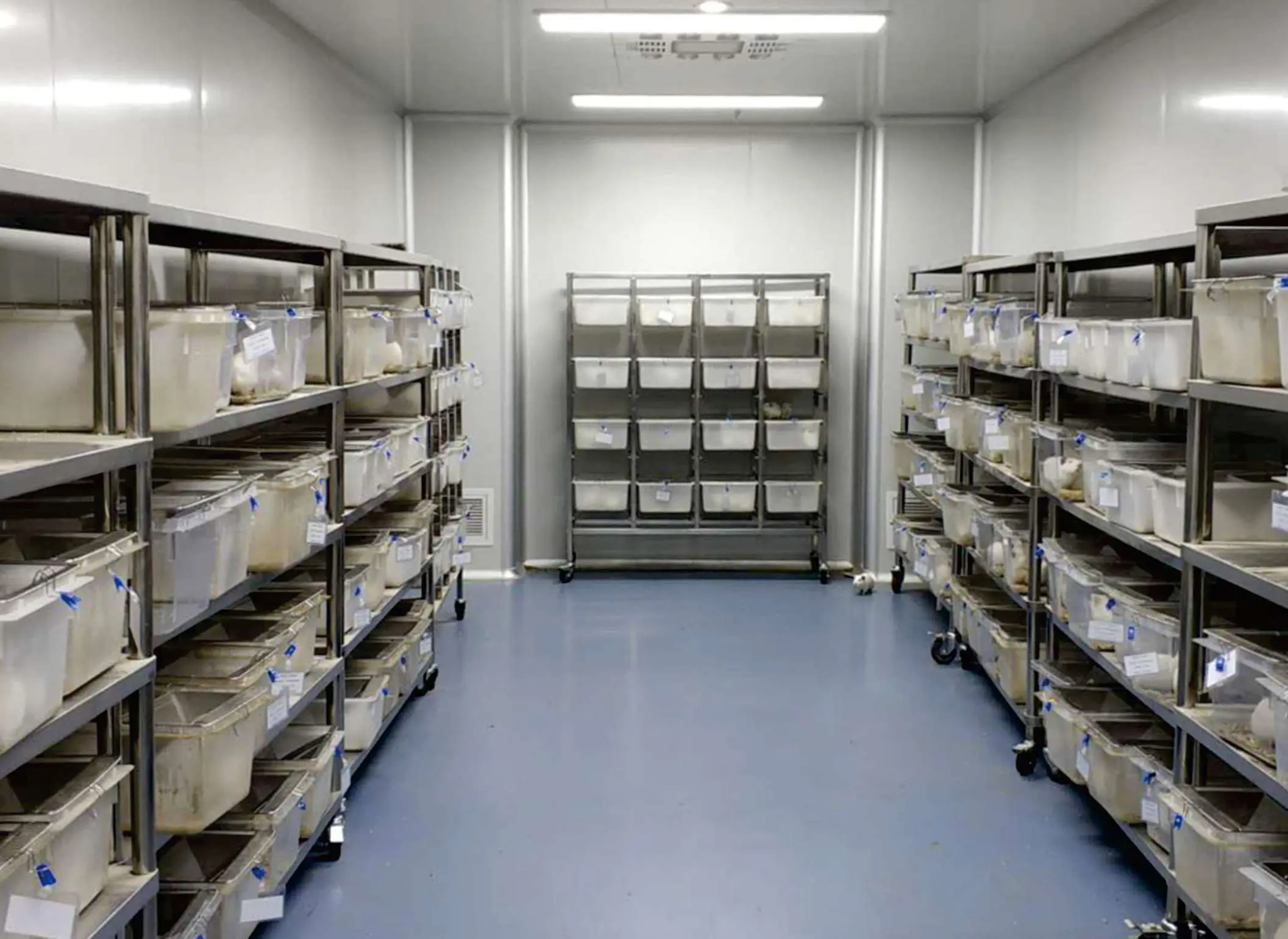

Key steps and considerations:
1. Principles of animal model selection
Consider similarities and differences between animal and human metabolism for drugs or adjunct devices.
Compare size differences between animal experiments and human use of devices.
Consider differences in anatomical points, surgical techniques, insertion sites, and tracking paths between animals and humans when optimizing device size and anatomical structure.
Consider the impact of size restrictions when selecting optimal dimensions and anatomical structure for devices.
2. Experiment assurance
Animal experiments should comply with GLP regulations.
3. Experiment objectives
Evaluate and validate the safety, effectiveness, and feasibility of new medical devices, equipment, or treatment methods.
Collect test data to assess device performance and effects on animal physiology, anatomy, pathology, and behavior.
Provide scientific basis for clinical trials and human use of medical devices.
Provide references for basic biomedical knowledge and research on relevant diseases.
4. Experiment planning
Define specific objectives and research questions for the experiment.
Develop a schedule and implementation steps for the experiment.
Determine the number and species of animals required for the experiment.
Identify equipment and materials needed for the experiment.
Write experimental operation specifications and records.
Determine statistical design and data analysis methods for the experiment.
Establish quality control and assurance measures for the experiment.
5. Experiment operations
Provide specific training and operational guidance to ensure accuracy and consistency of experimental operations.
Strictly follow experimental operation specifications and records, and promptly record experimental data.
Monitor animal physiological parameters and behavioral performance to ensure experiment stability and reliability.
Adjust and optimize experimental operations as needed.
6. Experiment data analysis
Organize, summarize, and analyze collected experimental data.
Use appropriate statistical methods and data analysis software to evaluate the reliability and significance of experimental results.
Interpret and discuss experimental results, and propose conclusions and recommendations.
7. Test and control groups
Establish test and control groups, following randomization principles, to compare and verify the reliability and significance of experimental results.
8. Auxiliary devices and equipment
Use syringes, catheters, monitoring devices, surgical equipment, imaging devices, and data processing equipment to ensure smooth conduct of experiments and accurate data collection.
9. Description of test groups
Describe the setup of test group animals, including quantity, species, and their care and management requirements, to ensure the reliability and consistency of experimental results.
Conclusion
Through scientific experiment design and rigorous experimental operations, animal experiments in the development of medical devices assess and validate the safety, effectiveness, and feasibility of new medical devices, equipment, or treatment methods. These experiments not only provide scientific basis for clinical trials but also advance basic biomedical knowledge and serve as important references for research on relevant diseases.
JJR Laboratory in China is an accredited laboratory under IEC 17025 and GLP, located in China, offering lower testing costs which can save you up to 30% in certification testing expenses. Feel free to contact us for a quotation."
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 ASTM D4169 Drop Test
ASTM D4169 Drop Test
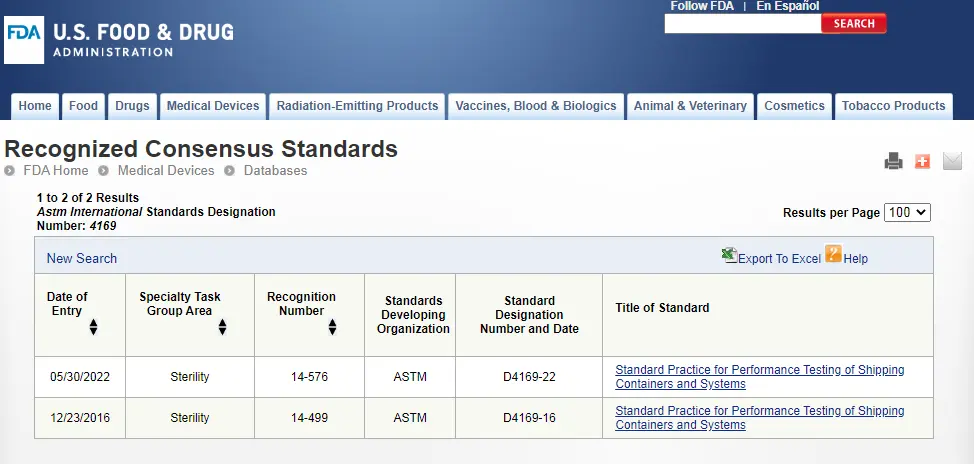 ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
ASTM D4169 Packaging Simulation Transportation Tes
 What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
What is ASTM D4169 Testing?
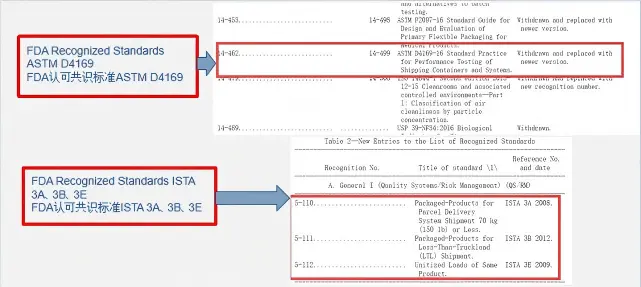
 ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
ASTM D4169-23 Test Standard Revision
 Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
Transport Simulation Testing for Medical Device Pa
 EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
EU CE Certification Guidelines for Lighting Fixtur
 Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
Lithium Battery Export: CB Certification & IEC
 How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
How to Apply for One FCC Certificate for Multiple
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




